- Lateral ventricles
-
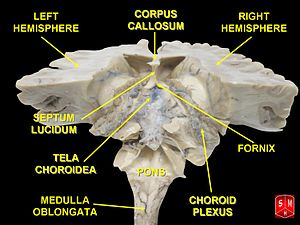
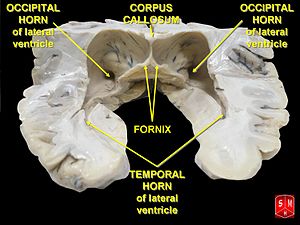
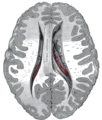
Brain: Lateral ventricles 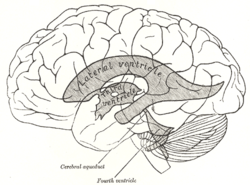
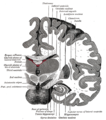
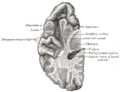
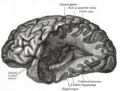
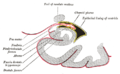
Scheme showing relations of the ventricles to the surface of the brain; oriented facing left. 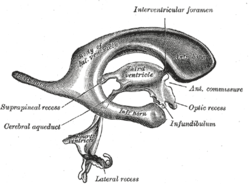
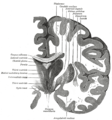
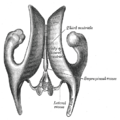
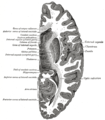
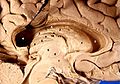
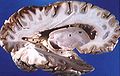
Drawing of a cast of the ventricular cavities, viewed from the side; oriented facing right. Latin ventriculus lateralis Gray's subject #189 829 NeuroNames hier-191 MeSH Lateral+Ventricles The lateral ventricles are part of the ventricular system of the brain. Classified as part of the telencephalon, they are the largest of the ventricles.
The lateral ventricles connect to the central third ventricle through the interventricular foramen of Monro.
Contents
Clinical significance
The volume of the lateral ventricles are known to increase with age. They are also enlarged in a number of neurological conditions and are on average larger in patients with schizophrenia,[1] bipolar disorder,[2] major depressive disorder [3] and Alzheimer's disease.[4]
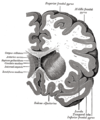
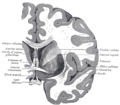
Divisions
Each lateral ventricle has three horns:
- the anterior or frontal horn extends into the frontal lobe
- the posterior or occipital horn into the occipital lobe
- the inferior or temporal horn into the temporal lobe
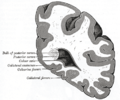
The body of the lateral ventricle is the central portion, just posterior to the frontal horn. The trigone of the lateral ventricle is a triangular area defined by the temporal horn inferiorly, the occipital horn posteriorly, and the body of the lateral ventricle anteriorly. The cella media is the central part of the lateral ventricle. Ependyma cover the inside of the lateral ventricles and are epithelial cells.[5]
Development
The lateral ventricles, similarly to other parts of the ventricular system of the brain, develop from the central canal of the neural tube. Specifically, the lateral ventricles originate from the portion of the tube that is present in the developing prosencephalon, and subsequently in the developing telencephalon.[6] During the first trimester of pregnancy central canal expands into lateral, third and fourth ventricles, connected by thinner channels.[7] In lateral ventricles specialized areas- choroid plexuses appear, which produce cerebrospinal fluid. If its production is bigger then resorption or its circulation is blocked- the enlargement of the ventricles may appear and cause a hydrocephalus. Fetal lateral ventricles may be diagnosed using linear or planar measurements.[8]
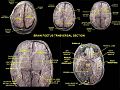
Additional images
References
- ^ Wright IC, Rabe-Hesketh S, Woodruff PW, David AS, Murray RM, Bullmore ET (January 2000). "Meta-analysis of regional brain volumes in schizophrenia". Am J Psychiatry 157 (1): 16–25. PMID 10618008. http://ajp.psychiatryonline.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=10618008.
- ^ Kempton, M.J., Geddes, J.R, Ettinger, U. et al. (2008). "Meta-analysis, Database, and Meta-regression of 98 Structural Imaging Studies in Bipolar Disorder," Archives of General Psychiatry, 65:1017–1032 see also MRI database at www.bipolardatabase.org.
- ^ Kempton MJ, Salvador Z, Munafò MR, Geddes JR, Simmons A, Frangou S, Williams SC. (2011). "Structural Neuroimaging Studies in Major Depressive Disorder: Meta-analysis and Comparison With Bipolar Disorder". Arch Gen Psychiatry 68 (7): 675–90. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.60. PMID 21727252. http://archpsyc.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/full/68/7/675. see also MRI database at www.depressiondatabase.org
- ^ S Nestor, R Rupsingh, M Borrie, M Smith, V Accomazzi, J Wells, J Fogarty, R Bartha. Ventricular Enlargement as a Surrogate Marker of Alzheimer Disease Progression Validated Using ADNI. Brain. 131(9): 2443-2454, September 2008. Epub July 11, 2008.
- ^ Crossman, A R (2005). Neuroanatomy. Elsevier. p. 32. ISBN 978-0-443-10036-9.
- ^ Le, Tao; Bhushan, Vikas; Vasan, Neil (2010). First Aid for the USMLE Step 1: 2010 20th Anniversary Edition. USA: The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.. pp. 126. ISBN 978-0-07-163340-6.
- ^ Carlson, Bruce M. (1999). Human Embryology & Developmental Biology. Mosby. pp. 237–238. ISBN 0-8151-1458-3.
- ^ Glonek M, Kedzia A, Derkowski W. Planar measurements of foetal lateral ventricles. Folia morphologica 2003;62(3):263-5.PMID: 14507062.
Human brain, cerebrum, Interior of the cerebral hemispheres: Lateral ventricles (TA A14.1.09.272–287, GA 9.829–831) Ventricular system:
Lateral ventriclesBody: Lamina affixa · Stria terminalis · Collateral eminence
Inferior hornCategories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.