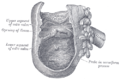
- Cecum
-
For the genus of sea snails, see Caecum (genus).Not to be confused with sacrum.
Cecum 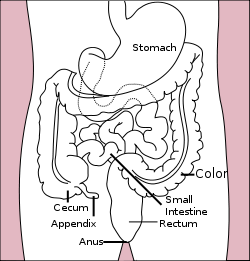
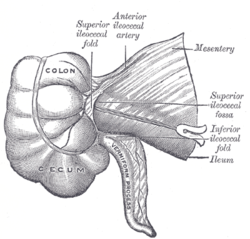
Superior ileocecal fossa (cecum labeled at bottom left) Gray's subject #249 1177 Precursor Midgut MeSH Cecum Dorlands/Elsevier Cecum The cecum or caecum (
 /ˈsiːkəm/, plural /ˈsiːkə/; from the Latin caecus meaning blind) is a pouch, connecting the ileum with the ascending colon of the large intestine. It is separated from the ileum by the ileocecal valve (ICV) or Bauhin's valve, and is considered to be the beginning of the large intestine. It is also separated from the colon by the cecocolic junction. The appendix is connected to the cecum[citation needed]. The cecum is usually peritoneal, while the ascending colon is retroperitoneal [1].
/ˈsiːkəm/, plural /ˈsiːkə/; from the Latin caecus meaning blind) is a pouch, connecting the ileum with the ascending colon of the large intestine. It is separated from the ileum by the ileocecal valve (ICV) or Bauhin's valve, and is considered to be the beginning of the large intestine. It is also separated from the colon by the cecocolic junction. The appendix is connected to the cecum[citation needed]. The cecum is usually peritoneal, while the ascending colon is retroperitoneal [1].Contents
Variation Across Species
A cecum is present in most amniote species, and also in lungfish, but not in any living species of amphibian. In reptiles, it is usually a single median structure, arising from the dorsal side of the large intestine. Birds typically have two paired ceca, as, unlike other mammals, do hyraxes.[2]
Most mammalian herbivores have a relatively large cecum, hosting a large number of bacteria, which aid in the enzymatic breakdown of plant materials such as cellulose; in many species, it is considerably wider than the colon. In contrast, obligatory carnivores, whose diets contain little or no plant material, have a reduced cecum, which is often partially or wholly replaced by the vermiform appendix.[2] Over 99% of the bacteria in the gut flora are anaerobes,[3][4][5][6][7] but in the cecum, aerobic bacteria reach high densities.[3]
Many fish have a number of small outpocketings, called pyloric ceca, along their intestine; despite the name they are not homologous with the cecum of amniotes, and their purpose is to increase the overall area of the digestive epithelium.[2] Some invertebrates, such as squid,[8] may also have structures with the same name, but these have no relationship with those of vertebrates.
Etymology
The term cecum comes from the Latin caecum, literally "blind", here in the sense "blind gut" or "cul de sac".[citation needed]
In dissections by the Greek philosophers, the connection between the ileum of the small intestines and the cecum was not fully understood. Most of the studies of the digestive tract were done on animals and the results were compared to human structures.[citation needed]
The junction between the small intestine and the colon, called the ileocecal valve, is so small in some animals that it was not considered to be a connection between the small and large intestines. During a dissection, the colon could be traced from the rectum, to the sigmoid colon, through the descending, transverse, and ascending sections. The colon seemed to dead-end into the cecum, or cul-de-sac.[citation needed]
The connection between the end of the small intestine (ileum) and the start of the colon (cecum) is now clearly understood, but the name has not changed.[citation needed]Development
The cecum and appendix are formed by the enlargement of the postarterial segment of the midgut loop.The proximal part of the bud grows rapidly to form the cecum. The lateral wall of the cecum grows much more rapidly than the medial wall with the result that the point of attachment of the appendix comes to lie on the medial side.[citation needed]
Diseases
A cecal carcinoid tumor is a carcinoid tumor of the cecum. A appendiceal carcinoid tumor (a carcinoid tumor of the appendix) is sometimes found next to a cecal carcinoid.[citation needed]
See also
Additional images
-
Endoscopic image of cecum with arrow pointing to ileocecal valve in foreground
References
- ^ http://download.videohelp.com/vitualis/med/large_intestine.htm
- ^ a b c Romer, Alfred Sherwood; Parsons, Thomas S. (1977). The Vertebrate Body. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International. pp. 353–354. ISBN 0-03-910284-X.
- ^ a b Guarner F, Malagelada JR (February 2003). "Gut flora in health and disease". Lancet 361 (9356): 512–9. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12489-0. PMID 12583961.
- ^ Sears CL (October 2005). "A dynamic partnership: celebrating our gut flora". Anaerobe 11 (5): 247–51. doi:10.1016/j.anaerobe.2005.05.001. PMID 16701579.
- ^ University of Glasgow. 2005. The normal gut flora. Available through web archive. Accessed May 22, 2008
- ^ Beaugerie L, Petit JC (April 2004). "Microbial-gut interactions in health and disease. Antibiotic-associated diarrhoea". Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 18 (2): 337–52. doi:10.1016/j.bpg.2003.10.002. PMID 15123074. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1521691803001276.
- ^ Vedantam G, Hecht DW (October 2003). "Antibiotics and anaerobes of gut origin". Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 6 (5): 457–61. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2003.09.006. PMID 14572537. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1369527403001176.
- ^ Williams, L.W. (1910). The anatomy of the common squid : Loligo pealii, Lesueur. American Museum Of Natural History.
External links
- Photo at mgccc.cc.ms.us
- SUNY Figs 37:03-08 - "Abdominal organs in situ."
- SUNY Figs 37:06-09 - "The larger intestine."
- SUNY Figs 39:05-09 - "The cecum with the distal portion of the ileum."
- SUNY Labs 39:14-0101 - "Incisions of the Cecum"
- Cross section at UV pelvis/pelvis-e12-2
- Video clip of worms in the Cecum
Categories:- Digestive system
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.