- Pyridoxine
-
Pyridoxine[1] 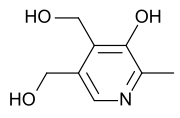 4,5-Bis(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpyridin-3-ol
4,5-Bis(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpyridin-3-olIdentifiers CAS number 65-23-6  ,
,
58-56-0 (HCl)PubChem 1054 ChemSpider 1025 
DrugBank DB00165 KEGG D08454 
ChEBI CHEBI:16709 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1364 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CC1=NC=C(C(=C1O)CO)CO
Properties Molecular formula C8H11NO3 Molar mass 169.18 g mol−1 Melting point 159-162 °C
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Pyridoxine is one of the compounds that can be called vitamin B6, along with pyridoxal and pyridoxamine. It differs from pyridoxamine by the substituent at the '4' position. It is often used as 'pyridoxine hydrochloride'.
Contents
Chemistry
It is based on a pyridine ring, with hydroxyl, methyl, and hydroxymethyl substituents. It is converted to the biologically active form pyridoxal 5-phosphate.
Function in the body
Pyridoxine assists in the balancing of sodium and potassium as well as promoting red blood cell production. It is linked to cardiovascular health by decreasing the formation of homocysteine. Pyridoxine may help balance hormonal changes in women and aid the immune system.[2] Lack of pyridoxine may cause anemia, nerve damage, seizures, skin problems, and sores in the mouth.[3]
It is required for the production of the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine and epinephrine, as it is the precursor to pyridoxal phosphate: cofactor for the enzyme aromatic amino acid decarboxylase. This enzyme is responsible for converting the precursors 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) into serotonin and levodopa (L-DOPA) into dopamine, noradrenaline and adrenaline. As such it has been implicated in the treatment of depression and anxiety.[citation needed]
Very good sources of pyridoxine are grains, nuts and dragon fruit from South East Asia.[4]
Medicinal uses
Pyridoxine is given to patients taking Isoniazid (INH) to combat the toxic side effects of the drug. It is given 10–50 mg/day to patients on to prevent peripheral neuropathy and CNS effects that are associated with the use of INH.
It is also essential for patients with extremely rare pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy, thought to be caused by mutations in the ALDH7A1 gene.
Vitamin B6 can be compounded into a variety of different dosage forms. It can be used orally as a tablet, capsule, or solution. It can also be used as a nasal spray or for injection when in its solution form.
Vitamin B6 is usually safe, at regular intakes up to 200 mg per day in adults. However, vitamin B6 can cause neurological disorders, such as loss of sensation in legs and imbalance, when taken in high doses (200 mg or more per day - 10,000% of US RDA) over a long period of time. Vitamin B6 toxicity can damage sensory nerves, leading to numbness in the hands and feet as well as difficulty walking. Symptoms of a pyridoxine overdose may include poor coordination, staggering, numbness, decreased sensation to touch, temperature, and vibration, and tiredness for up to six months.[5]
A contradictory publication on pyridoxine toxicity reported that over a 6 month period or longer, 21% of women taking doses of less than 50 mg daily experienced neurological toxicity.[6] The doses below 50 mg were not reported.
Based on the contradictory results of the two references cited above, some caution taking this vitamin at high doses and/or advise consulting with a physician or nutritional expert.
References
- ^ Pyridoxine at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ [1]
- ^ Vitamin B1, www.HowStuffWorks.com
- ^ Proximate analysis of dragon fruit
- ^ Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) - sources, benefits, dosage, deficiency, overdose, toxicity
- ^ K Dalton & MJT Dalton (1987). "Characteristics of pyridoxine overdose neuropathy syndrome". Acta Neurol Scand 76 (1): 8–11. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.1987.tb03536.x. PMID 3630649.
Vitamins (A11) Fat soluble D2 (Ergosterol, Ergocalciferol#) · D3 (7-Dehydrocholesterol, Previtamin D3, Cholecalciferol, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, Calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol), Calcitroic acid) · D4 (Dihydroergocalciferol) · D5 · D analogues (Dihydrotachysterol, Calcipotriol, Tacalcitol, Paricalcitol)Water soluble B1 (Thiamine#) · B2 (Riboflavin#) · B3 (Niacin, Nicotinamide#) · B5 (Pantothenic acid, Dexpanthenol, Pantethine) · B6 (Pyridoxine#, Pyridoxal phosphate, Pyridoxamine) · B7 (Biotin) · B9 (Folic acid, Dihydrofolic acid, Folinic acid) · B12 (Cyanocobalamin, Hydroxocobalamin, Methylcobalamin, Cobamamide) · CholineCombinations M: NUT
cof, enz, met
noco, nuvi, sysi/epon, met
drug(A8/11/12)
Categories:- Pyridines
- Alcohols
- B vitamins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
