Constant Object Proportion Rendering
- Constant Object Proportion Rendering
-
COPR (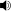 /ˈkɒpər/; Constant Object Proportion Rendering)[1], is a web development technique that gives web pages the same zoom in/out and stretch/shrink to fit functionality found in graphic design applications.
/ˈkɒpər/; Constant Object Proportion Rendering)[1], is a web development technique that gives web pages the same zoom in/out and stretch/shrink to fit functionality found in graphic design applications.
Screen size and resolution limitations have little effect on COPR-style pages. Screen objects are rendered in constant proportion to each other as the viewing size and zoom level changes.
Constituent technologies
COPR uses a combination of:
Advantages of COPR
Prior to the development of COPR, graphic artists were restricted to a set pixel width when designing web pages. If a page was re-sized in any way, the appearance of the design would be altered. By combining several existing technologies, COPR provides a solution to many problems caused by the mismatch between HTML and scalable graphic formats.
Accessibility
COPR-style pages can be scaled to fit on devices with screen resolutions with as few as 300 pixels or as many as 1920 pixels while keeping the same relative size and placement of text and graphics. The same page can be displayed without distortion on devices as small as a wrist watch or as large as a projection screen. It also allows for almost unlimited zooming with little or no pixelation. This allows pages to be zoomed in for easy viewing without losing page cohesion and/or quality.
Notes and references
External links
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
arts, East Asian — Introduction music and visual and performing arts of China, Korea, and Japan. The literatures of these countries are covered in the articles Chinese literature, Korean literature, and Japanese literature. Some studies of East Asia… … Universalium
India — /in dee euh/, n. 1. Hindi, Bharat. a republic in S Asia: a union comprising 25 states and 7 union territories; formerly a British colony; gained independence Aug. 15, 1947; became a republic within the Commonwealth of Nations Jan. 26, 1950.… … Universalium
photography, technology of — Introduction equipment, techniques, and processes used in the production of photographs. The most widely used photographic process is the black and white negative–positive system (Figure 1 >). In the camera the lens projects an image of… … Universalium
Europe, history of — Introduction history of European peoples and cultures from prehistoric times to the present. Europe is a more ambiguous term than most geographic expressions. Its etymology is doubtful, as is the physical extent of the area it designates.… … Universalium
South Asian arts — Literary, performing, and visual arts of India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka. Myths of the popular gods, Vishnu and Shiva, in the Puranas (ancient tales) and the Mahabharata and Ramayana epics, supply material for representational and… … Universalium
Western sculpture — ▪ art Introduction three dimensional artistic forms produced in what is now Europe and later in non European areas dominated by European culture (such as North America) from the Metal Ages (Europe, history of) to the present. Like… … Universalium
biblical literature — Introduction four bodies of written works: the Old Testament writings according to the Hebrew canon; intertestamental works, including the Old Testament Apocrypha; the New Testament writings; and the New Testament Apocrypha. The Old… … Universalium
literature — /lit euhr euh cheuhr, choor , li treuh /, n. 1. writings in which expression and form, in connection with ideas of permanent and universal interest, are characteristic or essential features, as poetry, novels, history, biography, and essays. 2.… … Universalium
painting, Western — ▪ art Introduction history of Western painting from its beginnings in prehistoric times to the present. Painting, the execution of forms and shapes on a surface by means of pigment (but see also drawing for discussion of depictions in … Universalium
china — /chuy neuh/, n. 1. a translucent ceramic material, biscuit fired at a high temperature, its glaze fired at a low temperature. 2. any porcelain ware. 3. plates, cups, saucers, etc., collectively. 4. figurines made of porcelain or ceramic material … Universalium
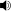 /ˈkɒpər/; Constant Object Proportion Rendering)[1], is a web development technique that gives web pages the same zoom in/out and stretch/shrink to fit functionality found in graphic design applications.
/ˈkɒpər/; Constant Object Proportion Rendering)[1], is a web development technique that gives web pages the same zoom in/out and stretch/shrink to fit functionality found in graphic design applications.