- Yohkoh
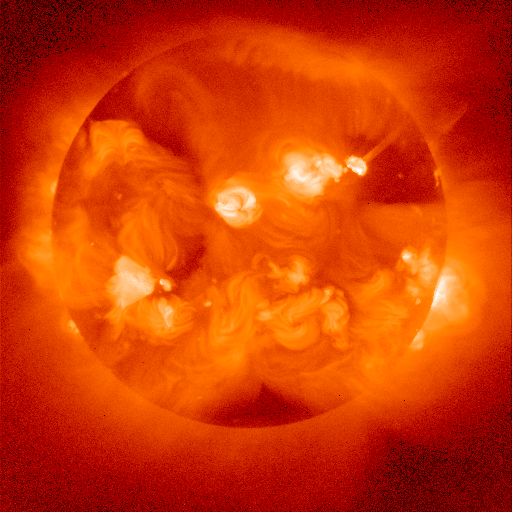
thumb|300px|right|The_X-ray_solar_corona_as_viewed_by_the_Yohkoh " observatory]Yohkoh ("Sunbeam" in Japanese), also known as Solar-A, was a Japanese Institute of Space and Astronautical Science Solar mission with
United States andUnited Kingdom collaboration. It was launched intoEarth orbitAugust 30 ,1991 by a M-3S-5 rocket fromKagoshima Space Center .The satellite was three-axis stabilized and in a near circular orbit. It carried four instruments - a Soft X-ray Telescope (SXT), a Hard X-ray Telescope (HXT), a Bragg Crystal Spectrometer (BCS), and a Wide Band Spectrometer (WBS). About 50 Mb were generated each day and this was stored onboard by a 10.5 Mb capacity recorder.
Because SXT utilized a
charge-coupled device (CCD) as its readout device, perhaps being the first X-ray astronomical telescope to do so, its "data cube" of images was both extensive and convenient, and it revealed much interesting detail about the behavior of the solar corona. Previous solar soft X-ray observations, such as those ofSkylab , had been restricted to film as a readout device. Many interesting new discoveries were also made; for glimpses of these see the [http://solar.physics.montana.edu/nuggets/ Yohkoh Science Nuggets] for example.The mission ended after more than ten years of successful observation when it went into its "safehold" mode during an annular eclipse on
December 14 ,2001 after the spacecraft lost lock on the Sun. Operational mistakes and other flaws conspired in such a way that its solar panels could no longer charge the batteries, which drained irreversibly. Ironically, several other solar eclipses had successfully been observed.On
September 12 ,2005 the spacecraft burned up during reentry over South Asia. The time of reentry, as provided by the U.S. Space Surveillance Network, was 6:16 pmJapan Standard Time (JST).External links
* [http://www.isas.jaxa.jp/e/enterp/missions/yohkoh/index.shtml JAXA/ISAS overview of mission]
* [http://www.lmsal.com/SXT/homepage.html SXT project page]
* [http://www.lmsal.com/SXT/Oimages.html SXT observation images]
* [http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9387680/Yohkoh Encyclopaedia Britannica, Yohkoh]
* [http://gedas22.stelab.nagoya-u.ac.jp/HXT/ HXT project page]
* [http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/database/MasterCatalog?sc=1991-062A NASA/NSSDC information on Yohkoh]
* [http://newton.nap.edu/books/NI000235/html U.S.-European-Japanese Workshop on Space Cooperation: Summary Report] , 1999
* [http://solar.physics.montana.edu/nuggets/ Yohkoh Science Nuggets]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.