- Demand-pull inflation
-
Demand-pull inflation is asserted to arise when aggregate demand in an economy outpaces aggregate supply. It involves inflation rising as real gross domestic product rises and unemployment falls, as the economy moves along the Phillips curve. This is commonly described as "too much money chasing too few goods". More accurately, it should be described as involving "too much money spent chasing too few goods", since only money that is spent on goods and services can cause inflation. This would not be expected to persist over time due to increases in supply, unless the economy is already at a full employment level.
The term demand-pull inflation is mostly associated with Keynesian economics.
How it happens
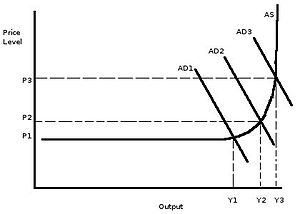
According to Keynesian theory, the more firms will employ people, the more people are employed, and the higher aggregate demand (AD) will become. This greater demand will make firms employ more people in order to output more. Due to capacity constraints, this increase in output will eventually become so small that the price of the good will rise. At first, unemployment will go down, shifting AD1 to AD2, which increases demand (noted as "Y") by (Y2 - Y1). This increase in demand means more workers are needed, and then AD will be shifted from AD2 to AD3, but this time much less is produced than in the previous shift, but the price level has risen from P2 to P3, a much higher increase in price than in the previous shift. This increase in price is called inflation.
See also
External links
- Theory 1 - Demand-pull inflation - is inflation demanding?, Bank of Biz/ed
Categories:- Demand
- Inflation
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.