- Middle meningeal artery
-
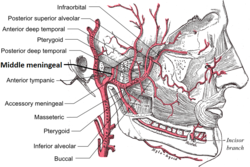
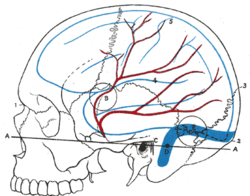
Artery: Middle meningeal artery Plan of branches of the maxillary artery. Relations of the brain and middle meningeal artery to the surface of the skull. Latin arteria meningea media Gray's subject #144 560 Supplies meninges Source internal maxillary artery Branches anterior: posterior: superior tympanic artery Vein middle meningeal vein The middle meningeal artery (Latin arteria meningea media) is typically the third branch of the first part (retromandibular part) of the maxillary artery, one of the two terminal branches of the external carotid artery. After branching off the maxillary artery in the infratemporal fossa, it runs through the foramen spinosum to supply the dura mater (the outermost meninges) and the calvaria. The middle meningeal artery is the largest of the three (paired) arteries which supply the meninges, the others being the anterior meningeal artery and the posterior meningeal artery.
In approximately half of subjects it branches into an accessory meningeal artery.
The middle meningeal artery runs beneath the pterion. It is vulnerable to injury at this point, where the skull is thin. Rupture of the artery may give rise to an epidural hematoma. In the dry cranium, the middle meningeal, which runs within the dura mater surrounding the brain, makes a deep indention in the calvarium.
The middle meningeal artery is intimately associated with the auriculotemporal nerve which wraps around the artery making the two easily identifiable in the dissection of human cadavers and also easily damaged in surgery.
Contents
Branches
Before entering cranium
It ascends between the sphenomandibular ligament and the Pterygoideus externus, and between the two roots of the auriculotemporal nerve to the foramen spinosum of the sphenoid bone, through which it enters the cranium; it then runs forward in a groove on the great wing of the sphenoid bone, and divides into two branches, anterior and posterior.
The anterior branch, the larger, crosses the great wing of the sphenoid, reaches the groove, or canal, in the sphenoidal angle of the parietal bone, and then divides into branches which spread out between the dura mater and internal surface of the cranium, some passing upward as far as the vertex, and others backward to the occipital region.
The posterior branch curves backward on the squamous part of the temporal bone, and, reaching the parietal bone some distance in front of its mastoid angle, divides into branches which supply the posterior part of the dura mater and cranium.
The branches of the middle meningeal artery are distributed partly to the dura mater, but chiefly to the bones; they anastomose with the arteries of the opposite side, and with the anterior and posterior meningeal arteries. The very smallest distal branches anastomose through the skull with small arterioles from the scalp.
Very rarely the ophthalmic artery may arise as a branch of the middle meningeal artery.
Branches upon entering cranium
On entering the cranium, the middle meningeal artery gives off the following branches:
- (1) Numerous small vessels supply the semilunar ganglion and the dura mater in this situation.
- (2) A superficial petrosal branch enters the hiatus of the facial canal, supplies the facial nerve, and anastomoses with the stylomastoid branch of the posterior auricular artery.
- (3) A superior tympanic artery runs in the canal of the tensor tympani muscle, and supplies this muscle and the lining of the canal.
- (4) Orbital branches pass through the superior orbital fissure or through separate canals in the great wing of the sphenoid, to anastomose with the lacrimal or other branches of the ophthalmic artery.
- (5) Temporal branches pass through foramina in the great wing of the sphenoid, and anastomose in the temporal fossa with the deep temporal arteries.
Clinical relevance
An injured middle meningeal artery is the cause of an epidural hematoma. A head injury (e.g. from a road traffic accident or sports injury) is required to rupture the artery. Emergency treatment requires decompression of the haematoma, usually by craniotomy. Subdural bleeding is usually venous in nature, rather than arterial.
The middle meningeal artery runs in a groove on the inside of the cranium. This can clearly be seen on a lateral skull X-ray, where it may be mistaken for a fracture of the skull. On a dry specimen the groove is easy to see. This means that the artery is easy to study, even in specimens centuries old, and several classifications of the branches have been proposed, e.g. Adachi's classification of 1928.
Additional images
External links
- SUNY Figs 27:04-03
- lesson4 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (infratempfossaart)
- Photos with captions at bubbasoft.org
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Categories:- Arteries of the head and neck
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.