- Dahlonega, Georgia
-
Dahlonega, Georgia, USA — City — Historic Lumpkin County Courthouse, which now houses the Dahlonega Gold Museum Historic Site Nickname(s): Gold City Location in Lumpkin County and the state of Georgia Coordinates: 34°32′N 83°59′W / 34.533°N 83.983°WCoordinates: 34°32′N 83°59′W / 34.533°N 83.983°W Country United States State Georgia County Lumpkin Government - Mayor Gary McCullough - City Marshall Stacy Jarrard - City Manager Bill Lewis. Area - Total 6.4 sq mi (16.6 km2) - Land 6.4 sq mi (16.6 km2) - Water 0.0 sq mi (0 km2) Elevation 1,450 ft (442 m) Population (2010) - Total 29,966 - Density 568.1/sq mi (219.5/km2) Time zone EST (UTC-5) - Summer (DST) EDT (UTC-4) ZIP codes 30533, 30597 Area code(s) 706 FIPS code 13-21240[1] GNIS feature ID 0355420[2] Website www.cityofdahlonega.com Dahlonega is a city in Lumpkin County, Georgia, United States, and is its county seat[3]. As of the 2000 census, it had a total population of 3,638.
Dahlonega is located at the north end of Georgia 400, which connects Atlanta to many affluent suburbs to the north. It is consistently named as a best place to retire by many different publications due to its low cost of living, vibrant activities, continuing education for seniors, festivals, and beautiful setting.
In 1828 Dahlonega was the site of the first major gold rush in the United States. The Dahlonega Gold Museum Historic Site sits in the middle of the town square, housed in the old Lumpkin County Courthouse built in 1836. From its steps in 1849, Dahlonega Mint assayor Dr. M. F. Stephenson tried to persuade miners to stay in Dahlonega instead of joining the California Gold Rush, saying, "There's gold in them thar hills." Corey Smith wrote a song about the town of Dahlonega. It is the first track on his second album "In the Mood."
Contents
History
See also: History of North Georgia College and State UniversityThis area was occupied by indigenous peoples for thousands of years before European contact. When European American settlers arrived, it was the traditional territory of the historical Cherokee nation.
In 1828, Dahlonega became the site of the first major gold rush in the USA and became a boom town in the Georgia Gold Rush. The United States Mint built a branch mint here, which it operated from 1838–1861. The Confederate Treasury Department took over the facility after the declaration of secession and operated it until 1 June 1861. Dahlonega, GA was home to many Creeks and Cherokees and still is today. There are a few Creek and Cherokee descendents in Dahlonega, GA today, though they are not in communities but scattered throughout Dahlonega. Most of the descendents are Creek-Cherokee mixed. Names like Corn, Davis, and Bird and the Chambers Families were of Cherokee blood. Surnames like Limley and Cagle were of Creek and Seminole blood. Though not part of state or federal recognition they still practice their traditions as Cherokee and Creek people. The word Dahlonega originally spelled Da-lo-ni-ge-i means Yellow.[citation needed]
Numerous gold mines were illegally developed in the area. Miners coming illegally into the Cherokee Nation as outlined in the treaty between the Federal Government and the Cherokee Nation in The Treaty of Washington 1819 to the area came into conflict with the Cherokee Nation, whose territory they were trespassing on. They raised political pressure against the Cherokee because they wanted to get the gold. The Federal Government forced the Native Americans west of the Mississippi River to Oklahoma on the Trail of Tears during Indian Removal. Dahlonega was founded two years before the Treaty of New Echota 1835, which made its founding a violation of The Treaty of Washington of 1819.[4][5]
In 1833 the city was named Talonega by the Georgia General Assembly on 21 December 1833.[6] The name was changed from Talonega by the Georgia General Assembly on 25 December 1837 to Dahlonega,[7] from the Cherokee-language word Dalonige, meaning "yellow" or "gold."[8] The city is just east of Auraria; each claims to be the site of the first discovery of gold. Senator John Calhoun of South Carolina (7th Vice President of the United States) owned the Calhoun Mine, just south of the City Square.
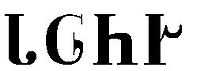 Cherokee for Da-lo-ni-ge English phonetics: dah low knee gay[9]
Cherokee for Da-lo-ni-ge English phonetics: dah low knee gay[9]
The Dahlonega Mint, like the one established in 1838 in Charlotte, North Carolina, only minted gold coins, in denominations of $1.00, $2.50 (quarter eagle), $3.00 (1854 only) and $5.00 (half eagle). This was cost effective in consideration of the economics, time, and risk of shipping gold to the main mint in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The Dahlonega Mint was a small operation, usually accounting for only a small fraction of the gold coinage minted annually in the US.
The government decided against re-opening the facility after the Civil War. By then, the U.S. government had established a mint in San Francisco, California. Given the large amount of gold discovered in California from the late 1840s on, that mint handled the national needs of gold mint production.
As a result, surviving Dahlonega coinage is today highly prized in American numismatics. The mint building burned in 1878. The North Georgia College campus built Price Memorial Hall on its foundation.[10] The building has a gold-leaf steeple to refer to the history of the site.
In recent years, Dahlonega and Lumpkin County have been recognized as "the heart of Georgia Wine Country." The county features five vineyards and wineries that attract many tourists.
The historic Dahlonega Square is also a popular tourist destination, with gift shops, restaurants, art galleries and artists' studios. The city's local festivals draw many tourists. "Bear on the Square", an annual three-day festival held the third weekend in April, marks the day that a black bear wandered onto the square. It features bluegrass and old-time music. It celebrates the culture of the Southern Appalachians with a juried artists' market and other activities. "Gold Rush Days", an annual two-day event the third weekend in October, attract over 200,000 people.[11]
Historical marker
Located at 384 Mountain Drive, WPA Historical Marker 19 B-7 explains:
This court house, built in 1836, replaced the small structure used since the establishment of Lumpkin County in 1832. The town was named Dahlonega in October, 1833, for the Cherokee word Talonega meaning "golden." From its steps in 1849, Dr. M.F. Stephenson, assayer [sic] at the Mint, attempted to dissuade Georgia miners from leaving to join the California Gold Rush. His oration gave rise to the sayings: "There's millions in it," and "Thar's gold in them thar hills."[12]
Geography
Dahlonega is located at 34°32′N 83°59′W / 34.533°N 83.983°W (34.5305, −83.9847)[13].
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 6.4 square miles (17 km2), all of it land.
Demographics
As of the census[1] of 2000, there were 3,638 people, 1,060 households, and 568 families residing in the city. The population density was 568.1 people per square mile (219.5/km²). There were 1,181 housing units at an average density of 184.4 per square mile (71.2/km²). The racial makeup of the city was 89.94% White, 4.95% African American, 0.44% Native American, 0.71% Asian, 0.11% Pacific Islander, 2.56% from other races, and 1.29% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 6.57% of the population.
There were 1,060 households out of which 23.4% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 41.1% were married couples living together, 9.3% had a female householder with no husband present, and 46.4% were non-families. 31.5% of all households were made up of individuals and 10.9% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.31 and the average family size was 2.96.
In the city the population was spread out with 13.5% under the age of 18, 42.9% from 18 to 24, 19.0% from 25 to 44, 13.2% from 45 to 64, and 11.4% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 22 years. For every 100 females there were 73.6 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 69.3 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $28,636, and the median income for a family was $44,904. Males had a median income of $30,500 versus $22,917 for females. The per capita income for the city was $16,572. About 11.4% of families and 24.4% of the population were below the poverty line, including 19.4% of those under age 18 and 13.8% of those age 65 or over.
Historical populations Year Pop. ±% 1820 385 — 1830 7,568 +1865.7% 1840 8,742 +15.5% 1850 6,245 −28.6% 1860 5,431 −13.0% 1870 3,937 −27.5% 1880 4,012 +1.9% 1890 4,014 +0.0% 1900 4,013 −0.0% 1910 3,128 −22.1% 1920 2,775 −11.3% 1930 2,610 −5.9% 1940 1,998 −23.4% 1950 1,765 −11.7% 1960 2,044 +15.8% 1970 2,376 +16.2% 1980 3,000 +26.3% 1990 3,246 +8.2% 2000 3,638 +12.1% Education
Lumpkin County School District
The Lumpkin County School District holds grades pre-school to grade twelve, that consists of three elementary schools, a middle school, and a high school.[14] The district has 215 full-time teachers and over 3,511 students.[15]
- Lumpkin County Elementary School
- Long Branch Elementary School
- Blackburn Elementary School
- Lumpkin County Middle School
- Lumpkin County High School
Higher education
Dahlonega is home to North Georgia College and State University, the Senior Military College of Georgia. The campus has a building, Price Hall, topped with a spire, which is covered with gold leaf from the town. The rotunda dome of the Georgia State Capitol in Atlanta is also covered with Dahlonega gold.
Other educational facilities
- Wahsega 4-H Center, an environmental education center and summer camp owned by the University of Georgia and administered through the UGA Cooperative Extension Service Georgia 4-H program
- Camp Glisson, a year-round retreat camp owned by the North Georgia Conference of the United Methodist Church
Famous residents
- Amy Ray, Indigo Girls singer and song-writer
- Max Burns, Former United States House of Representatives Member
- Sara Christian, NASCAR first female driver
- John Bell, Widespread Panic lead singer and guitarist
- Zac Brown, Zac Brown Band lead singer
- Dallas Kinney, Pulitzer Prize winning photographer.
References
- ^ a b "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. http://factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ "US Board on Geographic Names". United States Geological Survey. 2007-10-25. http://geonames.usgs.gov. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. http://www.naco.org/Counties/Pages/FindACounty.aspx. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- ^ James Loewen, (1996).
- ^ http://georgiainfo.galileo.usg.edu/washing5.htm
- ^ Acts passed by the General Assembly ,by J. Johnston, 1838
- ^ Acts passed by the General Assembly ,by J. Johnston, 1838
- ^ http://wehali.com/tsalagi/
- ^ http://wehali.com/tsalagi/
- ^ Price Memorial Building State Historical Marker (accessed 27 October 2006)
- ^ Dahlonega Jaycees
- ^ Georgia Historical Markers (accessed 27 October 2006)
- ^ "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. 2011-02-12. http://www.census.gov/geo/www/gazetteer/gazette.html. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- ^ Georgia Board of Education, Retrieved 23 June 2010.
- ^ School Stats, Retrieved 23 June 2010.
Further reading
- "Gold-Mining in Georgia." Harper's New Monthly Magazine 59, Issue 352 (September 1879): 517–519. Available here
- I Remember Dahlonega: Memories of Growing Up in Lumpkin County, by Anne Dismukes Amerson (Chestatee Publishing: 1993)
- Williams, David (1993). The Georgia Gold Rush: Twenty-Niners, Cherokees, and Gold Fever. Columbia, South Carolina: University of South Carolina Press. ISBN 1-57003-052-9.
External links
- City of Dahlonega Website
- Dahlonega Georgia Merchants Association
- Dahlonega Nugget Newspaper
- "Thar's Gold in Them Thar Hills": Gold and Gold Mining in Georgia, 1830s–1940s
- The Bear On the Square Mountain Festival
Municipalities and communities of Lumpkin County, Georgia County seat: Dahlonega City Dahlonega
Ghost town Categories:- Populated places in Lumpkin County, Georgia
- Cities in Georgia (U.S. state)
- County seats in Georgia (U.S. state)
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.




