- Dental lamina
-
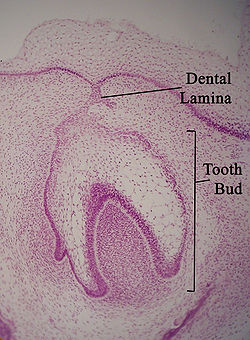
Dental lamina Micrograph of a dental lamina and tooth bud. H&E stain. Latin lamina dentalis Code TE E05.04.1.1.1.0.3 The dental lamina is a band of epithelial tissue seen in histologic sections of a developing tooth. The dental lamina is first evidence of tooth development and begins at the sixth week in utero or three weeks after the rupture of the buccopharyngeal membrane. It is formed when cells of the oral ectoderm proliferate faster than cells of other areas. Best described as an in-growth of oral ectoderm, the dental lamina is frequently distinguished from the vestibular lamina, which develops concurrently. This dividing tissue is surrounded by and, some would argue, stimulated by ectomesenchymal growth. When it is present, the dental lamina connects the developing tooth bud to the epithelium of the oral cavity. Eventually, the dental lamina disintegrates into small clusters of epithelium and is resorbed. In situations when the clusters are not resorbed, (this remnant of the dental lamina is sometimes known as the glands of Serres) eruption cysts are formed over the developing tooth and delay its eruption into the oral cavity. This invagination of ectodermal tissues is the progenitor to the later ameloblasts and enamel while the ectomesenchyme is responsible for the dental papilla and later odontoblasts.
References
- Cate AR. Ten. Oral histology: development, structure, and function. 5th ed. 1998. ISBN 0-8151-2952-1.
- Brand RW, Isselhard DE. Anatomy of orofacial structures. 7th ed. Mosby. 2003. ISBN 0323019544.
- Bhaskar SN. Orban's oral histology and embryology. 11th ed. 1991. ISBN 81-8147-012-5.
- Gartner, L. The Essentials of Oral Histology and Embryology. Jen House Publishing Company. Baltimore, MD. 1999. pg19-20
Tooth development (TE 5.4) -blast General Dental papilla · Epithelial root sheath · Epithelial cell rests of Malassez
Dental lamina
Enamel organ: Outer enamel epithelium · Inner enamel epithelium · Stellate reticulum · Stratum intermedium
Dentition · Teething · Tooth eruptionPulp occlusion Canalis amelodentineus · Fovea enamelea · Fovea dentineaCategories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.