- Royal Netherlands Army
-
Royal Netherlands Army 
Active 9 January 1814–present Country Netherlands Type Army Size 30,500 active full time and part time personnel Commanders Current
commanderLieutenant-General Mart de Kruijf [1] The Royal Netherlands Army (Koninklijke Landmacht) is the land forces element of the military of the Netherlands.
Contents
Short History
The Royal Netherlands Army was raised on 9 January 1814, but its origins date back to 1572, when the so-called Staatse Leger was raised. Therefore, the Netherlands is regarded to be one of the countries that have maintained the oldest standing army, dating back to the 16th century. This army of the Dutch Republic was one of the less organized, and not very-well trained armies of the seventeenth and early eighteenth century, and saw actions in the Eighty Year's War, the Dano-Swedish War 1658-1660, the Franco-Dutch War, the Nine Years War, the War of Spanish Succession, the War of Austrian Succession, and the French Revolutionary Wars until the French conquered the Netherlands in early 1795.
The Staatse Leger was replaced by the army of the Batavian Republic in 1795 which in its turn was replaced by the army of the Kingdom of Holland in 1806. It fought alongside the French in the Anglo-Russian Invasion of Holland in 1799 and several campaigns in Germany, Austria and Spain between 1800 and 1810. Most notable were the engagements of the Horse Artillery Korps Rijdende Artillerie at the battle of Friedland in 1807, the capture of the city of Stralsund in 1807 and 1809 and the participation of the Dutch Brigade in the Peninsular War between 1808 and 1810. The independent army was disbanded in 1810 when Napoleon decided to 'reunite' Holland into France (La Hollande est reunie à l'Empire). The army units became part of the Grande Armée. The present day 126e Régiment d'infanterie has Dutch origins. Dutch army elements participated in the French invasion of Russia in 1812. Most notable were the actions of the pontonniers company under captain Benthien at the Berezina river (Battle of Berezina).
An independent Dutch army was resurrected by the new Kingdom of the United Netherlands in 1814, following the Orangist uprising against Napoleonic rule in 1813. This new force, the Netherlands Mobile Army, formed an integral part of the allied army during the Hundred Days Campaign that culminated in the Battle of Waterloo. Units such as Baron Chassé's were key in securing victory for the allied army. Since 1814 (elements of) the army have been involved in several military conflicts (Waterloo campaign 1815, several colonial wars 1825-1925, the Belgian Revolution 1830-1832, the Second World War 1940-1945, the Indonesian War of Independence 1945-1949, and the Nieuw-Guinea insurgency 1960-1962).
Nowadays the army concentrates on peace-keeping and peace-enforcing operations and has been involved in several operations (in Lebanon between 1979-1985, and the former Yougoslavia (Bosnia-Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, and Kosovo) 1991-present, but also in Cambodja 1992-1994, Haiti 1995-1996, Cyprus 1998-1999, Eritrea and Ethiopia 2001, and most recent in Iraq 2003-2005, Afghanistan 2002-2010, and Chad 2008-2009).
Military academy
The military academy of the Royal Netherlands Army is the Koninklijke Militaire Academie in Breda.
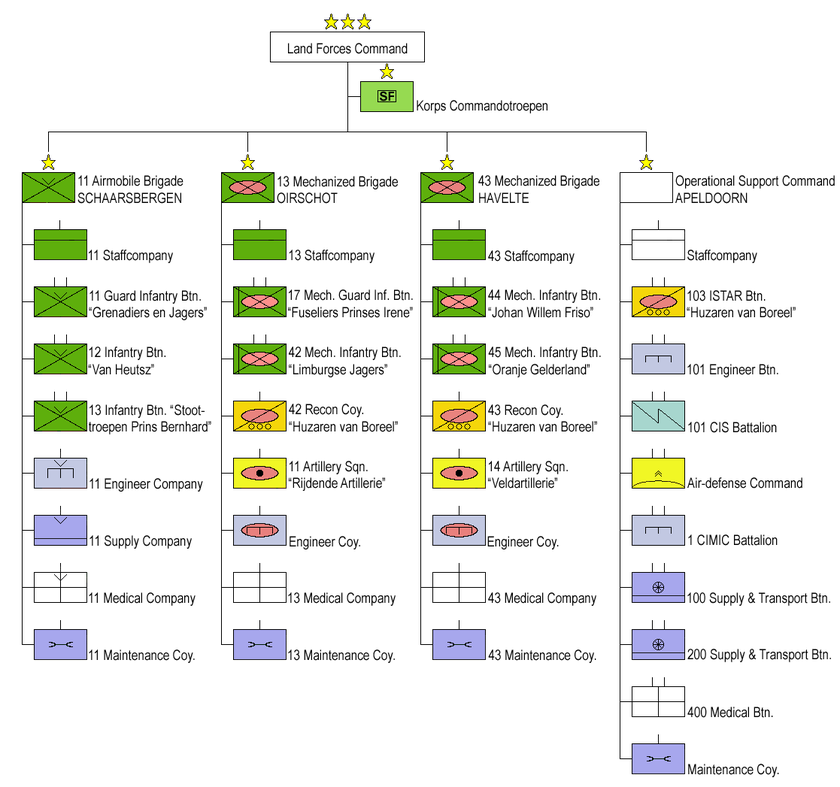
Structure of the Army
The core fighting element of the army consists of a single division sized element divided into three separate brigades: two mechanised brigades and one airborne brigade. The number of full-time professional personnel is 27,000. The Royal Netherlands Army is a volunteer force; compulsory military service has not been abolished but has been suspended. The other three services (Royal Netherlands Navy; Royal Netherlands Air Force and the Royal Marechaussee) are fully volunteer forces as well.
Unionized Army
Unlike many other military organizations, Dutch Army soldiers are represented by a union. This union is the General Federation Military Personnel (the acronym is AFMP), was recognized by the Dutch government in 1966 and represents both current and retired soldiers. The AFMP is a member of the Dutch Federation of Trade Unions, FNV.
Units of the Royal Netherlands Army
Cavalry
Royal Netherlands Army - brigades in 2011 - Regiment Huzaren Van Sytzama, former 1st Hussars Regiment (formed in 1814, origins date back to 1588) - Armoured (Will be disbanded)
- Regiment Huzaren Prins van Oranje, former 2nd Hussars Regiment (formed in 1815, origins date back to 1688) - Armoured (Will be disbanded)
- Regiment Huzaren Van Boreel, former 4th Hussars Regiment (formed in 1813, origins date back to 1585) - Reconnaissance/ISTAR
A fourth regiment, the Regiment Huzaren Prins Alexander, was disbanded in November 2007 due to budget cuts. This regiment represents the former 3rd Hussars Regiment, formed in 1814 (origins date back to 1672). It was known as the Red (because of the red colour on their uniform) or Guards Hussars, but was never really a Guards regiment. In 2011, news reached that all cavalry, thus tanks, will be disbanded due the largest budget cuts ever (see http://www.nu.nl/politiek/2470185/nederland-krijgt-leger-zonder-tanks.html)
Infantry
Each infantry regiment of the Royal Netherlands Army consists of a single battalion. The staff support compagnies of 11th Air Mobile Brigade, 13th Mechanized Brigade and 43rd Mechanized Brigade are part of the Garderegiment Grenadiers en Jagers, the Garderegiment Fusiliers Prinses Irene and Regiment Infanterie Johan Willem Friso respectively.
Guards
 Fennek RCV of the Royal Netherlands Army.
Fennek RCV of the Royal Netherlands Army.
- Garderegiment Grenadiers en Jagers, formed in 1995 through amalgamation of two regiments (formed 1829), origins date back to 1599 - Air Assault Infantry
- Garderegiment Fuseliers Prinses Irene, formed in 1941 - Mechanised Infantry
Line Infantry
- Regiment Infanterie Johan Willem Friso, former 1st Infantry Regiment (formed in 1813, origines date back to 1577)- Mechanised Infantry
- Regiment Limburgse Jagers, former 2nd Infantry Regiment (formed in 1813, origines date back to 1602) - Mechanised Infantry
- Regiment Infanterie Oranje Gelderland, former 5th Infantry Regiment (formed in 1814, origines date back to 1585) - Mechanised Infantry
- Regiment Van Heutsz, former Netherlands East Indies Army, formed in 1832 (origines date back to 1808) - Air Assault Infantry
- Regiment Stoottroepen Prins Bernhard, formed in 1944 from several resistance formations - Air Assault Infantry
The Regiment Limburgse Jagers and Regiment Infanterie Oranje Gelderland guard the traditions of the former 6th and 8th Infantry Regiment respectively. In the near future, the traditions of the Regiment Infanterie Menno van Coehoorn (former 3rd Infantry regiment, disbanded 1995) will be guarded by the Regiment Infantry Johan Willem Friso. The 4th Infantry Regiment (disbanded 1950) and the Regiment Infanterie Chassé (former 7th Infantry Regiment, disbanded 1995) remain disbanded.
Special Forces
- Korps Commandotroepen formed in 1942 - Special Forces unit
Support Arms
- Korps Veldartillerie, formed in 1677 - Field Artillery
- Korps Rijdende Artillerie, formed in 1793 - Horse Artillery
- Korps Luchtdoelartillerie, formed in 1917 - Air Defence Artillery
- Regiment Genietroepen, formed in 1748 - Engineers
- Regiment Verbindingstroepen, formed in 1874 - Communications
Services
- Regiment Bevoorradings-en Transporttroepen - Transport and Logistics
- Regiment Geneeskundige Troepen - Medical
- Regiment Technische Troepen - Electrical/Mechanical Engineers
- Dienstvak Technische Staf - Technical engineers
- Dienstvak Militair Juridische Dienst - Legal service
- Dienstvak Militair Psychologische en Sociologische Dienst - Psychological and Sociological service
- Korps Militaire Administratie - Administration
- Koninklijke Militaire Academie - Royal Military Academy
- Koninklijke Militaire School - Royal Military School
- LO/Sportorganisatie - Fisical training and Sports
Army Reserve
Korps Nationale Reserve - five mixed regional oriented battalions (mainly infantry with a light role), similar to UK Territorial Army. The battalions are placed under command of three Regional Support Commands, that will be integrated with the 11th Air Mobile Brigade, 13th Mechanized Brigade and 43rd Mechanized Brigade by 2011.
Bi-national Army Corps
The Netherlands and Germany work together in a Bi-national Army Corps structure, the I. German/Dutch Corps. This is a rapid deployable Army Corps headquarters which can be deployed in the frame of the NATO Response Force. The permanent elements of this corps are a bi-national Staff Support Battalion and a bi-national Communications and Informations Battalion. The Staff Support Battalion consists of a bi-national staff support company and a logistics company. The battalion is based at Münster (Germany) and Eibergen (Netherlands). The 101 Communications and Informations Battalion is based in Eibergen and Garderen.
Previously, during the Cold War, a full corps, I (NE) Corps, served as part of NATO's Northern Army Group. The corps consisted of three divisions during the 1980s, the 1st, 4th, and 5th (reserve) divisions. During the 1990s and 2000s this force was reduced to the First Division 7 December, which became part of I Ge/Nl Corps, and then later the division headquarters itself was disbanded.
Equipment
Armour
Tracked
- 82 Leopard 2A6 main battle tanks with 62 tanks and 11 hulls in reserve (28 tanks of the reserve are to be sold). Originally the Netherlands purchased 465 tanks but 114 tanks and 1 turret were sold to Austria, 100 to Canada, 57 to Norway, 1 driver training tank and 10 turrets to Germany and 38 to Portugal (1 driver training tank). 10 hulls from the reserves will be used for the 10 AEV-3 KODIAK acquired in cooperation with Germany & Sweden. On April 8, 2011 the Dutch Ministry of Defense announced the tank division will be dissolved and the remaining Leopard tanks sold due to large budget cuts.[2] On May 18, 2011 the last Leopard 2 fired the final shot at the Bergen-Hohne Training Area[3]
- 193 CV9035NL infantry fighting vehicles (deliveries until end of 2011)
- 568 AIFV (YPR-765) infantry fighting vehicles. Several versions: Armoured personnel carrier (APC), Anti-Tank, Reconnaissance, Engineering, Battle Damage Repair, Recovery (YPR806), Cargo, and Battlefield Ambulance. The YPR-765 is internationally known under the name AIFV, which was developed based on the M113. Originally 2082, sales have included 25 to Bahrain, 1030 to Egypt, 441 to Jordan and 18 to Chile. 366 vehicles still remain in service. The YPR vehicles still in service will be, as the already sold ones, replaced by a combination of CV9035NL, Fennek and Boxer vehicles.
Wheeled
- 410 Fennek armoured vehicles. Several versions: Reconnaissance, General Purpose/Cargo, Medium Range Anti-Tank, Air Defence Vehicle (Stinger Weapons Platform), Forward Observer and Tactical Air Control (Target Designation) party.
- 200 Boxer armoured fighting vehicles (deliveries between 2010-2015) 55 of the Command version, 19 of the Cargo version, 27 of the Cargo/C2 version, 41 of the Armoured Engineer Group version and 58 of the Ambulance version.
- 86 Bushmaster infantry mobility vehicles (10 lost during the Dutch mission in Afghanistan).
- 208 Airmobile Light Support Vehicles
Other armoured vehicles
- 25 Büffel (Leopard 2) recovery tanks
- 14 Biber (Leopard 1) bridgelayers (will be replaced by 4 upgraded ex-Norwegian Army Leguan bridgelayers on a wheeled chassis and 10 PSB2 on a Leopard 2A4 chassis)
- 14 Leopard 1 armoured engineer vehicles (to be replaced by 10 AEV-3 KODIAK acquired in cooperation with Germany & Sweden).
- 22 Leopard 1 recovery tanks
- 18 Fuchs 1 Electronic Warfare vehicles
- 6 Fuchs 1 NBC reconnaissance vehicles
Other vehicles
There are thousands of vehicles in several versions:
- 8,400 DAF Trucks, various versions with Broshuis trailers
- 555 Scania PLS Trucks, various versions
- 4,000 MB 290GD Wolf, 4WD car, various versions
- 128 Mercedes-Benz 280 CDI, various versions
- 12 Suzuki King Quad 750 AXI 4x4 Quad for Korps Commandotroepen
- 6 BOZENA-4 Mini Mine Clearing System
- 2 Scanjack 3500
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
- 20 EMT Aladin
- 72 RQ-11 Raven
- 32 SAGEM Sperwer
Artillery
 PzH 2000 155 mm Self-propelled howitzer of the Royal Netherlands Army.
PzH 2000 155 mm Self-propelled howitzer of the Royal Netherlands Army.
- 57 PzH 2000 (18 active, rest in storage and to be sold)
Air-defence system
NASAMS II
Personal weapons
- Accuracy International Arctic Warfare sniper rifle in 7.62
- Accuracy International AWM sniper rifle in .338 Lapua Magnum
- Diemaco C7 5.56 mm assault rifle (mechanized infantry)
- Diemaco C7A1 5.56mm assault rifle (airmobile infantry)
- Diemaco C8A1 5.56 mm carbine (special forces & marines)
- FIM-92C Stinger man-portable surface to air missile
- FN MAG 7.62 mm machine gun
- FN MINIMI 5.56 mm light machine gun
- FN P90 5.7mm submachine gun
- Glock 17 9 mm pistol
- Heckler & Koch AG-NL 40mm grenade launcher
- Heckler & Koch GMG 40 mm automatic grenade launcher
- Heckler & Koch HK416 5.56 mm carbine
- Heckler & Koch HK417 7.62 mm battle rifle/designated marksman rifle
- Heckler & Koch MP5 9mm submachine gun
- L16A2 81 mm mortar
- M2HB 12.7mm (.50cal) heavy machine gun
- M82A1 12.7mm sniper rifle
- Mauser SR93 sniper rifle in .300 Winchester Magnum (7.62 mm) or .338 Lapua Magnum (8.6 mm) used solely by the BBE
- Mossberg M590A1 12 gauge special purpose shotgun
- Panzerfaust 3 anti-tank weapon (short range)
- RT-120 (Habé Rayé) 120 mm mortar
- Sako TRG-41 sniper rifle in .338 Lapua Magnum
- SIG Sauer P226 9 mm pistol
- Gill anti-tank missile (medium range)
- Steyr SSG 69 7.62mm sniper rifle
Rank structure
See Military ranks of the Dutch armed forces.
Recent deployments
Korea
Dutch army troops have deployed as part of an international protection force since 1950. In total 3,972 Soldiers were sent to fight the war in Korea, 123 died in combat. Marines and Army were sent between 1950-1954
Lebanon
Dutch army troops have deployed as part of an international protection force since 1979 War in Lebanon, 1979-1985 UNIFIL. Of the 9,084 soldiers who served in Lebanon 9 soldiers died. Dutchbat South Lebanon, to protect and serve 44 painfbat.(44 Armored Battalion) Johan Willem Friso. All 9,084 Soldiers received the medal for peace keeping under war circumstances.
Bosnia-Herzegovina
Dutch army troops have deployed as part of an international protection force since 1992.
Kosovo
Dutch army troops have deployed as part of the NATO Kosovo Force since 1999.
Iraq
A contingent of 1,345 troops (comprising Landmacht and Dutch Marines, supported by Royal Netherlands Air Force helicopters) was deployed to Iraq in 2003, based at Camp Smitty near As Samawah (Southern Iraq) with responsibility for the Muthanna Province, as part of the Multinational force in Iraq. On June 1, 2004, the Dutch government renewed their stay through 2005. The Netherlands pulled its troops out of Iraq in March 2005, leaving half a dozen liaison officers until late 2005. The Dutch Government reportedly turned down an Iraqi Government request to extend the Dutch contingent for another year. The Netherlands lost 2 soldiers in separate attacks.
Afghanistan
In mid 2006, Dutch Special Forces Korps Commandotroepen teams deployed successfully to Tarin Kowt in Afghanistan, to lay the ground for the increasing numbers of engineers who were building a vast base there. At the same time other special forces units from other nations deployed throughout the area, and worked closely together in this volatile area. By August 2006 the Netherlands deployed the majority of 1,400 troops to Uruzgan province at southern Afghanistan at Tarin Kowt (1,200), at Kamp Holland, and Deh Rahwod (200). [1] The soldiers of Task Force Uruzgan were mostly from the Regiment Van Heutsz, supplemented with soldiers from 44 Pantserinfanteriebataljon Regiment Johan Willem Friso and the 42 Tankbataljon Regiment Huzaren Prins van Oranje. PzH 2000 self propelled artillery pieces were deployed and used in combat for the first time. Since 2006, Dutch forces were involved in some of the more intensive combat operations in southern Afghanistan, including Operation Medusa and the Battle of Chora. As of 10 August 2008, The Netherlands had a total of 1,770 troops in Afghanistan not including special forces troops.
References
External links
- Website Royal Netherlands Army
- Website Royal Netherlands Army Museum
- Dutch military vehicles and news
- Dutch Cavalry Museum
under the command of the Ministry of Defence Armies (land forces) in Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh Republic
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.