- Knoevenagel condensation
-
The Knoevenagel condensation reaction is an organic reaction named after Emil Knoevenagel. It is a modification of the Aldol condensation[1][2].
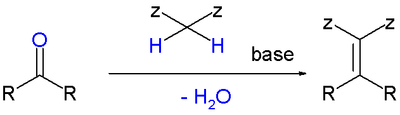
A Knoevenagel condensation is a nucleophilic addition of an active hydrogen compound to a carbonyl group followed by a dehydration reaction in which a molecule of water is eliminated (hence condensation). The product is often an alpha, beta conjugated enone.
In this reaction the carbonyl group is an aldehyde or a ketone. The catalyst is usually a weakly basic amine. The active hydrogen component has the form [3]
- Z-CH2-Z or Z-CHR-Z for instance diethyl malonate, Meldrum's acid, ethyl acetoacetate or malonic acid.
- Z-CHR1R2 for instance nitromethane.
where Z is an electron withdrawing functional group. Z must be powerful enough to facilitate hydrogen abstraction to the enolate ion even with a mild base. Using a strong base in this reaction would induce self-condensation of the aldehyde or ketone.
The Hantzsch pyridine synthesis, the Gewald reaction and the Feist-Benary furan synthesis all contain a Knoevenagel reaction step. The reaction also led to the discovery of CS gas.
Contents
Doebner modification
 The Doebner modification of the Knoevenagel condensation. Acrolein and malonic acid react in pyridine to give trans-2,4-pentadienoic acid with the loss of carbon dioxide.
The Doebner modification of the Knoevenagel condensation. Acrolein and malonic acid react in pyridine to give trans-2,4-pentadienoic acid with the loss of carbon dioxide.
With malonic compounds the reaction product can lose a molecule of carbon dioxide in a subsequent step. In the so-called Doebner modification [4] the base is pyridine. For example, the reaction product of acrolein and malonic acid in pyridine is trans-2,4-Pentadienoic acid with one carboxylic acid group and not two.[5]
Scope
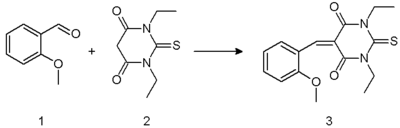
A Knoevenagel condensation is demonstrated in the reaction of 2-methoxybenzaldehyde 1 with the barbituric acid 2 in ethanol using piperidine as a base [6]. The resulting enone 3 is a charge transfer complex molecule.
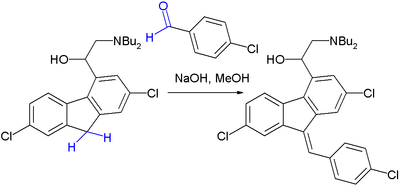
The Knoevenagel condensation is a key step in the commercial production of the antimalarial drug lumefantrine (a component of Coartem) [7]:
The initial reaction product is a 50:50 mixture of E and Z isomers but because both isomers equilibrate rapidly around their common hydroxyl precursor, the more stable Z-isomer can eventually be obtained.
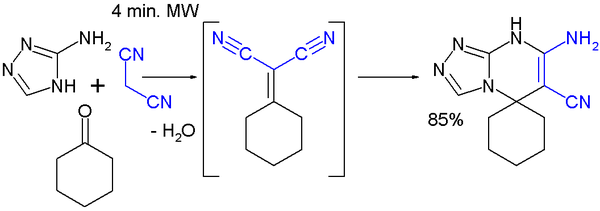
A multicomponent reaction featuring a Knoevenagel condensation is demonstrated in this MORE synthesis with cyclohexanone, malononitrile and 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole [8]:
See also
References
- ^ Jones, G. Org. React. 1967, 15.
- ^ Emil Knoevenagel (1898). "Condensation von Malonsäure mit Aromatiachen Aldehyden durch Ammoniak und Amine". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft 31 (3): 2596–2619. doi:10.1002/cber.18980310308. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k90751n/f268.chemindefer.
- ^ March, Jerry (1985), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (3rd ed.), New York: Wiley, ISBN 0-471-85472-7
- ^ O. Doebner (1902). "Ueber die der Sorbinsäure homologen, ungesättigten Säuren mit zwei Doppelbindungen". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft 35: 1136–1136. doi:10.1002/cber.190203501187.
- ^ Peter J. Jessup, C. Bruce Petty, Jan Roos, and Larry E. Overman (1988), "1-N-Acylamino-1,3-dienes from 2,4-pentadienoic acids by the curtius rearrangement: benzyl trans-1,3-butadiene-1-carbamate", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv6p0095; Coll. Vol. 6: 95
- ^ 1,3-Diethyl-5-(2-methoxybenzylidene)-2-thioxodihydropyrimidine-4,6(1H,5H)-dione Abdullah Mohamed Asiria, Khaled Ahmed Alamrya Abraham F. Jalboutb, Suhong Zhang Molbank 2004, M359 [1] publication.
- ^ An Improved Manufacturing Process for the Antimalaria Drug Coartem. Part II Ulrich Beutler, Peter C. Fuenfschilling, and Andreas Steinkemper Org. Process Res. Dev.; 2007; 11(3) pp 341 - 345; (Article) doi:10.1021/op060244p
- ^ Mild and ecofriendly tandem synthesis of 1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-a]pyrimidines in aqueous medium Arkivoc 2007 (06-2251BP) Anshu Dandia, Pritima Sarawgi, Kapil Arya, and Sarita Khaturia Link
Categories:- Condensation reactions
- Name reactions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.