- NRLMSISE-00
-
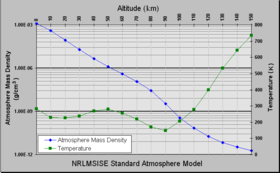
NRLMSISE-00 is an empirical, global model of the Earth's atmosphere from ground to space. It models the temperatures and densities of the atmosphere's components. A primary use of this model is to aid predictions of satellite orbital decay due to atmospheric drag. This model has also been used by astronomers to calculate the mass of air between telescopes and laser beams in order to assess the impact of laser guide stars on the non-lasing telescopes.[1]
The model, developed by Mike Picone, Alan Hedin, and Doug Drob, is based on the earlier models MSIS-86 and MSISE-90, but updated with actual satellite drag data. It also predicts anomalous oxygen.
NRL stands for the US Naval Research Laboratory. MSIS stands for Mass Spectrometer and Incoherent Scatter Radar respectively, the two primary data sources for development of earlier versions of the model. E indicates that the model extends from the ground through exosphere and 00 is the year of release.
According to the NRL website, NRLMSISE-00 is the standard for international space research.
The inputs for the model are;
- Year and day
- time of day
- altitude
- geodetic latitude
- geodetic longitude
- local apparent solar time
- 81 day average of F10.7 solar flux
- daily F10.7 solar flux for previous day
- Daily magnetic index
Output of the model is;
- Helium Number density
- Oxygen(O) Number density
- Oxygen (O2) Number density
- Nitrogen (N) Number density
- Nitrogen (N2) Number density
- Argon Number density
- H Hydrogen Number density
- total mass density
- Anomalous oxygen Number density
- Exospheric temperature
- temperature at altitude
Contents
See also
- Atmospheric models
- International Standard Atmosphere links to 1976 standard.
External links
- NRL NRLMSISE-00 website
- Fortran source code
- Compiled dll and GUI front end source code
- other NRL weather models
- more atmosphere models from NASA
- publication
- C source code
NOTES
- ^ Coulson, Dolores M. & Roth, Katherine C., Adaptive Optics Systems II. Edited by Ellerbroek, Brent L.; Hart, Michael; Hubin, Norbert; Wizinowich, Peter L. Proceedings of the SPIE, Volume 7736, pp. 773652-773652-9 (2010)
Further reading
- Coulson, Dolores M. & Roth, Katherine C., Adaptive Optics Systems II. Edited by Ellerbroek, Brent L.; Hart, Michael; Hubin, Norbert; Wizinowich, Peter L. Proceedings of the SPIE, Volume 7736, pp. 773652-773652-9 (2010)
url=http://spiedigitallibrary.org/proceedings/resource/2/psisdg/7736/1/773652_1
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.