- Culture of Sweden
-

Life in Sweden • Architecture
• Art
• Culture
• Demographics
• Economy
• Education• Geography
• Geology
• History
• Language
• Military
• PoliticsSwedish culture has been described as Lutheranism,[1] trade unionism, and self-reliance are aspects that have been associated with Swedish mentality.[2]
Sweden did not formally abolish slavery until the middle of the 14th century, but did not have serfdom in the Middle Ages and peasant freeholders constituted about 40% of the population and was one of four estates (together with nobles, clergy, and burghers) in the Diet.
Contents
Foreign influences on Sweden
The greatest sources of influence on Swedish culture have been Denmark, Norway and England in the early Middle Ages, Germany during the high and late Middle Ages, an influx of a foreign aristocracy during the 17th century, France during the 18th century, Germany again between the mid 19th and 20th century, and then the English-speaking world after World War II[citation needed].
See also: Post-war Sweden#Culture and mass mediaRegions
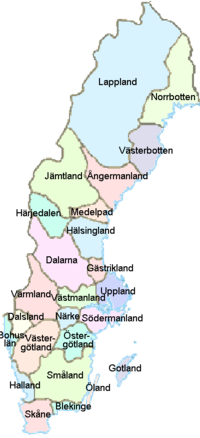
See also: Provinces of SwedenThe 25 provinces (landskap) of Sweden, which early in their histories had poor communication, each have a distinct culture. The provinces long ago lost their importance as administrative and political regions but are still seen as cultural ones, and the population of Sweden identifies with them. Each province has a specific history, each with their own robust nature. Some constituted separated parts of Sweden with their own laws. Other regions have been independent and/or a part of another country, such as (Denmark or Norway), etc. They have different indigenous dialects of North Germanic, and some have ethnic minorities. For more information about these cultural regions, see the provinces' articles:
- Blekinge
- Bohuslän
- Dalarna
- Dalsland
- Gotland
- Gästrikland
- Halland
- Hälsingland
- Härjedalen
- Jämtland
- Lappland
- Medelpad
- Norrbotten
- Närke
- Skåne
- Småland
- Södermanland
- Uppland
- Värmland
- Västmanland
- Västerbotten
- Västergötland
- Ångermanland
- Öland
- Östergötland
Food
Main article: Swedish cuisineSwedish food has traditionally been practical and sustaining. A typical old fashioned meal consists of boiled potatoes, some kind of meat or fish, a sauce and some vegetables. Fish has historically been very important. Swedes are among the heaviest coffee drinkers in the world, second only to Finland. Brewed coffee is dominant. For meals cider, beer, milk, juice, or water is standard. Swedish cider is sweeter and frutier than foreign ciders, and is enjoyed in almost as large quantities as beer is.
Film
 Poster for The Seventh Seal
Poster for The Seventh Seal Main article: Cinema of Sweden
Main article: Cinema of SwedenSwedish cinema is one of the most widely-known national film industries in the world. The silent period saw the flourish of the gifted visionaries Mauritz Stiller and Victor Sjöström, who brought international attention to Swedish filmmaking and its particular vision of the world[citation needed].
Ingmar Bergman, regarded as one of the most influential filmmakers of the 20th Century, emerged as a prominent figure in world cinema during the 1950s with his existential epic The Seventh Seal, which he followed with a host of critically revered psychological dramas. Two of his films in particular, Persona and Cries and Whispers, received unparalleled critical adoration and put Sweden in the map as a one of the most progressive cinematic entities. The revered naturalist Jan Troell as well as the socially conscious Bo Widerberg would quickly follow Bergman as the country's foremost visual artists[citation needed].
Famous actresses and actors include Ingrid Bergman, Greta Garbo, Max von Sydow, Alexander Skarsgård, Stellan Skarsgård, Ingrid Thulin, Lena Olin, Dolph Lundgren and Peter Stormare.
Music
Main article: Music of SwedenSinging is popular in Sweden, and of its 9,000,000 inhabitants, 600,000 belong to various choirs. ([1])
Two of the world's leading songwriters, Jörgen Elofsson and Max Martin live in Sweden.
In popular music, the group ABBA became the essence of Swedish music during the 1970s and early 1980s. Later Roxette emerged, mostly performing joyful songs in the late 1980s and early 1990s. This band was also successful in the USA. Europe, Ace of Base and The Cardigans are Swedish pop groups that have been popular in the world.
It can be noted that Britney Spears had at least one of her early albums produced in Sweden, and so did Bon Jovi and the Backstreet Boys[citation needed].
Pop promo director Jonas Åkerlund is from Sweden. He is perhaps best known for The Prodigy's Smack My Bitch Up video.
Indie pop/rock is very big in Sweden. Especially Gothenburg has spawned a great deal of prominent bands and artists thanks to labels such as Sincerely Yours, Service and Luxury. Notable Swedish indie bands and artists include Jens Lekman, The Knife, Love Is All, The Concretes, Broder Daniel, The Tough Alliance, Peter, Bjorn and John, Fever Ray, Popsicle, Studio, The Embassy, The Honeydrips, Brainpool, Air France, jj, Joel Alme, Pacific! etc.
In contrast to the large pop music scene in Sweden, they also boast one of the most prolific death metal scenes in the world. Gothenburg is famed in the scene for the "melodic death metal" sound. Many of these bands such as In Flames, Dark Tranquillity, At the Gates, The Haunted, as well as Stockholm's Amon Amarth and Opeth have seen growing commercial success throughout Europe and the United States. Melodic death metal is quite a broad genre with many variations, but with its more obvious roots in traditional death metal, black metal and classic metal such as Iron Maiden. Still, many bands are influenced by genres as broad as Swedish folk music, alternative music, electronica, gothic music, progressive music and even neo-classical music. Sweden is known for in the extreme metal community for its famous late 80s-early 90s death metal scene, spawning important bands as Entombed, Dismember, Grave and Unleashed as well as more obscure, brutal bands as God Macabre, Obscurity, Treblinka (later Tiamat) and Grotesque. Highly influential band Bathory also had a huge impact on the then-to-come black metal scene of Norway and the 1990s with albums Bathory (1984), The Return (1985), and Under the Sign of the Black Mark (1987), as well as being the first Viking metal band[citation needed].
There is a notable Swedish hip hop scene. This culture has spawned a new sociolect/dialect (see Rinkeby Swedish), so named after the Rinkeby suburb)[citation needed].
Sweden has produced several notable opera singers. In the 1850s, Jenny Lind (a.k.a. the Swedish Nightingale) toured the United States, and the price of admission for her performances was at a rate never before seen. In the 1950s, Jussi Björling was one of few non-Italian opera singers, and he is to this day a household name in opera circles[citation needed].
Other Swedish bands and artists that seem to manage the international crowd better than others are Dungen, José González, Mando Diao, The Sounds, The Hives, Neverstore, Sahara Hotnights, Robyn, Tages, The Mascots, The Shanes etc. However, there are a lot of other bands and artists that dominate the national music scene, such as Kent, Håkan Hellström and Lars Winnerbäck.
Literature
Main article: Swedish literatureSwedish literature is vibrant and active[citation needed]. Sweden ranks joint fifth in the list of countries with most Nobel Prize laureates in literature. Famous Swedish writers and poets are Astrid Lindgren, Selma Lagerlöf, August Strindberg, Hjalmar Söderberg, Tomas Tranströmer, Karin Boye, Stieg Larsson, Henning Mankell etc.
Architecture
Main article: Architecture of SwedenBefore the 13th century most buildings were made of Brick. But a shift began towards stone. Early Swedish stone buildings are the Romanesque churches on the country side. As so happens, many of them were built in Scania and are in effect Danish churches. This would include the magnificent Lund Cathedral from the 11th century and the somewhat younger church in Dalby, but also many early Gothic churches built through influendes of the Hanseatic League, such as in Ystad, Malmö and Helsingborg.
Cathedrals in other parts of Sweden were also built as seats of Sweden's bishops. The Skara Cathedral is of bricks from the 14th century, and the Uppsala Cathedral in the 15th. In 1230 the foundations of the Linköping Cathedral were made, the material was there limestone, but the building took some 250 years to finish.
Older (Iron Age and medieval) structures also include some significant fortresses and other historical buildings such as Borgholm Castle, Eketorp fortress (both on Öland) and the Visby city wall.
 The Kalmar Castle.
The Kalmar Castle.
In the 1520s Sweden emerged from the Middle Ages and once again asserted her independence under King Gustav Vasa. The king initiated a building program of grand mansions and fortresses, for reasons of defence and to express the new monarchy; much of this was continued by his sons in the later half of the century. The more imposing include the castles of Kalmar, Gripsholm and Vadstena.
In the next two centuries, Sweden was designated by Baroque architecture and later the rococo. Notable projects from that time include the city Karlskrona, which has been declared a World Heritage Site, the Drottningholm Palace and Stockholm Palace, still the official seat of the monarchy.
Clothing
Current clothing is very internationally influenced, but traditional Swedish national costumes are sometimes used on special occasions, such as Midsummer.
Fashion
Sweden has in late years taken an interest in the fashion industry, through headquartering famous brands like Hennes & Mauritz (operating as H&M), J. Lindeberg (operating as JL), Gina Tricot, Tiger of Sweden, Acne Jeans and Filippa K within its borders. These companies, however, are largely made up of buyers who import fashionable goods from throughout Europe and the Americas, continuing the trend of Swedish business toward multinational economic dependency like many of its neighbours.[citation needed]
A new breed of smaller Swedish fashion labels like Diana Orving, So Last Season, Odd molly, WESC, Whyred, Hope, Nakkna, Velour, Carin Wester, Ida Sjöstedt, Unwind Clothing, Fifth Avenue Shoe Repair, Acne, Cheap Monday, Nudie Jeans and The Local Firm are emerging and getting recognition.[3][4] I Love Ines
Arts
Main article: Art of SwedenThe oldest remains of Swedish art are found in the churches: frescos, altar pieces and baptismal founts. Little unique beauty is generally attributed to these, except for occasional. The motifs evolve around religious beliefs, focused on purgatory, the devil, Jesus Christ, and Virgin Mary[citation needed].
In the 19th century, the painter Carl Larsson (1853–1919) shaped the image of the idyllic countryside home with his naïve picturesque illustrations.
References
External links
- Sweden at geographia.com
Culture of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities - European Union
Categories:- Swedish culture
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.