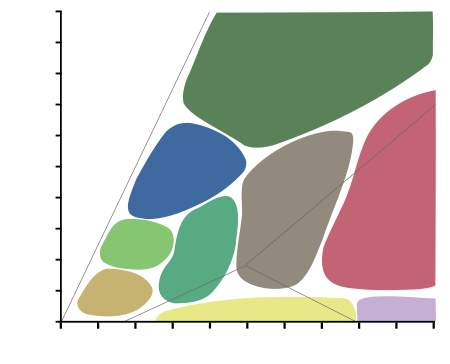- Metamorphic facies
-
EclogiteBlueschistGreenschistGranuliteAmphiboliteHornfelsSanidiniteT (°C)0100200300400500600700800900100002468101214161820
Diagram showing metamorphic facies in pressure-temperature space. The domain of the
graph corresponds to circumstances within the Earth's crust and upper mantle.The metamorphic facies are groups of mineral compositions in metamorphic rocks, that are typical for a certain field in pressure-temperature space. Rocks which contain certain minerals can therefore be linked to certain tectonic settings.
Historic definition
The name facies was first used for specific sedimentary environments in sedimentary rocks by Swiss geologist Amanz Gressly in 1838. Analogous with these sedimentary facies a number of metamorphic facies were proposed in 1921 by Finnish petrologist Pentti Eskola. Eskola's classification was refined in the 1970s by New-Zealand geologist Francis John Turner.
 Triangular diagrams showing the aluminium (A), calcium (C) and iron (F) content of the main phases (dark dots) in metamorphic rocks in various facies. Thin grey lines are stable phase equilibria.
Triangular diagrams showing the aluminium (A), calcium (C) and iron (F) content of the main phases (dark dots) in metamorphic rocks in various facies. Thin grey lines are stable phase equilibria.
 Triangular diagrams showing the aluminium (A), iron (F) and magnesium (M) content of the main phases (dark dots and, when the composition can vary, stripes). Thin grey lines represent equilibria between phases.
Triangular diagrams showing the aluminium (A), iron (F) and magnesium (M) content of the main phases (dark dots and, when the composition can vary, stripes). Thin grey lines represent equilibria between phases.
Underlying principles
The different metamorphic facies are defined by the mineralogical composition of a rock. When the temperature or pressure in a rock body change, the rock can cross into a different facies and some minerals become stable while others become unstable or metastable. Whether minerals really react depends on the reaction kinetics, the activation energy of the reaction and how much fluid is present in the rock.
The minerals in a metamorphic rock and their age relations can be studied by optical microscopy or Scanning Electron Microscopy of thin sections of the rock. Apart from the metamorphic facies of a rock, a whole terrane can be described by the abbreviations LT, MT, HT, LP, MP, HP (from low, medium or high; pressure or temperature). Since the 1980s the term UHP (ultra high pressure) is used for rocks that saw extreme pressures.
Which minerals grow in a rock is also dependent of the original composition of the protolith (the original rock before metamorphosis). Carbonate rocks have a different composition from say a basalt lava, the minerals that can grow in them are different too. Therefore a metapsammite and a metapelite will have different mineralogical compositions even though they were in the same metamorphic facies.
Index minerals
Main article: index mineralEvery metamorphic facies has some index minerals by which it can be recognized. That does not mean these minerals will necessarily be visible with the naked eye, or even exist in the rock; when the rock did not have the right chemical composition they will not grow.
Very typical index minerals are the polymorphs of aluminosilicate (Al2SiO5, all are nesosilicates). Andalusite is stable at low pressure, kyanite is stable at high pressure but relatively low temperature and sillimanite is stable at high temperature.
Metamorphic facies and their mineral assemblages
Zeolite facies (LP/LT)
Main article: zeolite faciesThe zeolite facies is the metamorphic facies with the lowest metamorphic grade. At lower temperature and pressure processes in the rock are called diagenesis. The facies is named for zeolites, strongly hydrated tectosilicates. It can have the following mineral assemblages:
In meta-igneous rocks and greywackes:
- heulandite + analcime + quartz ± clay minerals
- laumontite + albite + quartz ± chlorite
In metapelites:
Prehnite-pumpellyite-facies (LP/LT)
Main article: prehnite-pumpellyite faciesThe prehnite-pumpellyite facies is a little higher in pressure and temperature than the zeolite facies. It is named for the minerals prehnite (a Ca-Al-phyllosilicate) and pumpellyite (a sorosilicate). The prehnite-pumpellyite is characterized by the mineral assemblages:
In meta-igneous rocks and greywackes:
- prehnite + pumpellyite + chlorite + albite + quartz
- pumpellyite + chlorite + epidote + albite + quartz
- pumpellyite + epidote + stilpnomelane + muscovite + albite + quartz
In metapelites:
Greenschist facies (MP/MT)
Main article: greenschist faciesThe greenschist facies is at medium pressure and temperature. The facies is named for the typical schistose texture of the rocks and green colour of the minerals chlorite, epidote and actinolite. Characteristic mineral assemblages are:
In metabasites:
- chlorite + albite + epidote ± actinolite, quartz
In metagreywackes:
- albite + quartz + epidote + muscovite ± stilpnomelane
In metapelites:
- muscovite + chlorite + albite + quartz
- chloritoid + chlorite + muscovite + quartz ± paragonite
- biotite + muscovite + chlorite + albite + quartz + Mn-garnet (spessartine)
In Si-rich dolostones:
Amphibolite-facies (MP/MT-HT)
Main article: amphibolite faciesThe amphibolite facies is a facies of medium pressure and average to high temperature. It is named after amphiboles that form under such circumstances. It has the following mineral assemblages:
In metabasites:
In metapelites:
- muscovite + biotite + quartz + plagioclase ± garnet, staurolite, kyanite/sillimanite
In Si-dolostones:
- dolomite + calcite + tremolite ± talc (lower pressure and temperature)
- dolomite + calcite + diopside ± forsterite (higher pressure and temperature)
Granulite facies (MP/HT)
Main article: granulite faciesThe granulite facies is the highest grade of metamorphism at medium pressure. The depth at which it occurs is not constant. A characteristic mineral for this facies and the pyroxene-hornblende facies is orthopyroxene. The granulite facies is characterized by the following mineral assemblages:
In metabasites:
- orthopyroxene + clinopyroxene + hornblende + plagioclase ± biotite
- orthopyroxene + clinopyroxene + plagioclase ± quartz
- clinopyroxene + plagioclase + garnet ± orthopyroxene (higher pressure)
In metapelites:
- garnet + cordierite + sillimanite + K-feldspar + quartz ± biotite
- sapphirine + orthopyroxene + K-feldspar + quartz ± osumilite (at very high temperature)
Blueschist facies (MP-HP/LT)
Main article: blueschist faciesThe blueschist facies is at relatively low temperature but high pressure, such as occurs in rocks in a subduction zone. The facies is named after the schistose character of the rocks and the blue minerals glaucophane and lawsonite. The blueschist facies forms the following mineral assemblages:
In metabasites:
- glaucophane + lawsonite + chlorite + sphene ± epidote ± phengite ± paragonite, omphacite
In metagreywackes:
In metapelites:
- phengite + paragonite + carpholite + chlorite + quartz
In carbonate-rocks (marbles):
Eclogite facies (HP/HT)
Main article: eclogite faciesThe eclogite facies is the facies at the highest pressure and high temperature. It is named for the metabasic rock eclogite. The eclogite facies had the mineral assemblages:
In metabasites:
In metagranodiorite:
In metapelites:
- phengite + garnet + kyanite + chloritoid (Mg-rich) + quartz
- phengite + kyanite + talc + quartz ± jadeite
Albite-epidote-hornfels facies (LP/LT-MT)
The albite-epidote-hornfels facies is a facies at low pressure and relatively low temperatures. It is named for the two minerals albite and epidote, though they are stable in more facies. Hornfels is a rock formed in contact metamorphism, a process that characteristically involves high temperatures but low pressures/depths. This facies is characterized by the following minerals:
In metabasites:
- albite + epidote + actinolite + chlorite + quartz
In metapelites:
Hornblende-hornfels facies (LP/MT)
The hornblende-hornfels facies is a facies with the same low pressures but slightly higher temperatures as the albite-epidote facies. Though it is named for the mineral hornblende, the appearance of that mineral is not constrained to this facies. The hornblende-hornfels facies has the following mineral assemblages:
In metabasites:
In metapelites:
- muscovite + biotite + andalusite + cordierite + quartz + plagioclase
In K2O-poor sediments or meta-igneous rocks:
- cordierite + anthophyllite + biotite + plagioclase + quartz
In Si-rich dolostones:
Pyroxene-hornfels facies (LP/MT-HT)
The pyroxene-hornfels facies is the contact-metamorphic facies with the highest temperatures and is, like the granulite facies, characterized by the mineral orthopyroxene. It is characterized by the following mineral assemblages:
In metabasites:
- orthopyroxene + clinopyroxene + plagioclase ± olivine or quartz
In metapelites:
- cordierite + quartz + sillimanite+ K-feldspar (orthoclase) ± biotite ± garnet
(If the temperature is below 750 there will be andalusite instead of sillimanite)
- cordierite + orthopyroxene + plagioclase ± garnet, spinel
In carbonate rocks:
Sanidinite facies (LP/HT)
The sanidinite facies is a rare facies of extremely high temperatures and low pressure. It can only be reached under certain contact-metamorphic circumstances. Due to the high temperature the rock experiences partial melting and glass is formed. This facies is named for the mineral sanidine. It is characterized by the following mineral assemblages:
In metapelites:
- cordierite + mullite + sanidine + tridymite (often altered to quartz) + glass
In carbonates:
- wollastonite + anorthite + diopside
- monticellite + melilite ± calcite, diopside (also tilleyite, spurrite, merwinite, larnite and other rare Ca- or Ca-Mg-silicates.
References
- Phillpots, Anthony R., 1990: Principles of Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology
- Duff, P. McL. D., 1996; Holmes' Principles of Physical Geology
- Visser, W.A., 1980; Geological Nomenclature
- Metamorphic facies by Dave Waters
See also
Categories:- Metamorphic petrology
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.