- Diene
-
This article is about organic chemicals. For the surname "Diene" used in West Africa, see Serer people.
In organic chemistry a diene (
 /ˈdaɪ.iːn/ dy-een) or diolefin (/daɪˈoʊləfɨn/ dy-oh-lə-fin) is a hydrocarbon that contains two carbon double bonds. Conjugated dienes are functional groups, with a general formula of CnH2n-2. Dienes and alkynes are functional isomers. Dienes occur occasionally in nature but are widely used in the polymer industry.
/ˈdaɪ.iːn/ dy-een) or diolefin (/daɪˈoʊləfɨn/ dy-oh-lə-fin) is a hydrocarbon that contains two carbon double bonds. Conjugated dienes are functional groups, with a general formula of CnH2n-2. Dienes and alkynes are functional isomers. Dienes occur occasionally in nature but are widely used in the polymer industry.Contents
Classes
Dienes can be divided into three classes, depending on the relative location of the double bonds:
- Cumulated dienes have the double bonds sharing a common atom as in a group of compounds called allenes.
- Conjugated dienes have conjugated double bonds separated by one single bond.
- Unconjugated dienes have the double bonds separated by two or more single bonds. They are usually less stable than isomeric conjugated dienes. This can also be known as an isolated diene.
Compounds that contain more than two double bonds are called polyenes. Polyenes and dienes, share many of their properties.
 Some dienes: A: 1,2-Propadiene, also known as allene, is the simplest cumulated diene. B: Isoprene, also known as 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, the precursor to natural rubber. C: 1,3-Butadiene, a precursor to synthetic polymers. D: 1,5-Cyclooctadiene, an unconjugated diene (notice that each double bond is two carbons away from the other). E: Norbornadiene, a strained bicyclic and unconjugated diene. F: Dicyclopentadiene. G: Linoleic acid, a fatty acid that is required in the human diet.
Some dienes: A: 1,2-Propadiene, also known as allene, is the simplest cumulated diene. B: Isoprene, also known as 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, the precursor to natural rubber. C: 1,3-Butadiene, a precursor to synthetic polymers. D: 1,5-Cyclooctadiene, an unconjugated diene (notice that each double bond is two carbons away from the other). E: Norbornadiene, a strained bicyclic and unconjugated diene. F: Dicyclopentadiene. G: Linoleic acid, a fatty acid that is required in the human diet.
Synthesis of dienes
On an industrial scale, butadiene is prepared by thermal cracking of butanes. In a similarly non-selective process, dicyclopentadiene is obtained from coal tars.
In the laboratory, more directed and more delicate processes are employed such as dehydrohalogenations and condensations. Myriad methods have been developed, such as the Whiting reaction. Families of nonconjugated dienes are derived from the oligomerization and dimerization of conjugated dienes. For example, 1,5-cyclooctadiene and vinylcyclohexene are produced by dimerization of 1,3-butadiene.
Diene-containing fatty acids are biosynthesized from acetyl CoA.
Reactivity and uses
Polymerization
The most heavily practiced reaction of alkenes, dienes included, is polymerization. Butadiene is a precursor to rubber used in tires, and isoprene is the precursor to natural rubber. Chloroprene is a related but synthetic monomer.
Cycloadditions
An important reaction for conjugated dienes is the Diels-Alder reaction. Many specialized dienes have been developed to exploit this reactivity for the synthesis of natural products, e.g. Danishefsky’s diene.
Other addition reactions
Conjugated dienes add reagents such as bromine and hydrogen by both 1,2-addition and 1,4-addition pathways. Addition of polar reagents can generate complex architectures:[1]
Metathesis reactions
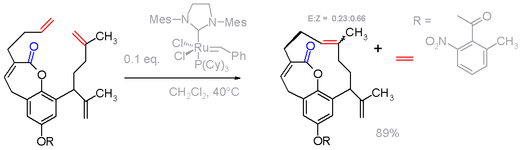
Nonconjugated dienes are substrates for ring-closing metathesis reactions. These reactions require metal catalyst:
Acidity
Conjugated and 1,4-dienes generally are somewhat acidic since deprotonation of both classes gives pentadienyl anions. The acidifying effect of the diene is very pronounced in cyclopentadiene.
As ligands
Dienes are widely used chelating ligands in organometallic chemistry. In some cases they serve as placeholder ligands, being removed during a catalytic cycle. For example, the cyclooctadiene ("cod") ligands in bis(cyclooctadiene)nickel(0) are labile. In some cases, dienes are spectator ligands, remaining coordinated throughout a catalytic cycle and influencing the product distributions. Chiral dienes have also been described.[2]
See also
External links
References
- ^ Roger Bishop, "9-Thiabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane-2,6-dione", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=CV9P0692; Coll. Vol. 9: 692Díaz, David Díaz; Converso, Antonella; Sharpless, K. Barry; Finn, M. G. (2006). "2,6-Dichloro-9-thiabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane: Multigram Display of Azide and Cyanide Components on a Versatile Scaffold". Molecules 11 (4): 212–218. doi:10.3390/11040212. http://www.mdpi.org/molecules/papers/11040212.pdf.
- ^ RyoShintani, Tamio Hayashi, "Chiral Diene Ligands for Asymmetric Catalysis" Aldrich Chimica Acta 2009, vol. 42, number 2, pp. 31-38.
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


![2,6-Dichloro-9-thiabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane, synthesis and reactions](/pictures/enwiki/52/450px-CODSCl2.png)