- Desorption electrospray ionization
-
Desorption Electrospray Ionization (DESI) Acronym DESI Classification Mass spectrometry Analytes Organic molecules
BiomoleculesOther techniques Related Electrospray ionization
Atmospheric pressure chemical ionizationDesorption electrospray ionization (DESI) is an ambient ionization technique that can be used in mass spectrometry for chemical analysis. It is an atmospheric pressure ion source that ionizes gases, liquids and solids in open air under ambient conditions. It was developed in 2004 by Professor Graham Cooks et al.. from Purdue University and is now available commercially by Prosolia Inc.[1] DESI is a similar ionization technique to Direct Analysis in Real Time (DART) in its versatility, applications and analysis time.
Contents
Principle of operation
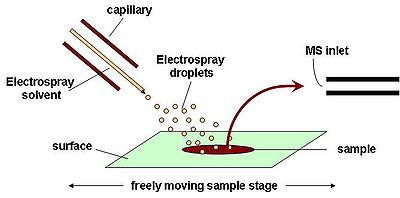
DESI is a combination of electrospray (ESI) and desorption (DI) ionization methods. Ionization takes place by directing an electrically charged mist to the sample surface that is a few millimeters away.[2] The electrospray mist is attracted to the surface by applying a voltage on the sample holder. After ionization, the ions travel through air into the atmospheric pressure interface which is connected to the mass spectrometer. DESI is a technique that allows for ambient ionization of a trace sample at atmospheric pressure, with little sample preparation.
Ionization mechanism
In DESI there are two kinds of ionization mechanism, one that applies to low molecular weight molecules and another to high molecular weight molecules.[2] High molecular weight molecules, such as proteins and peptides show electrospray like spectra where multiply charged ions are observed. This suggests desorption of the analyte, where multiple charges in the droplet can easily be transferred to the analyte. The charged droplet hits the sample, spreads over a diameter greater than its original diameter, dissolves the protein and rebounces. The droplets travel to the mass spectrometer inlet and are further desolvated. The solvent typically used for the electrospray is a combination of methanol and water.
For the low molecular weight molecules, ionization occurs by charge transfer: an electron or a proton. There are three possibilities for the charge transfer. First, charge transfer between a solvent ion and an analyte on the surface. Second, charge transfer between a gas phase ion and analyte on the surface; in this case the solvent ion is evaporated before reaching the sample surface. This is achieved when the spray to surface distance is large. Third, charge transfer between a gas phase ion and a gas phase analyte molecule. This occurs when a sample has a high vapour pressure.
The ionization mechanism of low molecular weight molecules in DESI is similar to DART’s ionization mechanism, in that there is a charge transfer that occurs in the gas phase.
Ionization efficiency
The ionization efficiency of DESI is complex and depends on several parameters such as, surface effects, electrospray parameters, chemical parameters and geometric parameters.[2] Surface effects include chemical composition, temperature and electric potential applied. Electrospray parameters include electrospray voltage, gas and liquid flow rates. Chemical parameters refers to the sprayed solvent composition, e.g. addition of NaCl. Geometric parameters are α, β, d1 and d2 (see figure on the right).
Furthermore, α and d1 affect the ionization efficiency, while β and d2 affect the collection efficiency. Results of a test performed on a variety of molecules to determine optimal α and d1 values show that there are two sets of molecules: high molecular weight (proteins, peptides, oligosaccharide etc.) and low molecular weight (dizazo dye, stereoids, caffeine, nitroaromatics etc.). The optimal conditions for the high molecular weight group are high incident angles (70-90º) and short d1 distances (1–3 mm). The optimal conditions for the low molecular weight group are the opposite, low incident angles (35-50º) and long d1 distances (7–10 mm). These test results indicate that each group of molecules has a different ionization mechanism; described in detail in the Principle of operation section.
The sprayer tip and the surface holder are both attached to a 3D moving stage which allow to select specific values for the four geometric parameters: α, β, d1 and d2.
References
- ^ Z. Takáts, J.M. Wiseman, B. Gologan, R.G. Cooks (2004). "Mass Spectrometry Sampling Under Ambient Conditions with Desorption Electrospray Ionization". Science 306 (5695): 471–473. doi:10.1126/science.1104404. PMID 15486296.
- ^ a b c Takáts Z, Wiseman JM, Cooks RG (2005). "Ambient mass spectrometry using desorption electrospray ionization (DESI): instrumentation, mechanisms and applications in forensics, chemistry, and biology". Journal of mass spectrometry : JMS 40 (10): 1261–75. doi:10.1002/jms.922. PMID 16237663.
External links
- Purdue Aston Lab - DESI
- Prosolia, Inc. - Manufacturer of DESI sources
- Method and System for Desorption Electrospray Ionization - US application 20,050,230,635
- Method and System for Desorption Electrospray Ionization - WO 2005094389
- Ionization by droplet impact - US application 20,060,108,539
Mass spectrometry Mass • m/z • Mass spectrum • MS software • Acronyms Ion source Mass analyzer Detector MS combination Fragmentation Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.