- Vomitoxin
-
Vomitoxin 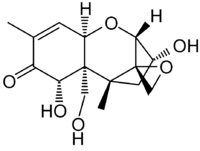 (3α,7α)-3,7,15-trihydroxy-12,13-epoxytrichothec-9-en-8-oneOther names
(3α,7α)-3,7,15-trihydroxy-12,13-epoxytrichothec-9-en-8-oneOther names
Deoxynivalenol (DON)
VomitoxinIdentifiers CAS number 51481-10-8 
PubChem 40024 ChemSpider 36584 
KEGG C09747 
ChEMBL CHEMBL513300 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C4\C(=C/[C@H]3O[C@H]2[C@]1(OC1)[C@](C[C@H]2O)([C@@]3(CO)[C@@H]4O)C)C
- InChI=1S/C15H20O6/c1-7-3-9-14(5-16,11(19)10(7)18)13(2)4-8(17)12(21-9)15(13)6-20-15/h3,8-9,11-12,16-17,19H,4-6H2,1-2H3/t8-,9-,11-,12-,13-,14-,15+/m1/s1

Key: LINOMUASTDIRTM-QGRHZQQGSA-N
InChI=1/C15H20O6/c1-7-3-9-14(5-16,11(19)10(7)18)13(2)4-8(17)12(21-9)15(13)6-20-15/h3,8-9,11-12,16-17,19H,4-6H2,1-2H3/t8-,9-,11-,12-,13-,14-,15+/m1/s1
Key: LINOMUASTDIRTM-QGRHZQQGBF
Properties Molecular formula C15H20O6 Molar mass 296.32 g mol−1 Hazards MSDS External MSDS  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Vomitoxin, also known as deoxynivalenol (DON), is a type B trichothecene, an epoxy-sesquiterpeneoid. This mycotoxin occurs predominantly in grains such as wheat, barley, oats, rye, and maize, and less often in rice, sorghum, and triticale. The occurrence of deoxynivalenol is associated primarily with Fusarium graminearum (Gibberella zeae) and F. culmorum, both of which are important plant pathogens which cause Fusarium head blight in wheat and Gibberella ear rot in maize. A direct relationship between the incidence of Fusarium head blight and contamination of wheat with deoxynivalenol has been established [1]. The incidence of Fusarium head blight is strongly associated with moisture at the time of flowering (anthesis), and the timing of rainfall, rather than the amount, is the most critical factor. However, increased amount of moisture towards harvest time has been associated with lower amount of vomitoxin in wheat grain due to leaching of toxins [2] Furthermore, deoxynivalenol contents are significantly affected by the susceptibility of cultivars towards Fusarium species, previous crop, tillage practices, and fungicide use [3]
F. graminearum grows optimally at a temperature of 25 °C and at a water activity above 0.88. F. culmorum grows optimally at 21 °C and at a water activity above 0.87. The geographical distribution of the two species appears to be related to temperature, F. graminearum being the commoner species and occurring in warmer climates. Deoxynivalenol has been implicated in incidents of mycotoxicoses in both humans and farm animals.
When compared to other trichothecene mycotoxins which can form in grains and forages, vomitoxin is relatively mild. Reduced feed intake, and the accompanying decrease in performance, are the only symptoms of vomitoxin toxicity livestock producers will likely encounter. This response to vomitoxin appears to occur through the central nervous system. Vomitoxin belongs to a class of mycotoxins (tricothecenes) which are strong protein inhibitors. Inhibition of protein synthesis following exposure to vomitoxin causes the brain to increase its uptake of the amino acid tryptophan and, in turn, its synthesis of serotonin. Increased levels of serotonin are believed to be responsible for the anorexic effects of DON and other tricothecenes. Irritation of the gastrointestinal tract may also play a role in reducing feed intake... This fact may also partially explain the high incidence of paraesophageal stomach ulcers observed in sows off feed during feed refusal.
- Human foods: Vomitoxin is not a known carcinogen as with aflatoxin. Large amounts of grain with vomitoxin would have to be consumed to pose a health risk to humans. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has established a level of 1 ppm (parts per million) restriction of vomitoxin.
- Companion animals: Dogs and cats are restricted to 5 ppm and of grains and grain byproducts and that the grains not exceed 40% percent of the diet.
- Livestock and farm animals: In animals and livestock, vomitoxin causes a refusal to feed and lack of weight gain when fed above advised levels. Restrictions are set at 10 ppm for poultry and ruminating beef and feedlot cattle older than 4 months. Ingredients may not exceed 50% of the animal's diet. Dairy cow limits are set at 2 ppm.
References
- ^ Gautam, P. and Dill-Macky, R. 2011. Type I host resistance and Trichothecene Accumulation in Fusarium-infected Wheat Heads. American Journal of Agricultural and Animal Sciences 6(2):231-241. [1]
- ^ Gautam, P. and Dill-Macky, R. 2012. Impact of moisture, host genetics and Fusarium graminearum isolates on Fusarium head blight development and trichothecene accumulation in spring wheat. Mycotoxin Research 28 (1) DOI: 10.1007/s12550-011-0115-6 [2]
- ^ Beyer M, Klix MB, Klink H, Verreet J-A (2006): Quantifying the effects of previous crop, tillage, cultivar and triazole fungicides on the deoxynivalenol content of wheat grain – a review. Journal of Plant Diseases and Protection 113: 241–246. [3]
External links
- A comprehensive review on vomitoxin
- Microbiology of Animal Feeds
- Detailed information on different mycotoxins
- DON vendor's page from Fermentek
- How Vomitoxin production is impacted by wheat resistance and growth stages
Categories:- Mycotoxins
- Epoxides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
