- Procainamide
-
Procainamide 
Systematic (IUPAC) name 4-amino-N-(2-diethylaminoethyl) benzamide Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com monograph Pregnancy cat. C(US) Legal status POM (UK) Routes IV, IM, oral Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 85% (oral) Protein binding 15 to 20% Metabolism Hepatic (CYP2D6-mediated) Half-life ~2.5 to 4.5 hours Excretion Renal Identifiers CAS number 51-06-9 
ATC code C01BA02 PubChem CID 4913 DrugBank APRD00509 ChemSpider 4744 
UNII L39WTC366D 
KEGG D08421 
ChEBI CHEBI:8428 
ChEMBL CHEMBL640 
Chemical data Formula C13H21N3O Mol. mass 235.325 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Procainamide INN (
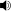 /proʊˈkeɪnəmaɪd/; trade names Pronestyl, Procan, Procanbid) is a pharmaceutical antiarrhythmic agent used for the medical treatment of cardiac arrhythmias, classified by the Vaughan Williams classification system as class Ia.
/proʊˈkeɪnəmaɪd/; trade names Pronestyl, Procan, Procanbid) is a pharmaceutical antiarrhythmic agent used for the medical treatment of cardiac arrhythmias, classified by the Vaughan Williams classification system as class Ia.Contents
History
Procainamide was approved by the US FDA on June 2, 1950, under the brand-name Pronestyl[1]. It was launched by Squibb in 1951.[2]
Mechanism
It blocks open sodium (Na+) channels and prolongs the cardiac action potential (outward potassium (K+) currents may be blocked). This results in slowed conduction, and ultimately the decreased rate of rise of the action potential, which may result in widening of QRS on electrocardiogram (ECG).
Uses
This drug is used for both supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias. For example, it can be used to convert new-onset atrial fibrillation, though it is suboptimal for this purpose. It can also be used to treat Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome by prolonging the refractory period of the accessory pathway. Typically use is secondary to lidocaine in patients who are allergic to lidocaine or dysrhythmias that are refractory to lidocaine.
Administration
Procainamide is administered intravenously or orally. When administered intravenously, a loading dose should first be given, though care should be taken not to cause hypotension. Procainamide's major active metabolite is N-acetyl procainamide (NAPA), which is approximately equipotent with the parent drug as an antiarrhythmic agent.[3] NAPA has an elimination half-life about twice that of procainamide, and it can reach somewhat higher plasma levels during chronic procainamide administration.[4] Loading dose is 100 mg IV bolus given slowly over 5 minutes. Max dose is 17 mg/kg. Use is discontinued when dysrhythmia is suppressed, or if hypotension ensues, QRS complex widens by 50% or more, or maximum dose is achieved.
Side effects
Adverse effects include rash, myalgia, hypersensitivity reactions (fever, agranulocytosis), Drug-Induced Lupus Erythematosus[5] (particularly in slow-acetylators), and proarrhythmic effects (e.g., torsades de pointes). Treatment with procainamide can cause antibody production against cellular components, accounting for the systemic lupus erythematosus-like adverse reactions.
External links
References
- ^ http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/drugsatfda/index.cfm
- ^ Hollman A (February 1992). "Procaine and procainamide". Br Heart J 67 (2): 143. doi:10.1136/hrt.67.2.143. PMC 1024743. PMID 18610401. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1024743.
- ^ Dutcher JS, Strong JM, Lucas SV, Lee WK, Atkinson AJ Jr. Procainamide and N-acetylprocainamide kinetics investigated simultaneously with stable isotope methodology. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Oct;22(4):447-57.
- ^ Drayer DE, Reidenberg MM, Sevy RW. N-acetylprocainamide: an active metabolite of procainamide. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Jun;146(2):358-63.
- ^ Kameda H, Mimori T, Kaburaki J, et al. (November 1998). "Systemic sclerosis complicated by procainamide-induced lupus and antiphospholipid syndrome". Br. J. Rheumatol. 37 (11): 1236–9. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/37.11.1236. PMID 9851277. http://rheumatology.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=9851277.
Antiarrhythmic agents (C01B) Channel blockers class Ib (Phase 3←)class Ic (Phase 0→)Amiodarone • Dronedarone • Bretylium • Bunaftine • Dofetilide • Ibutilide • Nifekalant • Sotalol • Tedisamil • Vernakalant • E-4031Receptor agonists
and antagonistsIon transporters Categories:- Benzamides
- Anilines
- Sodium channel blockers
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
