- DsrA RNA
-
DsrA RNA 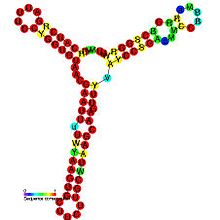
Predicted secondary structure and sequence conservation of DsrA Identifiers Symbol DsrA Rfam RF00014 Other data RNA type Gene; sRNA Domain(s) Bacteria SO 0000378 DsrA RNA is a non-coding RNA that regulates both transcription, by overcoming transcriptional silencing by the nucleoid-associated H-NS protein,[1] and translation, by promoting efficient translation of the stress sigma factor, RpoS.[2][3] These two activities of DsrA can be separated by mutation: the first of three stem-loops of the 85 nucleotide RNA is necessary for RpoS translation but not for anti-H-NS action, while the second stem-loop is essential for antisilencing and less critical for RpoS translation. The third stem-loop, which behaves as a transcription terminator, can be substituted by the trp transcription terminator without loss of either DsrA function. The sequence of the first stem-loop of DsrA is complementary with the upstream leader portion of RpoS messenger RNA, suggesting that pairing of DsrA with the RpoS message might be important for translational regulation.
There is evidence that DsrA RNA can self-assemble into nanostructures through antisense interactions of three self-complementary regions.[4] [5]
Contents
Targets of DsrA
There is experimental evidence to suggest that DsrA interacts with the protein-coding genes hns,[6][7][8], rbsD,[6] argR,[6] ilvI[6] and rpoS[9][10][11][12] via an anti-sense mechanism.
References
- ^ Sledjeski, D; Gottesman S (1995). "A small RNA acts as an antisilencer of the H-NS-silenced rcsA gene of Escherichia coli". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92 (6): 2003–2007. Bibcode 1995PNAS...92.2003S. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.6.2003. PMC 42411. PMID 7534408. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=42411.
- ^ Majdalani, N; Cunning C, Sledjeski D, Elliott T, Gottesman S (1998). "DsrA RNA regulates translation of RpoS message by an anti-antisense mechanism, independent of its action as an antisilencer of transcription". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95 (21): 12462–12467. Bibcode 1998PNAS...9512462M. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.21.12462. PMC 22853. PMID 9770508. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=22853.
- ^ Gottesman, S (2005). "Micros for microbes: non-coding regulatory RNAs in bacteria". Trends Genet 21 (7): 399–404. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2005.05.008. PMID 15913835.
- ^ Cayrol B, Nogues C, Dawid A, Sagi I, Silberzan P, Isambert H (2009). "A Nanostructure Made of a Bacterial Noncoding RNA.". J Am Chem Soc 131 (47): 17270–6. doi:10.1021/ja906076e. PMID 19821568.
- ^ Cayrol B, Geinguenaud F, Lacoste J, Busi F, Le Dérout J, Piétrement O, Le Cam E, Régnier P, Lavelle C, Arluison V (2009). "Auto-assembly of E. coli DsrA small noncoding RNA: Molecular characteristics and functional consequences..". RNA Biol. 6 (4): 434–45. doi:10.4161/rna.6.4.8949. PMID 19535898.
- ^ a b c d Lease RA, Cusick ME, Belfort M (1998). "Riboregulation in Escherichia coli: DsrA RNA acts by RNA:RNA interactions at multiple loci.". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95 (21): 12456–61. Bibcode 1998PNAS...9512456L. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.21.12456. PMC 22852. PMID 9770507. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=22852.
- ^ Urban JH, Vogel J (2007). "Translational control and target recognition by Escherichia coli small RNAs in vivo.". Nucleic Acids Res 35 (3): 1018–37. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl1040. PMC 1807950. PMID 17264113. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1807950.
- ^ Lease RA Belfort M (2000). "A trans-acting RNA as a control switch in Escherichia coli: DsrA modulates function by forming alternative structures.". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97 (18): 9919–24. Bibcode 2000PNAS...97.9919L. doi:10.1073/pnas.170281497. PMC 27626. PMID 10954740. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=27626.
- ^ Majdalani N, Cunning C, Sledjeski D, Elliott T, Gottesman S (1998). "DsrA RNA regulates translation of RpoS message by an anti-antisense mechanism, independent of its action as an antisilencer of transcription.". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95 (21): 12462–7. Bibcode 1998PNAS...9512462M. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.21.12462. PMC 22853. PMID 9770508. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=22853.
- ^ Majdalani N, Chen S, Murrow J, St John K, Gottesman S (2001). "Regulation of RpoS by a novel small RNA: the characterization of RprA.". Mol Microbiol 39 (5): 1382–94. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2001.02329.x. PMID 11251852.
- ^ Sledjeski DD, Gupta A, Gottesman S (1996). "The small RNA, DsrA, is essential for the low temperature expression of RpoS during exponential growth in Escherichia coli.". EMBO J 15 (15): 3993–4000. PMC 452119. PMID 8670904. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=452119.
- ^ Sledjeski DD, Whitman C, Zhang A (2001). "Hfq is necessary for regulation by the untranslated RNA DsrA.". J Bacteriol 183 (6): 1997–2005. doi:10.1128/JB.183.6.1997-2005.2001. PMC 95095. PMID 11222598. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=95095.
Further reading
- Santillano, D.; Boetius, A.; Ramette, A. (2010). "Improved dsrA-based Terminal Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Analysis of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria". Applied and Environmental Microbiology 76 (15): 5308–5311. doi:10.1128/AEM.03004-09. PMC 2916486. PMID 20543035. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2916486.
- Vecerek, B.; Beich-Frandsen, M.; Resch, A.; Blasi, U. (2009). "Translational activation of rpoS mRNA by the non-coding RNA DsrA and Hfq does not require ribosome binding". Nucleic Acids Research 38 (4): 1284–1293. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp1125. PMC 2831331. PMID 19969548. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2831331.
- Leduc, I.; Olsen, B.; Elkins, C. (2008). "Localization of the Domains of the Haemophilus ducreyi Trimeric Autotransporter DsrA Involved in Serum Resistance and Binding to the Extracellular Matrix Proteins Fibronectin and Vitronectin". Infection and Immunity 77 (2): 657–666. doi:10.1128/IAI.00819-08. PMC 2632028. PMID 19015257. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2632028.
- Soper, J.; Woodson, A. (Sep 2008). "The rpoS mRNA leader recruits Hfq to facilitate annealing with DsrA sRNA" (Free full text). RNA 14 (9): 1907–1917. doi:10.1261/rna.1110608. ISSN 1355-8382. PMC 2525945. PMID 18658123. http://www.rnajournal.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=18658123.
- Li, H.; Granat, A.; Stewart, V.; Gillespie, J. R. (2008). "RpoS, H-NS, and DsrA influence EHEC hemolysin operon (ehxCABD) transcription inEscherichia coliO157:H7 strain EDL933". FEMS Microbiology Letters 285 (2): 257–262. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01240.x. PMID 18616595.
- Leduc, I.; White, C. D.; Nepluev, I.; Throm, R. E.; Spinola, S. M.; Elkins, C. (2008). "Outer Membrane Protein DsrA Is the Major Fibronectin-Binding Determinant of Haemophilus ducreyi". Infection and Immunity 76 (4): 1608–1616. doi:10.1128/IAI.00994-07. PMC 2292853. PMID 18212073. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2292853.
- Resch, A.; Afonyushkin, T.; Lombo, T. B.; McDowall, K. J.; Blasi, U.; Kaberdin, V. R. (2008). "Translational activation by the noncoding RNA DsrA involves alternative RNase III processing in the rpoS 5′-leader". RNA 14 (3): 454–459. doi:10.1261/rna.603108. PMC 2248258. PMID 18192613. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2248258.
- Ben-Dov, E.; Brenner, A.; Kushmaro, A. (2007). "Quantification of Sulfate-reducing Bacteria in Industrial Wastewater, by Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Using dsrA and apsA Genes". Microbial Ecology 54 (3): 439–451. doi:10.1007/s00248-007-9233-2. PMID 17351812.
- Koleva, R.; Austin, C.; Kowaleski, J.; Neems, D.; Wang, L.; Vary, C.; Schlax, P. (2006). "Interactions of ribosomal protein S1 with DsrA and rpoS mRNA☆". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 348 (2): 662–668. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.07.102. PMID 16890206.
- Jones, A. M.; Goodwill, A.; Elliott, T. (2006). "Limited Role for the DsrA and RprA Regulatory RNAs in rpoS Regulation in Salmonella enterica". Journal of Bacteriology 188 (14): 5077–5088. doi:10.1128/JB.00206-06. PMC 1539969. PMID 16816180. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1539969.
- Sun, X.; Wartell, R. M. (2006). "Escherichia coliHfq Binds A18and DsrA Domain II with Similar 2:1 Hfq6/RNA Stoichiometry Using Different Surface Sites†". Biochemistry 45 (15): 4875–4887. doi:10.1021/bi0523613. PMID 16605255.
- Rolle, K.; Zywicki, M.; Wyszko, E.; Barciszewska, M. Z.; Barciszewski, J. (2006). "Evaluation of the Dynamic Structure of DsrA RNA from E. Coli and Its Functional Consequences". Journal of Biochemistry 139 (3): 431–438. doi:10.1093/jb/mvj045. PMID 16567408.
- Abdullah, M.; Nepluev, I.; Afonina, G.; Ram, S.; Rice, P.; Cade, W.; Elkins, C. (2005). "Killing of dsrA Mutants of Haemophilus ducreyi by Normal Human Serum Occurs via the Classical Complement Pathway and Is Initiated by Immunoglobulin M Binding". Infection and Immunity 73 (6): 3431–3439. doi:10.1128/IAI.73.6.3431-3439.2005. PMC 1111860. PMID 15908371. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1111860.
- White, C. D.; Leduc, I.; Olsen, B.; Jeter, C.; Harris, C.; Elkins, C. (2005). "Haemophilus ducreyi Outer Membrane Determinants, Including DsrA, Define Two Clonal Populations". Infection and Immunity 73 (4): 2387–2399. doi:10.1128/IAI.73.4.2387-2399.2005. PMC 1087395. PMID 15784585. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1087395.
- Lease, R. A.; Woodson, S. A. (2004). "Cycling of the Sm-like Protein Hfq on the DsrA Small Regulatory RNA". Journal of Molecular Biology 344 (5): 1211–1223. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.10.006. PMID 15561140.
- Mikulecky, P. J.; Kaw, M. K.; Brescia, C. C.; Takach, J. C.; Sledjeski, D. D.; Feig, A. L. (2004). "Escherichia coli Hfq has distinct interaction surfaces for DsrA, rpoS and poly(A) RNAs". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 11 (12): 1206–1214. doi:10.1038/nsmb858. PMC 3071270. PMID 15531892. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=3071270.
- Lease, R. A.; Smith, D.; McDonough, K.; Belfort, M. (2004). "The Small Noncoding DsrA RNA Is an Acid Resistance Regulator in Escherichia coli". Journal of Bacteriology 186 (18): 6179–6185. doi:10.1128/JB.186.18.6179-6185.2004. PMC 515158. PMID 15342588. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=515158.
- Repoila, F.; Gottesman, S. (2003). "Temperature Sensing by the dsrA Promoter". Journal of bacteriology 185 (22): 6609–6614. doi:10.1128/JB.185.22.6609-6614.2003. PMC 262114. PMID 14594834. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=262114.
- Worhunsky, D. J.; Godek, K.; Litsch, S.; Schlax, P. J. (2003). "Interactions of the Non-coding RNA DsrA and RpoS mRNA with the 30 S Ribosomal Subunit". Journal of Biological Chemistry 278 (18): 15815–15824. doi:10.1074/jbc.M301684200. PMID 12600997.
- Brescia, C. C.; Mikulecky, P. J.; Feig, A. L.; Sledjeski, D. D. (2003). "Identification of the Hfq-binding site on DsrA RNA: Hfq binds without altering DsrA secondary structure". RNA 9 (1): 33–43. doi:10.1261/rna.2570803. PMC 1370368. PMID 12554874. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1370368.
- Cole, L. E.; Kawula, T. H.; Toffer, K. L.; Elkins, C. (2002). "The Haemophilus ducreyi Serum Resistance Antigen DsrA Confers Attachment to Human Keratinocytes". Infection and immunity 70 (11): 6158–6165. doi:10.1128/IAI.70.11.6158-6165.2002. PMC 130365. PMID 12379693. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=130365.
- Repoila, F.; Gottesman, S. (2001). "Signal Transduction Cascade for Regulation of RpoS: Temperature Regulation of DsrA". Journal of Bacteriology 183 (13): 4012–4023. doi:10.1128/JB.183.13.4012-4023.2001. PMC 95285. PMID 11395466. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=95285.
- Sledjeski, D. D.; Whitman, C.; Zhang, A. (2001). "Hfq Is Necessary for Regulation by the Untranslated RNA DsrA". Journal of Bacteriology 183 (6): 1997–2005. doi:10.1128/JB.183.6.1997-2005.2001. PMC 95095. PMID 11222598. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=95095.
- Bong, C. T. H.; Throm, R. E.; Fortney, K. R.; Katz, B. P.; Hood, A. F.; Elkins, C.; Spinola, S. M. (2001). "DsrA-Deficient Mutant of Haemophilus ducreyi Is Impaired in Its Ability To Infect Human Volunteers". Infection and Immunity 69 (3): 1488–1491. doi:10.1128/IAI.69.3.1488-1491.2001. PMC 98046. PMID 11179317. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=98046.
- Lease, R. A.; Belfort, M. (2000). "Riboregulation by DsrA RNA: trans-actions for global economy". Molecular microbiology 38 (4): 667–672. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.02162.x. PMID 11115103.
- Lease, R. A.; Belfort, M. (2000). "A trans-acting RNA as a control switch in Escherichia coli: DsrA modulates function by forming alternative structures". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 97 (18): 9919–9924. Bibcode 2000PNAS...97.9919L. doi:10.1073/pnas.170281497. PMC 27626. PMID 10954740. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=27626.
- Elkins, C.; Morrow Jr, K. J.; Olsen, B. (2000). "Serum Resistance in Haemophilus ducreyi Requires Outer Membrane Protein DsrA". Infection and immunity 68 (3): 1608–1619. doi:10.1128/IAI.68.3.1608-1619.2000. PMC 97321. PMID 10678980. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=97321.
- Majdalani, N.; Cunning, C.; Sledjeski, D.; Elliott, T.; Gottesman, S. (1998). "DsrA RNA regulates translation of RpoS message by an anti-antisense mechanism, independent of its action as an antisilencer of transcription". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 95 (21): 12462–12467. Bibcode 1998PNAS...9512462M. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.21.12462. PMC 22853. PMID 9770508. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=22853.
- Lease, R. A.; Cusick, M. E.; Belfort, M. (1998). "Riboregulation in Escherichia coli: DsrA RNA acts by RNA:RNA interactions at multiple loci". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 95 (21): 12456–12461. Bibcode 1998PNAS...9512456L. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.21.12456. PMC 22852. PMID 9770507. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=22852.
- Klauck, E; Böhringer, J; Hengge-Aronis, R (1997). "The LysR-like regulator LeuO in Escherichia coli is involved in the translational regulation of rpoS by affecting the expression of the small regulatory DsrA-RNA". Molecular microbiology 25 (3): 559–69. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.4911852.x. PMID 9302018.
- Sledjeski, D. D.; Gupta, A.; Gottesman, S. (1996). "The small RNA, DsrA, is essential for the low temperature expression of RpoS during exponential growth in Escherichia coli". The EMBO journal 15 (15): 3993–4000. PMC 452119. PMID 8670904. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=452119.
External links
Categories:- Non-coding RNA
- Molecular and cellular biology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
