- Classical complement pathway
-
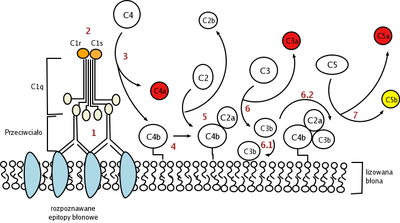
The Classical pathway of activation of the complement system is a group of blood proteins that mediate the specific antibody response. The main activators of the Classical Pathway are antigen-antibody complexes.
Contents
Initiation
It is triggered by antigen-bound antibody molecules. (The only antibodies capable of binding are two units of IgG or one IgM, although IgM is more effective at activating complement. IgG4 cannot bind, but the other three IgG types can.) It is the binding of a specific part of the antibody molecule to the C1 component that initiates this pathway.
C1 and its subunits
This initial enzyme, C1, is a complex formed through a calcium-dependent association between two reversibly interacting subunits, C1q and C1 (C1qr2s2). Approximately 70% of C1 is at all times present in this complex form. C1 occurs in serum as a proenzyme that tends to undergo autoactivation but is strictly controlled by C1-inhibitor (C1-In or C1 esterase). Upon the binding of C1 to immune complexes by virtue of the affinity of C1q for immunoglobulins (to be specific, IgM and IgG), the controlling action of C1-In is overcome, and C1q effects activation of C1r2s2.
C1q possesses no intrinsic catalytic activity, but, when any of several activators bind to the C1q subcomponent of C1, the homologous C1r and C1s subcomponents are converted into catalytically active species, namely C1r* and C1s*, triggering the first step of the classical pathway of complement activation.
Thus, on binding to immune complexes through C1q, the subunits of C1 become firmly associated and autoactivation commences even in the presence of the Cl-In.
Steps leading to C3-convertase
At first, a conformational change in C1r occurs, followed by proteolytic activation, which results in the cleavage of all four polypeptide chains of C1r2s2.
The two activated C1s subunits are then able to catalyse the assembly of the C3-convertase, C4bC2a, which has been formed from C2 and C4.
See also
External links
Immunology: Lymphocytic adaptive immune system and complement Lymphoid AntigensAntibodiesImmunity vs.
toleranceaction: Immunity · Autoimmunity · Alloimmunity · Allergy · Hypersensitivity · Inflammation · Cross-reactivity
inaction: Tolerance (Central, Peripheral, Clonal anergy, Clonal deletion, Tolerance in pregnancy) · ImmunodeficiencyLymphocytes Substances Complement Proteins: complement system (C, L, A) Activators/enzymes EarlyMiddleLateInhibitors Complement receptors Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.