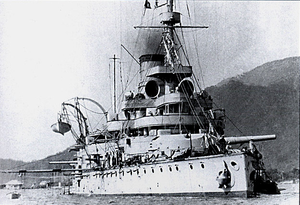
- Monarch class battleship
-
Austro-Hungarian battleship WienClass overview Operators:  Austro-Hungarian Navy
Austro-Hungarian NavySucceeded by: Habsburg class battleship Built: 1893–1896 In commission: 1895–1920 Completed: 3 Lost: 1 General characteristics [1][2] Type: Pre-dreadnought battleship, Coastal defence ship Displacement: 5,878 tonnes (5,785 long tons) Length: 99.22 m (325.5 ft) Beam: 17 m (55 ft 9 in) Draught: 6.6 m (22 ft) Propulsion: 12 coal-fired Belleville boilers without economizers outputting 9,180 hp (6,846 kW) (for SMS Budapest only)
coal-fired cylindrical boilers (SMS Wien and SMS Monarch); inverted vertical triple expansion engines outputting 8,500 hp (6,338 kW)Speed: 15.5 knots (17.8 mph; 28.7 km/h) (Monarch and Wien)
17.5 knots (20.1 mph; 32.4 km/h) (Budapest)Range: 2,200 nmi (4,100 km) Complement: 469 Armament: • 4 × 240 mm (9 in) L/40 guns (2×2)
• 6 × 150 mm (6 in) L/40 guns
• 10 × 47 mm (1.9 in) L/44 guns
• 4 × 47 mm (1.9 in) L/33 guns
• 1 × 8 mm (0.31 in) MG gun
• 4 × torpedo tubesArmour: Harvey armour
Belt: 270 mm (11 in)
Turrets: 11 in (280 mm)
Conning tower: 220 mm (8.7 in)
Deck: 60 mm (2.4 in)The Monarch class was a class of battleships, although resembling coastal defence ships, built by Austria-Hungary at the end of the 19th century. The Monarchs were the first ships of their type to utilize turrets. The class comprised three ships: knots (20.1 mph; 32.4 km/h).
Monarch was launched on 9 May 1895, Wien on 7 July 1895, and Budapest just over a year later on 24 July 1896. The ships saw very little service during World War I in the V Division of the Austro-Hungarian fleet. Budapest and Wien took part in the bombardment of Italian positions along the Adriatic coast in 1915 and 1917, but the three battleships went largely inactive for the remainder of war.
In 1917, Wien was struck by Italian torpedoes and sank in her home port of Trieste. The remaining two ships were ceded to Great Britain following the end of the war and were scrapped between 1920 and 1922.
Contents
Construction
SMS Wien in 1896
In the 1890s the Austro-Hungarian Navy consisted of two obsolescent battleships, the Rudolph and the Stephanie. By 1893, sufficient funds were available to build three replacement ships, but the Hungarian and Austrian parliaments authorized only the construction of a smaller class of coastal defense battleships,[2] given that Austria-Hungary believed that the role of her navy was solely revolved around coastal defense. The three new ships—the SMS Budapest, SMS Wien, and SMS Monarch—weighed about 5,600 tonnes (5,512 long tons), half the size of the battleships of other navies.[3] The Budapest was fitted with more powerful engines than her sister ships, giving her a higher top speed. SMS Budapest and SMS Wien were built in the Stabilimento Tecnico Trietino yards in Trieste, and the SMS Monarch was constructed at the Naval Arsenal in Pola.[2]
The first ship of the class, the Wien was laid down on 16 February 1893. She was launched on 7 July 1895, about a month after the Monarch. Despite this, the Wien was the first ship of the new class to be commissioned into the Austro-Hungarian Navy, on 13 May 1897. The second ship of the class, the Monarch, was laid down on 31 July 1893, launched on 9 May 1895, and was commissioned into the Austro-Hungarian Navy on 11 May 1898. The Budapest was the third and final ship of the class. She was laid down on the same day as the Wien, on 16 February 1893, and launched from the Naval Arsenal in Pola on 24 July 1896. She was commissioned on 12 May 1898, a day after the Monarch.[2]
Design
Armament and armor
The members of the Monarch class displaced 5,878 tonnes (5,785 long tons). Their armament consisted of four 240 mm (9 in) L/40 guns with two guns in each of the two turrets, six 150 mm (6 in) L/40 guns, 10 47 mm (1.9 in) L/44 guns, four 47 mm (1.9 in) L/33 guns, one 8 mm (0.31 in) MG gun, and four torpedo tubes.[1][2]
Ships of the Monarch class were fitted with Harvey armour throughout. Their belt armor was 270 mm (11 in) thick except for the turrets, which had 203 mm (8.0 in). The conning tower was protected by armor 220 mm (8.7 in) thick, and the deck by 64 mm (2.5 in); the redoubt and casemates had 76 mm (3.0 in) of armor.[1][2]
Propulsion and crew
Monarch class ships normally carried 300 tons of coal, but could hold up to 500 tons. The Budapest was fitted with 12 coal-fired Belleville boilers without economizers, giving an output of 9,180 hp (6,846 kW). The Wien and the Monarch had coal-fired cylindrical boilers and vertical triple expansion engines with an output of 8,500 hp (6,338 kW). The Wien and the Monarch had a maximum speed of 15.5 knots (17.8 mph; 28.7 km/h), compared to the Budapest's top speed of 17.5 knots (20.1 mph; 32.4 km/h). Each ship was manned by 26 officers and 397 crewmen, a total of 423 personnel per ship.[1][2]
Service history
Peace time
Upon being commissioned into the Austro-Hungarian Navy, the three ships of the Monarch class were used for a variety of purposes. All three ships of the Monarch class partook in a cruise around the Adriatic and Aegean in 1899, to display the Austro-Hungarian flag in foreign waters.[2] The Monarch class formed the I Battleship Division of the Austro-Hungarian Navy. The battleship Wien participated in the Diamond Jubilee of the crowning of Queen Victoria in 1897, as well as the international blockade off Crete during the Greco-Turkish War of 1897.[2] However, less than five years after their completion, the Monarch class battleships were rendered obsolete by the newly commissioned Habsburg class.[1] The newly completed Habsburg conducted a training cruise with the three Monarch class battleships in January 1903; they were joined by the Árpád the following year.[4] During the 1904 training exercises, the three Habsburg class battleships engaged the three Monarchs in simulated combat; the maneuver marked the first time two homogeneous squadrons consisting of modern battleships operated in the Austro-Hungarian Navy.[4] The three Habsburg class ships took over the position of the I Division while the Monarchs formed the newly created II Division.[5] With other new classes of pre-dreadnoughts being built such as the Erzherzog Karl class, and later the Radetzky class, the Monarchs were demoted even further, and ended up in the V Battleship Division. They were serving as coastal defense ships by the beginning of World War I.[1]
World War I
At the outbreak of World War I in July 1914, the three ships of the Monarch class were serving as the V Battleship Division, deployed as coastal defense ships. They also served as training ships, and were used to bombard coastal positions during the early years of the war.[1][2] In August 1914, the Budapest was transferred from Pola to Cattaro to shell Mount Lovcen.[1] On 9 August 1914 the Monarch shelled the French radio station at Budva. She also bombarded the Montenegrin radio station off Bar on 17 August and another station off Volovica Point on 19 August where she attacked the local radio station and barracks. Following these operations, the Monarch served as a harbor defense ship.[2] On 28–29 December 1915 the Budapest supported the cruisers and destroyers of the Austro-Hungarian Navy that were to raid Durazzo, but the detachment returned to port without having opened fire on the enemy. On 9 January 1916, the Budapest again bombarded the fortifications on Mount Lovcen, and helped to capture the enemy-held mountain.[1] In late 1917 the Budapest and Wien were sent to Trieste, and participated in shelling Italian troops in the Gulf of Trieste.[6] On 10 December 1917, two Italian torpedo boats managed to penetrate the port of Trieste undetected, and fired torpedoes at the battleships Budapest and Wien.[1][2][7][8] The torpedo fired at the Budapest missed, but the Wien was hit twice and sank in less than five minutes in the shallow water of the Trieste harbor. Forty-six men serving on the Wien were killed in the attack.[7] The Budapest was subsequently given the task that the Monarch had been performing for over three years, and was demoted to a floating barrack for German U-boat crews.[1] In June 1918 the Budapest was renovated and had a 380 mm (15 in) L/17 howitzer installed in her bow to use for coastal bombardment, but she never saw action with the new gun in place.[2] At the end of the war in 1918, the remaining Monarch class battleships, the Budapest and the Monarch, were handed over to Great Britain as war reparations.[9] In 1920 the two ships were sold for scrap to Italy, and were broken up between 1920 and 1922.[1]
Citations
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "The Monarch Class (1895/1898)". Austria's Monarch Class Monitors (1895). Cityofart.net. http://www.cityofart.net/bship/sms_monarch.html. Retrieved 23 July 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "Monarch Class". Habsburg Class Battleships-Austria Hungary. battleships-cruisers.co.uk. http://www.battleships-cruisers.co.uk/monarch_class.htm#Monarch. Retrieved 22 July 2010.
- ^ Sokol, p. 67
- ^ a b Sondhaus, p. 158
- ^ United Service Magazine, p. 437
- ^ Sokol, p. 125
- ^ a b Sokol, p. 124
- ^ Hovgaard, p. 129
- ^ Sokol, p. 162
References
- Hovgaard, William (1971). Modern history of warships. London: Taylor & Francis. ISBN 9780851770406.
- Sokol, Anthony (1968). The Imperial and Royal Austro-Hungarian Navy. Annapolis: United States Naval Institute.
- Sondhaus, Lawrence (1994). The Naval Policy of Austria-Hungary, 1867–1918. West Lafayette, Indiana: Purdue University Press. ISBN 9781557530349.
- The United Service Magazine, Volume 150. H. Colburn. 1904.
Monarch-class battleshipsAustro-Hungarian Navy (list of ships)
Austro-Hungarian Navy ship classes of World War IDreadnought battleships Pre-dreadnought battleships Coastal defense ships Armored cruisers
Kaiserin und Königin Maria Theresia · Protected cruisers
Scout cruisers Light cruisers U-boats
Military of Austria-Hungary Army k. u. k. Armee • Imperial Austrian Army • Royal Hungarian Army • Formations • Army ranks and insignia of the Austro-Hungarian Army • Military Intelligence • Weapons of the Austro-Hungarian Empire
Navy k. u. k. Kriegsmarine · List of battleships of the Austro-Hungarian Navy · List of U-Boats of the Austro-Hungarian NavyAirforce Ministers for War Feldmarschalleutnant Franz Freiherr von John • Feldmarschalleutnant Franz Kuhn Freiherr Kuhn von Kuhnenfeld • General der Kavallerie Alexander Freiherr von Koller • Feldzeugmeister Arthur Maximilian Graf Bylandt-Rheydt (der Ältere) • Feldzeugmeister Ferdinand Freiherr Bauer • Feldzeugmeister Rudolf Freiherr Merkl • General der Kavallerie Edmund Freiherr von Krieghammer • Feldzeugmeister Heinrich Ritter von Pitreich • General der Infanterie Franz Freiherr Schönaich • General der Infanterie Moritz Ritter Auffenberg von Komarów • Feldmarschal Alexander Freiherr von Krobatin • Generaloberst Rudolf Stöger-Steiner von SteinstättenCommanders Archduke Eugen of Austria • Franz Rohr von Denta • Eduard von Böhm-Ermolli • Svetozar Boroevic von Bojna • Archduke Joseph August of Austria • Franz Böhme • Josip Jelačić • Günther Burstyn • Georg Dragičević • Karol Durski-Trzaska • Gheorghe Flondor • Tadeusz Jordan-Rozwadowski • Archduke Josef Ferdinand, Prince of Tuscany • Rudolf Maister • Artur Phleps • Oskar Potiorek • Alfred Redl • Maximilian Ronge • Viktor Dankl von Krasnik • Viktor Graf von Scheuchenstuel • Stjepan Sarkotić • Gottfried von Banfield • Archduke Charles Stephen of Austria • Miklós Horthy • Franz von Keil • Giovanni Luppis • Georg Ludwig von Trapp • Janko VukovićCommanders-in-Chief of the Navy VAdm. Wilhelm von Tegetthoff • VAdm. Friedrich Freiherr von Pöck • VAdm. Maximilian Daublebsky Freiherr von Sterneck • VAdm. Hermann Freiherr von Spaun VAdm. • Rudolf Graf/Conte Montecuccoli • Grand Adm. Anton Haus • Grand Adm. Anton Haus • Adm. Maximilian Njegovan • Adm. Miklós HorthyChief of the General Staff Feldmarschalleutnant Josef Wilhelm Freiher von Gallina • Feldmarschalleutnant Franz Freiherr von John • Feldmarschalleutnant Anton Freiherr von Schönfeld • Feldzeugmeister Friedrich Graf von Beck-Rzikowsky • Franz Graf Conrad von Hötzendorf • Generalmajor Blasius Schemua • General der Infanterie Arthur Arz von StraußenburgCommanders-in-Chief of the Army Supreme Commanders Franz Joseph • Karl ICategories:- Monarch class battleships
- Battleship classes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.