- Froissy Dompierre Light Railway
-
Coordinates: 49°55′24″N 2°43′45″E / 49.92333°N 2.72917°E
Froissy Dompierre Light Railway 
Franco-Belge 0-8-0 type KDL Locale France Terminus Froissy - Dompierre Commercial operations Name Le P'tit train de la Haute Somme Built by British and French armies Original gauge 600 mm (1 ft 11 5⁄8 in) Preserved operations Operated by APPEVA (Association Picarde pour la Préservation et l'Entretien des Véhicules Anciens) Stations 4 Length 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) Preserved gauge 600 mm (1 ft 11 5⁄8 in) Commercial history Opened 1916 Closed 1972 Preservation history The Froissy Dompierre Light Railway (CFCD) is a narrow-gauge light railway near the village of Cappy, in the Somme department, France. It is run as a heritage railway by APPEVA (Association Picarde pour la Préservation et l'Entretien des Véhicules Anciens). It is the last survivor of the 600 mm (1 ft 11 5⁄8 in) gauge trench railways of the World War I battlefields.
Contents
History
In 1915, the French Army built a railway along the Somme Canal between Péronne and Froissy. Between 1916 and 1918 the railway was at the Allied front line, and transporting 1,500 tonnes of materials daily. At Froissy, the metre gauge Réseau Albert connected with the CFCD.[1]
After the war, the railway was used in assisting with the reconstruction and also to bring food into the villages it served. New lines were laid including a zig-zag to reach the Santerre Plateau. The line was by this time being used for the transportation of sugar beet to the sugar refinery in Dompierre. In 1927, a further deviation was built to avoid Cappy Port, which required a 300 metres (330 yd) tunnel. The line was extended to Chaulnes in 1931. The line escaped World War II with little damage, although one train of molasses was attacked by a British aircraft. Two Coferna diesel locomotives were acquired in 1942, working alongside the Feldbahn 0-8-0s. The steam locomotives were retired in 1946 and replaced by three Plymouth loco-tracteurs. The extensions to Péronne and Chaulnes had been removed by 1954 and increased competition from road traffic meant that the line ceased operations in 1972, by which time a preservation society had already started operations.[1]
Preservation
APPEVA was formed in 1970 with the aim of preserving a 600mm gauge railway as a working museum. The CFCD was a good location, being between Paris and Lille near A1 motorway and close to Amiens. APPEVA operated its first train in June 1971 between Cappy and Froissy, a distance of 1 kilometre (1,100 yd). By 1974 the line was operating as far as the top of the zig-zag and in 1976 the full line to Dompierre was opened to traffic, following improvements to the level crossing on the Santerre Plateau. In 1996, a new museum was opened in Froissy.[1]
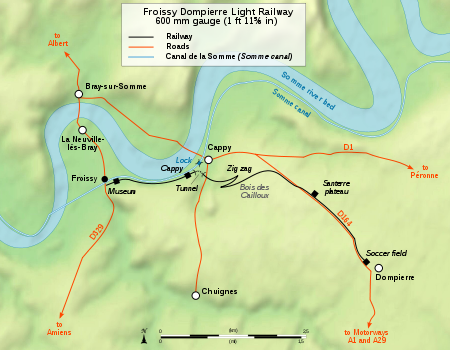
The line starts from the Froissy terminus and follows the towpath along the Somme canal to the little station of Cappy. It then runs through a curved tunnel more than 200 metres (220 yd) long followed by a bridge to cross the road from Cappy to Chuignes and a zig zag which was built after WWI to allow locomotives to climb the very steep slope towards the Santerre upland area. Once on the Santerre, the line runs on the side of the road to Dompierre. The terminus is located near the former sugar refinery of Dompierre.
APPEVA owns or has in store 13 steam locomotives, of which four are operating and some are considered as a Monument historique, and 25 diesel engines. The Froissy Dompierre Railway operates from April till the end of September, on Sundays and holidays, and every day of the week (except Monday) in July and August. The journey between the Froissy museum and the Dompierre terminus takes one hour. The CFCD is twinned with the Leighton Buzzard Light Railway.
APPEVA publishes a monthly magazine in French devoted to narrow gauge railways and touristic railways (Standard, metric and narrow gauge) called Voie Étroite.
Museum
The Musée des chemins de fer Militaires et Industriels (Military and Industrial railways Museum), located near the line terminus in the hamlet of Froissy (French commune of La Neuville-lès-Bray), features a large collection of 600mm gauge railway material, steam engines, diesel engines and wagons, in a 1800 m² exhibition hall inaugurated in 1996.
It also features an interesting Fairbanks-Morse speeder of 1917, used by the US Army.
Rolling stock
Steam locomotives
No. Name Builder Wheel Arrangement Power Works Number Year Built Origin Notes 1 Floralie Henschel 0-4-0 T 90 hp (67 kW) 23735 1937 Ex Parc floral de La Source (Orléans) Type Fulda 2 Neumeyer 0-4-0 T 35 hp (26 kW) 19 1922 Ex Briqueterie Roumazières 3 Decauville 0-6-0 T 50 hp (37 kW) 1825 1928 Port de Bordeaux Type Progrès 4 Krauss 0-8-0 T 70 hp (52 kW) 7373 1917 German Army Type DFB. Operated till end of 2007. 5 Decauville 0-6-0 WT 50 hp (37 kW) 1652 1916 Ex-Réseau Nord-Est (Reims) Type 17. In working order. 6 Henschel 0-8-0 T 70 hp (52 kW) 15271 1917 Ex-Râperie Cramaille Type DFB. 7 Geneviève Borsig 0-8-0 TT 50 hp (37 kW) 10334 1918 Poland Type DFB. In working order. 8 Vulcan, Stettin 0-8-0 T 150 hp (110 kW) to 180 hp (130 kW) 3852 1925 Ex Deutsche Reichsbahn No 99 3461, Ex Mecklenburg - Pommersche Bahn No 9. Prototype. Under restoration to working order (goal is 2011). 9 Alco-Cooke 2-6-2 T 120 hp (89 kW) 57148 1917 Ex Tramway de Pithiviers à Toury (TPT) No. 3-20. Operated till 2009. 10 Franco-Belge 0-8-0 TT 250 hp (190 kW) to 300 hp (220 kW) 2836 1945 Ex Sucreries Ternynck, Coucy-le-Château and TPT No. 4-14. Type KDL (Kriegsdampflokomotive).
In working order.11 Orenstein & Koppel 0-6-0 T about 100 hp (75 kW) 8083 1915 ex TPT No. 3-6. 12 Orenstein & Koppel 0-10-0 T about 195 hp (145 kW) 8285 1917 ex TPT No. 5-3. 13 Orenstein & Koppel 0-8-0 T DFB 70 hp (52 kW) 8627 1918 Ex Sucreries Coucy-le-Château Type DFB. On loan from AMTUIR Diesel locomotives
No. Name Builder Wheel Arrangement Power Works Number Year Built Origin Notes T23 Plymouth 75 hp (56 kW) 5117 1946 Loco-tracteur. One of the original CFCD locomotives. T24 Tatra Société de Construction Ferroviaires et Navales (Coferna) 200 hp (150 kW) 122 1941 Diesel locomotive. Fitted with a 212 horsepower (158 kW) Tatra air-cooled engine, one of the original CFCD locomotives. In working order. T25 Iveco Coferna 180 hp (130 kW) 123 1941 Diesel locomotive. Fitted with a 280 horsepower (210 kW) Iveco water-cooled engine, one of the original CFCD locomotives. In working order. T31 Billard 100 hp (75 kW) 233 T75 G 1958 Diesel locomotive. In working order. T32 Simplex Motor Rail Ltd 40 hp (30 kW) 588/191 1917 Tractor. T37 Simplex Motor Rail Ltd 20 hp (15 kW) 7433 1939 Tractor. In working order. T33 Baldwin 0-4-0 D 50 hp (37 kW) 49192 1917 Tractor. T36 Baldwin 50 hp (37 kW) 49966 1917 Tractor. T29 Socofer 40 hp (30 kW) 333 SCF 303 1968 Tractor. In working order. Speeder Fairbanks-Morse 1917 Draisine Passenger stock
The CFCD operates a variety of open and closed passenger stock, most of which is built on chassis of freight vehicles dating from World War One.
Freight stock
The CFCD has a variety of goods wagons, both open and closed, that date from World War One, and also examples of wagons from the industrial use of the line after World War One.
References
- ^ a b c Organ, John (2002). Northern France Narrow Gauge. Midhurst: Middleton Press. ISBN 0 901706 753.
See also
External links
- APPEVA, official web site
- Voie Étroite, official web site
- Description of a visit to the line
Categories:- Heritage railways in France
- Industrial railways
- Narrow gauge railways in France
- Somme
- 600 mm gauge railways
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.