- Dehydration reaction
-
This article is about chemical reactions resulting in the loss of water from a molecule. For the removal of water from solvents and reagents, see desiccation.
In chemistry and the biological sciences, a dehydration reaction is usually defined as a chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecule. Dehydration reactions are a subset of elimination reactions. Because the hydroxyl group (-OH) is a poor leaving group, having a Brønsted acid catalyst often helps by protonating the hydroxyl group to give the better leaving group, -OH2+. The reverse of a dehydration reaction is a hydration reaction.
Dehydration reactions and dehydration synthesis have the same meaning, and are often used interchangeably. Two monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose, can be joined together (to form sucrose) using dehydration synthesis. The new molecule, consisting of two monosaccharides, is called a disaccharide.
The process of hydrolysis is the reverse reaction, meaning that the water is recombined with the two hydroxyl groups and the disaccharide reverts to being monosaccharides.
In the related condensation reaction water is released from two different reactants.
Dehydration reactions
In organic synthesis, there are many examples of dehydration reactions for example dehydration of alcohols or sugars.
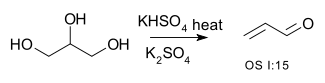
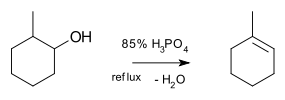
Reaction Equation Conversion of alcohols to ethers 2 R-OH → R-O-R + H2O Conversion of alcohols to alkenes R-CH2-CHOH-R → R-CH=CH-R + H2O for example the conversion of glycerol to acrolein [1]: or the dehydration of 2-methyl-1-cyclohexanol to (mainly) 1-methylcyclohexene [2]
Conversion of carboxylic acids to acid anhydrides 2 RCO2H → (RCO)2O + H2O Conversion of amides to nitriles RCONH2 → R-CN + H2O dienol benzene rearrangement 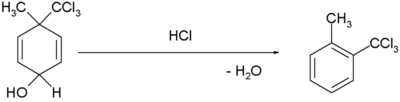 [3][4]
[3][4]Dehydration reactions
Some dehydration reactions can be mechanistically complex, for instance the reaction of a sugar (sucrose) with concentrated sulfuric acid: [5] to form carbon involves formation of carbon carbon bonds.[6]- C12H22O11 + 98% Sulfuric acid → 12 C (graphitic foam) + 11 H2O steam + Sulfuric acid/water mixture
The reaction is driven by the strongly exothermic reaction sulfuric acid has with water. [7]
Common dehydrating agents; concentrated sulfuric acid, concentrated phosphoric acid, hot aluminium oxide, hot ceramic.
See also
References
- ^ Organic syntheses OS I:15 Link
- ^ Dehydration of 2-Methyl-1-cyclohexanol: New Findings from a Popular Undergraduate Laboratory Experiment J. Brent Friesen and Robert Schretzman J. Chem. Educ., 2011, 88 (8), pp 1141–1147 doi:10.1021/ed900049b
- ^ H. Plieninger and Gunda Keilich (1956). "Die Dienol-Benzol-Umlagerung". Angew. Chem. 68 (19): 618–618. doi:10.1002/ange.19560681914.
- ^ Margaret Jevnik Gentles, Jane B. Moss, Hershel L. Herzog, and E. B. Hershberg (1958). "The Dienol-Benzene Rearrangement. Some Chemistry of 1,4-Androstadiene-3,17-dione". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80 (14): 3702–3705. doi:10.1021/ja01547a058.
- ^ youtube clip reaction sugar with sulfuric acid
- ^ http://www.exo.net/~pauld/activities/astronomy/transitvenus/sugarsulfuricacid.htm
- ^ (Beware that this reaction produces dangerous sulfuric-acid containing steam, and should only be performed in a fume-hood or well ventilated area.)
Categories:- Elimination reactions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.