- Dioxygenyl
-
The dioxygenyl ion, O2+, is a rarely encountered oxycation in which both oxygen atoms have a formal oxidation state of +½. It is formally derived from oxygen by the removal of an electron:
- O2 → O2+ + e−
The energy change for this process is called the ionization energy of the oxygen molecule. Relative to most molecules, this ionization energy is very high at 1175 kJ/mol.[1] As a result, the scope of the chemistry of O2+ is quite limited, acting mainly as a 1-electron oxidiser.[2]
Contents
Structure and molecular properties
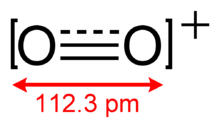
O2+ has a bond order of 2.5, and a bond length of 112.3 pm in solid O2[AsF6].[3] It has the same number of valence electrons as nitric oxide. The bond energy is 625.1 kJ mol−1 and the stretching frequency is 1858 cm−1,[4] both of which are high relative to most molecules.
Synthesis
The reaction of oxygen, O2, with platinum hexafluoride, PtF6, yields dioxygenyl hexafluoroplatinate, O2[PtF6]+:
- O2 + PtF6 → O2+[PtF6]–
PtF6 is one of the few oxidising agents sufficiently powerful to oxidise O2.Dioxygenyl hexafluoroplatinate played a pivotal role in the discovery of noble gas compounds. After Neil Bartlett found that PtF6 could oxidise O2 to O2+, he investigated its reaction with noble gases and discovered "xenon hexafluoroplatinate".
O2+ is also found in similar compounds of the form O2MF6, where M is arsenic (As),[5] gold (Au),[6] niobium (Nb), ruthenium (Ru), rhenium (Re), rhodium (Rh),[7] vanadium (V),[8] or phosphorus (P).[9] Other forms are also attested, including O2GeF5 and (O2)2SnF6.[8]
The tetrafluoroborate and hexafluorophosphate salts may be prepared by the reaction of dioxygen difluoride with boron trifluoride or phosphorus pentafluoride at −126 °C:[9]
- 2 O2F2 + 2 BF3 → 2 O2BF4 + F2
- 2 O2F2 + 2 PF5 → 2 O2PF6 + F2
These compounds rapidly decompose at room temperature:
- 2 O2BF4 → 2 O2 + F2 + 2 BF3
- 2 O2PF6 → 2 O2 + F2 + 2 PF5
Reactions
The reaction of O2BF4 with xenon at 173 K produces a white solid believed to be F–Xe–BF2, containing an unusual xenon-boron bond:[10]
- 2 O2BF4 + 2 Xe → 2 O2 + F2 + 2 FXeBF2
The dioxygenyl salts O2BF4 and O2AsF6 react with carbon monoxide to give oxalyl fluoride, F–(C=O)–(C=O)–F, in high yield.[11]
References
- ^ Michael Clugston; Rosalind Flemming (2000). Advanced Chemistry, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0199146330, ISBN 9780199146338, p. 355.
- ^ Foote, Christopher S.; Valentine, Joan S. (1995). Active oxygen in chemistry. Joel F. Liebman, A. Greenberg. Springer. ISBN 0412034417.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0080379419. p. 616
- ^ J. Shamir, J. Binenboym, H. H. Claassen (1968). "The vibrational frequency of the O2+ cation". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 90 (22): 6223−6224. doi:10.1021/ja01024a054.
- ^ A. R. Young, T. Hirata, S. I. Morrow (1964). "The Preparation of Dioxygenyl Salts from Dioxygen Difluoride". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 86 (1): 20−22. doi:10.1021/ja01055a006.
- ^ Nakajima, Tsuyoshi (1995). Fluorine-carbon and fluoride-carbon materials: chemistry, physics, and applications. CRC Press. ISBN 0824792866.
- ^ Vasile, M. J.; Falconer, W. E. (1975). "Vapour transport of dioxygenyl salts". Journal of the Chemical Society Dalton Transactions (4): 316–318. doi:10.1039/DT9750000316.
- ^ a b Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon (2001). Inorganic chemistry. Academic Press. p. 475. ISBN 0123526515.
- ^ a b Solomon, I. J.; Brabets, R. I.; Uenishi, R. K.; Keith, J. N.; McDonough, J. M. (1964). "New Dioxygenyl Compounds". Inorganic Chemistry 3 (3): 457. doi:10.1021/ic50013a036.
- ^ Goetschel, C. T.; Loos, K. R. (1972). "Reaction of xenon with dioxygenyl tetrafluoroborate. Preparation of FXe-BF2". Journal of the American Chemical Society 94 (9): 3018–3021. doi:10.1021/ja00764a022.
- ^ Pernice, H. (2001). "The reaction of dioxygenyl salts with 13
CO Formation of F13
C(O)13
C(O)F". Journal of Fluorine Chemistry 112 (2): 277–590. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(01)00512-7.
Categories:- Oxycations
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.