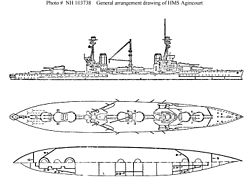
- HMS Agincourt (1913)
-
For other ships of the same name, see HMS Agincourt.

HMS Agincourt 1915Career (Brazil) 
Name: Rio de Janeiro Namesake: Rio de Janeiro Ordered: 1911 Builder: Armstrong, Newcastle upon Tyne Yard number: 792 Laid down: 14 September 1911 Launched: 22 January 1913 Fate: Sold December 1913 to the Ottoman Empire Career (Ottoman Empire) 
Name: Sultan Osman I Namesake: Sultan Osman I Acquired: December 1913 Fate: Seized in August 1914 by the United Kingdom Career (United Kingdom) 
Name: HMS Agincourt Namesake: The Battle of Agincourt of 1415 Cost: £2,900,000 (estimated) Completed: 20 August 1914 Acquired: 3 August 1914 Commissioned: 7 August 1914 Decommissioned: April 1921 Nickname: Gin Palace Fate: Sold 1922, scrapped 1924 General characteristics (in British service) Type: Dreadnought battleship Displacement: 27,850 long tons (28,300 t) (load)
30,860 long tons (31,360 t) (deep load)Length: 671 ft 6 in (204.7 m) Beam: 89 ft (27.1 m) Draught: 29 ft 10 in (9.1 m) Installed power: 34,000 shp (25,000 kW) Propulsion: 4 shafts, 4 Parsons steam turbines
22 Babcock and Wilcox water-tube boilersSpeed: 22 knots (41 km/h; 25 mph) Range: 7,000 nmi (13,000 km; 8,100 mi) at 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph) Complement: 1268 (1917) Armament: 7 × 2 - BL 12-inch Mk XIII guns
20 × 1 - BL 6-inch Mk XIII guns
10 × 1 - 3 in (76 mm) guns
3 × 21 in (533 mm) torpedo tubesArmour: Belt: 9 in (229 mm)
Deck: 1–2.5 in (25–64 mm)
Barbettes: 2–9 in (51–229 mm)
Turrets: 8–12 in (203–305 mm)
Conning tower: 12 in (305 mm)
Bulkheads: 2.5–6 in (64–152 mm)HMS Agincourt was a dreadnought built in the early 1910s. The ship was originally ordered by Brazil, but the collapse of the rubber boom plus a lessening of the rivalry with Argentina led to her resale while still under construction to the Ottoman Empire who renamed her as Sultan Osman I. Then, with completion just as World War I began, she was seized for use by the Royal Navy, an act which contributed to the decision of the Ottoman Empire to support Germany in the war.
Renamed as Agincourt by the British, she joined the Grand Fleet in the North Sea. The ship spent the bulk of her time during the war on patrols and exercises, although she did participate in the Battle of Jutland in 1916. Agincourt was put into reserve in 1919 and sold for scrap in 1922 to meet the terms of the Washington Naval Treaty.
Contents
Design
Agincourt was ordered in 1911 as part of a dreadnought arms race in South America between Brazil, Argentina and Chile in the first decade of the Twentieth Century under the name of Rio de Janeiro. The Brazilians wished to purchase a ship that would outclass those ships building for their rivals. The chief designer of Armstrong, Eustace Tennyson d'Eyncourt, had travelled to Brazil to settle on a design and sign the contract. He brought with him a variety of options for the government to consider and they chose the one with the 12-inch (305 mm) guns, partially to maintain commonality with their other battleships already in service.[1]
General characteristics
Agincourt had an overall length of 671 feet (204.5 m), a beam of 89 feet (27.1 m), and a draught of 29 feet 10 inches (9.1 m) at deep load. She displaced 27,850 long tons (28,297 t) at load and 30,860 long tons (31,355 t) at deep load. She had a metacentric height of 4.9 feet (1.5 m) at deep load.[2] She had a large turning circle, but manoeuvered well despite her great length. Agincourt was considered to be a good gun platform.[3]
She was one of the most comfortable ships in the Royal Navy and very well-appointed internally. A knowledge of Portuguese was necessary to work many of the fittings—including those in the heads—as the original instruction plates had not all been replaced when she was taken over by the British.[3]
Propulsion
Agincourt had four Parsons direct-drive steam turbines, each of which drove one propeller shaft. The high-pressure ahead and astern turbines drove the wing shafts while the low-pressure ahead and astern turbines drove the inner shafts. The three-bladed propellers were 9 feet 6 inches (2.9 m) in diameter. The turbines were designed to produce a total of 34,000 shaft horsepower (25,000 kW), but achieved more than 40,000 shp (30,000 kW) during her sea trials, slightly exceeding her designed speed of 22 knots (41 km/h; 25 mph).[4]
The steam plant consisted of 22 Babcock and Wilcox water-tube boilers with an operating pressure of 235 psi (1,620 kPa; 17 kgf/cm2). Agincourt normally carried 1,500 long tons (1,500 t) of coal, but could carry a maximum of 3,200 long tons (3,300 t), as well as 620 long tons (630 t) of fuel oil to be sprayed on the coal to increase its burn rate. At full capacity, she could steam for 7,000 nautical miles (13,000 km; 8,100 mi) at a speed of 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph). Electrical power was provided by four steam-driven reciprocating generators.[5]
Armament
Agincourt mounted fourteen BL 12-inch Mk XIII 45-calibre guns in seven twin hydraulically powered turrets,[6] unofficially called after the days of the week, starting from Sunday, forward to aft.[7] This was the greatest number of turrets and heavy guns ever mounted on a battleship.[8] The guns could be depressed to −3° and elevated to 13.5°. They fired 850-pound (386 kg) projectiles at a muzzle velocity of 2,725 ft/s (831 m/s); at 13.5°, this provided a maximum range of just over 20,000 yards with 4crh armour-piercing (AP) shells. During the war the turrets were modified to increase their maximum elevation to 16°, but this only extended the range to 20,435 yards (18,686 m). The rate of fire of these guns was 1.5 rounds per minute.[9] When a full broadside was fired, observers said that: "The resulting sheet of flame was big enough to create the impression that a battle cruiser had blown up; it was awe inspiring."[10] No damage was done to the ship when firing full broadsides, despite the common idea that doing so would break her back, but much of the ship's crockery and glassware would shatter.[11]
As built Agincourt mounted eighteen BL 6-inch Mk XIII 50-calibre guns. Fourteen were placed in armoured casemates on the upper deck and two each in the fore and aft superstructures, protected by gun shields. Two more were added abreast the bridge in pivot mounts protected by gun shields when the ship was purchased by the British.[12] The guns could be depressed to −7° and elevated to 13°, but this was later increased to 15°. They had a range of 13,475 yards (12,322 m) at 15° when firing a 100-pound (45 kg) shell with a muzzle velocity of 2,770 ft/s (840 m/s). Their rate of fire was about five to seven rounds per minute, but this dropped to about three rounds per minute after the ready ammunition was used up because the ammunition hoists were too slow or few to keep the guns fully supplied. About 150 rounds were carried per gun.[13]
Close-range defense against torpedo boats was provided by ten 3-inch (76 mm) 45-calibre quick-firing guns. These were mounted in the superstructure in pivot mounts and protected by gun shields. Agincourt also carried three 21-inch (533 mm) submerged torpedo tubes; one was on each beam and the last was in the stern. The water that entered the torpedo tubes when they were fired was discharged into the torpedo flat to facilitate reloading the tube and then pumped overboard. This meant that the crew would be operating in 3 feet (0.9 m) of water if rapid fire was required. Ten torpedoes were carried for them.[14]
Fire control
Each turret was fitted with an armoured rangefinder in the turret roof. In addition another one was mounted on top of the foretop. By the time of the Battle of Jutland in 1916, Agincourt was possibly the only dreadnought of the Grand Fleet not fitted with a Dreyer fire-control table.[15] A fire-control director was later fitted below the foretop and one turret was modified to control the entire main armament later in the war.[5] A director for the 6-inch (152 mm) guns was added on each side in 1916–17.[12]
Armour
So much weight had been devoted to Agincourt's armament that little remained for her armour. Her waterline belt was just 9 inches (229 mm) thick, compared with twelve inches or more found in other British dreadnoughts. It ran some 365 feet (111.3 m), from the forward edge of 'Monday' barbette to the middle of 'Friday' barbette. Forward of this the belt thinned to six inches for about 50 feet (15.2 m) before further reducing to 4 inches (102 mm) all the way to the bow. Aft of the midships section the belt reduced to six inches for about 30 feet (9.1 m) and then thinned to four inches (102 mm); it did not reach the stern, but terminated at the rear bulkhead. The upper belt extended from the main to the upper deck and was six inches thick. It ran from 'Monday' barbette to 'Thursday' barbette. The armour bulkheads at each end of the ship angled inwards from the ends of the midships armoured belts to the end barbettes and were three inches thick. Four of Agincourt's decks were armoured with thicknesses varying from 1 to 2.5 inches (25 to 63 mm).[16]
The armour of the barbettes constituted a major weakness in Agincourt's protection. They were nine inches thick above the upper deck level, but decreased to three inches between the upper and main decks and had no armour at all below the main deck except for 'Sunday' barbette (which had three inches), and 'Thursday' and 'Saturday' barbettes (which had two inches). The turret armour was twelve inches thick on the face, 8 inches (203 mm) on the side and 10 inches (254 mm) in the rear. The turret roofs were three inches thick at the front and two inches at the rear. The casemates for the secondary armament were protected by six inches of armour and were defended from raking fire by six-inch thick bulkheads.[5]
The main conning tower was protected by twelve inches of armor on its sides and it had a four-inch roof. The aft conning tower (sometimes called the torpedo control tower) had nine-inch sides and a three-inch roof. The communications tube down from each position was six-inches thick above the upper deck and two-inches thick below it. Each magazine was protected by two armour plates on each side as torpedo bulkheads, the first one inch thick and the second one and a half inches thick.[12]
Agincourt had another weakness in that she was not subdivided to Royal Navy standards as the Brazilians preferred to eliminate all possible watertight bulkheads that might limit the size of the compartments and interfere with the crew's comfort. One example was the officer's wardroom, which was 85 by 60 feet (25.9 by 18.3 m) in size; much larger than anything in the Grand Fleet.[17]
Wartime modifications
Approximately 70 long tons (71 t) of high-tensile steel to the main deck was added after the Battle of Jutland to protect the magazines. Two 3-inch (76 mm) anti-aircraft guns were added to the quarterdeck in 1917–18. A 9-foot (2.7 m) rangefinder was added to the former searchlight platform on the foremast at the same time. A high-angle rangefinder was added to the spotting top in 1918.[12]
 Agincourt at sea during her builder's trials in 1914, when it was still intended to deliver her to the Ottoman Empire as Sultan Osman I. Note the massive flying deck over the midships turrets; this was removed prior to commissioning her into British service.
Agincourt at sea during her builder's trials in 1914, when it was still intended to deliver her to the Ottoman Empire as Sultan Osman I. Note the massive flying deck over the midships turrets; this was removed prior to commissioning her into British service.
Construction
Rio de Janeiro, as Agincourt was named by her first owners, was laid down on 14 September 1911 by Armstrongs in Newcastle upon Tyne and launched on 22 January 1913.[5] However, the rubber trade on which Brazil was reliant collapsed shortly afterward and she was put up for sale in October 1913.[18] Brazil sold the vessel to the Ottoman Navy for £2,750,000 on 28 December 1913.[19] Renamed the Sultan Osman I, she underwent trials in July 1914 and was completed in August, just as World War I began.[20]
Seizure
The war broke out during her sea trials before delivery. Even though the Ottoman crew had arrived to collect her, the British Government took over the vessel for incorporation into the Royal Navy. At the same time the British also took over a second Ottoman battleship, a King George V class-derived vessel being built by Vickers—the Reshadiye—which was renamed HMS Erin. Such an action was allowed for in the contracts, as then-First Lord of the Admiralty Winston Churchill did not want to risk the ships being used against the British, but it had consequences.[21]
The takeover caused considerable ill will in the Ottoman Empire, where public subscriptions had partially funded the ships. When the Ottoman government had been in a financial deadlock over the budget of the battleships, people's donations were solicited. In taverns, cafés, schools and markets many donated some amount of money for the Ottoman Navy. To encourage this campaign, plentiful donations were awarded with a medal called the "Navy Donation Medal". This proved an important factor in turning Ottoman public opinion against Britain, especially as the Ottoman Navy had been pro-Britain — the Army having been pro-German. It helped bring the Ottoman Empire into the war on the side of Germany and the Austro-Hungarian Empire against the Triple Entente of Britain, France, and Russia on 29 October 1914.[22]
The Royal Navy made modifications before commissioning her: in particular they removed the flying deck over the two centre turrets. The ship was also initially fitted with Turkish-style lavatories that had to be replaced.[23] Her name, "Agincourt", was a favourite of Churchill's, and had initially been allocated to a sixth vessel of the Queen Elizabeth-class ordered under the 1914-15 Naval Estimates, but not yet begun at the war's outbreak.[24] Her nickname, The Gin Palace, came from her luxurious fittings and a corruption of her name (A Gin Court), Pink Gin having been a popular drink among Royal Navy officers at the time.[25]
The Admiralty was unprepared to man a ship of Agincourt's size on such short notice and her crew was drawn "from the highest and lowest echelons of the service: the Royal yachts, and the detention barracks." Agincourt's captain and executive officer came from HMY Victoria and Albert III, most of whose crew was also transferred to Agincourt on 3 August 1914. Most of the naval reservists had already been called up by this time and sent to other ships so a number of minor criminals who had had their sentences remitted were received from various naval prisons and detention camps.[26]
Service
Agincourt was shaking down until 7 September 1914 when she joined the 4th Battle Squadron (BS) of the Grand Fleet.[27] The fleet anchorage at Scapa Flow was not yet secure against submarine attack and much of the fleet was kept at sea where Agincourt spent forty of her first eighty days with the Grand Fleet. This was the beginning of "a year and a half of inaction, only broken by occasional North Sea "sweeps" intended to draw the enemy from his bases."[28]
On 1 January 1915 she was still assigned to the 4th BS, but had been assigned to the 1st Battle Squadron before the Battle of Jutland on 31 May 1916. Agincourt was the last ship of the Sixth Division of the 1st BS, along with HMS Hercules, HMS Revenge and the flagship, HMS Marlborough, the most heterogeneous group possible as each ship was from a different class. The Sixth Division was the starboardmost column of the Grand Fleet as it headed south to rendezvous with Admiral Beatty's Battlecruiser Fleet, then engaged with their opposite numbers from the German High Seas Fleet in the North Sea.[29] Admiral Jellicoe, commander of the Grand Fleet, kept it in cruising formation until 6:15 p.m.[Note 1] when he ordered it to deploy from column into a single line based on the port division, each ship turning 90° in succession. This turn made the Sixth Division the closest ships in the Grand Fleet to the battleships of the High Seas Fleet and they fired on each ship as they made their turn to port. This concentration of fire later became known as "Windy Corner" to the British as the ships were drenched by German shell splashes although none were hit.[30]
At 6:24 Agincourt opened fire on a German battlecruiser with her main guns. Shortly afterwards her six-inch guns followed suit as German destroyers made torpedo attacks on the British battleships to cover the turn to the south of the High Seas Fleet.[31] Agincourt successfully evaded two torpedoes.[32] Visibility cleared around 7:15 and Agincourt engaged a Kaiser-class battleship without result before it was lost in the smoke and haze.[33] Around 8:00 Marlborough was forced to reduce speed because of the strain on her bulkheads from her torpedo damage and her division mates conformed to her speed.[34] In the reduced visibility the division lost sight of the Grand Fleet during the night, passing the badly damaged battlecruiser SMS Seydlitz without opening fire.[35] Dawn found them with only the detritus from the previous day's battle in sight and the division arrived back at Scapa Flow on 2 June.[36] Agincourt fired 144 twelve-inch shells and 111 six-inch shells during the battle although she is not known to have hit anything.[27]
Although the Grand Fleet made several sorties over the next few years it is not known if Agincourt participated in them. On 23 March 1918, Agincourt and Hercules were stationed at Scapa Flow to provide cover for the Scandinavian convoys between Norway and Britain when the High Seas Fleet sortied in an attempt to destroy the convoy. The reports from German Intelligence were slightly off schedule, however, as both the inbound and outbound convoys were in port when the Germans reached their normal route so Admiral Scheer ordered the fleet to return to Germany without spotting any British ships.[37]
Agincourt was later transferred to the 2nd Battle Squadron[27] and she was present at the surrender of the High Seas Fleet on 21 November 1918.[38] She was placed in reserve at Rosyth in March 1919. After unsuccessful attempts to sell her to the Brazilian Government, she was briefly recommissioned for experimental purposes in 1921. She was sold for scrap on 19 Dec 1922 to comply with the tonnage limitations of the Washington Naval Treaty, although she was not actually broken up until the end of 1924.[12]
Notes
Footnotes
- ^ Topliss, pp. 263–64, 269, 280–81
- ^ Burt, p. 244
- ^ a b Parkes, p. 604
- ^ Burt, pp. 245, 250
- ^ a b c d Burt, p. 245
- ^ Gardiner and Gray, p. 37
- ^ Hough, p. 150
- ^ Gibbons, p. 201
- ^ "British 12"/45 (30.5 cm) Mark XIII". 20 February 2009. http://www.navweaps.com/Weapons/WNBR_12-45_mk13.htm. Retrieved 4 May 2010.
- ^ Parkes, p. 603
- ^ Hough, p. 160
- ^ a b c d e Burt, p. 250
- ^ "British 6"/50 (15.2 cm) BL Mark XIII". navweaps.com. 22 January 2009. http://www.navweaps.com/Weapons/WNBR_6-50_mk13.htm. Retrieved 4 May 2010.
- ^ Parkes, pp. 600, 603
- ^ Friedman, p. 46
- ^ Burt, pp. 244–45
- ^ Hough, pp. 89–90
- ^ Hough, p. 72
- ^ Hough, p. 75
- ^ Hough, pp. 109–22
- ^ Hough, p. 121
- ^ Hough, pp. 143–44
- ^ Hough, pp. 152–53
- ^ Parkes, p. 600
- ^ Hough, p. 147
- ^ Hough, pp. 148–52
- ^ a b c Parkes, p. 605
- ^ Hough, p. 161
- ^ Hough, p. 174
- ^ Hough, p. 179
- ^ Tarrant, pp. 131, 133
- ^ Massie, p. 630
- ^ Hough, p. 183
- ^ Burt, p. 206
- ^ Massie, p. 651
- ^ Hough, pp. 184–85
- ^ Newbolt, pp. 236–37
- ^ Hough, p. 186
Bibliography
- Burt, R. A. (1986). British Battleships of World War One. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-863-8.
- Friedman, Norman (2008). Naval Firepower: Battleship Guns and Gunnery in the Dreadnought Era. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-59114-555-4.
- Gardiner, Robert; Gray, Randal, eds (1984). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships: 1906–1922. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-85177-245-5.
- Gibbons, Tony (1983). The Complete Encyclopedia of Battleships: A Technical Directory of Capital Ships from 1860 to the Present Day. New York: Crescent Books. ISBN 0-517-37810-8.
- Hough, Richard (1967). The Great Dreadnought: The Strange Story of H.M.S. Agincourt: The Mightiest Battleship of World War I. New York: Harper & Row. OCLC 914101.
- Massie, Robert (2004). Castles of Steel: Britain, Germany and the Winning of the Great War. New York: Random House. ISBN 0224040928.
- Newbolt, Henry. Naval Operations. History of the Great War: Based on Official Documents. V (reprint of the 1931 ed.). London and Nashville, Tennessee: Imperial War Museum and Battery Press. ISBN 1-870423-72-0.
- Parkes, Oscar (1990). British Battleships (reprint of the 1957 ed.). Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 1-55750-075-4.
- Tarrant, V. E. (1999). Jutland: The German Perspective: A New View of the Great Battle, 31 May 1916 (reprint of the 1995 ed.). London: Brockhampton Press. ISBN 1-86019-917-8.
- Topliss, David (1988). "The Brazilian Dreadnoughts, 1904-1914". Warship International (Toledo, Ohio: International Naval Research Organization) XXV (3): 240–89. ISSN 0043-0374.
External links
- Dreadnought Project Technical material on the weaponry and fire control for the ships
- Maritimequest HMS Agincourt Photo Gallery
- Agincourt Class Battleship - includes a diagram of her layout
- Navypedia - Agincourt battleship
Categories:- Battleships of the Brazilian Navy
- Battleships of the Ottoman Navy
- Battleships of the Royal Navy
- Armstrong Whitworth ships
- Tyne-built ships
- 1913 ships
- Unique battleships
- World War I battleships of the United Kingdom
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.