- Koronadal
-
Koronadal
Ciudad sang Koronadal— 1st Class City — City of Koronadal 
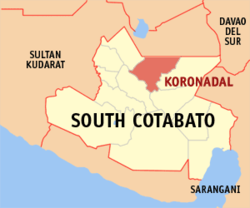
SealNickname(s): Marbel Motto: "Kanami Koronadal, Kanami Guid" Map of South Cotabato showing the location of Koronadal City. Location in the Philippines Coordinates: 6°30′2″N 124°51′6″E / 6.50056°N 124.85167°ECoordinates: 6°30′2″N 124°51′6″E / 6.50056°N 124.85167°E Country  Philippines
PhilippinesRegion SOCCSKSARGEN (Region XII) Province South Cotabato District 2nd District of South Cotabato Founded August 18, 1947 Cityhood 2000 Barangays 27 Government – Mayor Peter B. Miguel, MD., FPSO-HNS (2010 Mayor-elect) Area – Total 277.00 km2 (107 sq mi) Population (2009) – Total 184,573 – Density 666.3/km2 (1,725.8/sq mi) Time zone PHT (UTC+8) ZIP Code 9506 Income class 1st Class City Website Official website Koronadal, also known as Marbel is a 1st class city in the Philippines. It is the capital of South Cotabato province and regional center of region 12. According to the 2009 census, it had a population of 184,573.
Koronadal became a component city of South Cotabato in 2000, by virtue of Republic Act 8803 on October 8, 2000. In 2003 and 2005 the city was recognized "Most Competitive City" in the small-city category, and also in 2005 and 2006, as the most business friendly city in Mindanao.
Contents
History
The settlement of Koronadal and its creation as a municipality by virtue of Executive Order No. 82 dated August 18, 1947 was marked by a rapid initial development, so that when the province of South Cotabato was created under Republic Act No. 4849 on July 18, 1966, it easily became the capital town. In the past, the place was populated by B'laans and Maguindanaos. The word Koronadal is believed to have been derived from two B'laan words- koron or kolon meaning cogon grass and nadal or datal meaning plain which aptly described the place to the natives. On the other hand, Marbel, which is another name for the poblacion, is a B'laan term "Marb-El" which means "murky waters" referring to a river, now called Marbel River.
Koronadal used to comprise the area extending from the banks of Buluan Lake to the north to Barangay Polonoling in the municipality of Tupi to the south from Quezon mountain range to the northeast to the municipality of T'Boli to the southeast.
It was on August 18, 1947 when President Manuel Roxas signed the Executive Order creating the municipalities in the entire province of South Cotabato, one of which was Koronadal. The same executive order likewise mandated the official function of the municipal government which began after the qualification and election of the first set of municipal officials.
The municipal government of Koronadal began its official function on January 1, 1948 with an approved Annual Estimated Budget of P30,000.00. The land area of the municipality by then was comparable with the Province of Bata-an embracing the present municipalities of Tampakan, Tupi, Banga, Lake Sebu, Surallah, T'Boli, Sto. Niño, Norala, and Isulan.
Municipal Council Resolution No. 32, Series of 1948 mandated and proclaimed January 10 of each year as the Municipal Town Fiesta commemorating the foundation of Marbel Settlement District of the National Land Settlement.
Koronadal was converted into a component city of South Cotabato now known as the City of Koronadal by virtue of Republic Act 8803 on October 8, 2000. At present, Koronadal is a fast developing growth center composed of twenty seven (27) barangays including the four (4) zones in the poblacion. Being the capital city of South Cotabato, it is the center of the province in terms of political, cultural and socio-economic activities,
Barangays
Koronadal City is politically subdivided into twenty-seven barangays.
- Assumption (Bulol)
- Avanceña (Bo. 3)
- Cacub
- Caloocan
- Carpenter Hill
- Concepcion (Bo. 6)
- Esperanza
- General Paulino Santos (Bo. 1
- Mabini
- Magsaysay
- Mambucal
- Morales
- Namnama
- New Pangasinan (Bo. 4)
- Paraiso
- Zone I (Pob.)
- Zone II (Pob.)
- Zone III (Pob.)
- Zone IV (Pob.)
- Rotonda
- San Isidro
- San Jose (Bo. 5)
- San Roque
- Santa Cruz
- Santo Niño (Bo. 2)
- Sarabia (Bo. 8)
- Zulueta (Bo. 7)
Culture
Discovering City of Koronadal (and/or Marbel to many) is a very simple thing. Here, vivid tapestry of history are still alive, dating from the accupation of Islamic traders and indigenous peoples up to the settlement of Ilonggo, Ilocano and Tagalog people. Yet modern as it is today, old legends still continue to influence and inspire the existence of this young city. it is the diversity of this culture in the city that spawns a colorful extravaganza of cultural dances.
B'laan Culture
The B'laan tribe is one of the indigenous peoples of the Southern Philippine island of Mindanao. Another tribe called the Maguindanao also inhabits the same area. The two tribes consider themselves to be brothers and sisters. Long ago, an Arab male (ancestral brother) married a B'laan female (ancestral sister) and through this marriage union, Islam infiltrated Southern Mindanao so when the Spaniards arrived, their attempts to establish Catholicism were unsuccessful in the south. Eventually the B'laan and the Maguindanao became trade partners with the B'laan settling in the mountains and the Maguindanao settling along the coastal areas. From that time until now, B'laan have been producing rice, vegetables, livestock, and rainforest products. The original religion of the B'laan is Animist. Presently, only 5% of the 8,000 B'laan tribal people are considered to be evangelical.
Christian Culture
The Christian Filipinos make up the great majority (over 70%) of the Southern Philippine population. They are relative newcomers to the area; the first wave of Christian migrants came in the seventeenth century when the Spaniards sought to populate Zamboanga, Jolo, Dapitan and other areas by encouraging people from Luzon and the Visayas to settle there. In the nineteenth century Spanish policy found considerable success in encouraging migrations to Iligan and Cotabato. The Americans continued this pattern during their colonial administration. In 1913 the American colonial government provided resources for the establishment of agricultural colonies in Mindanao. By the time the Philippine Commonwealth was established, Mindanao had become a veritable frontier. Wave upon wave of migrants poured into the region, chief among them the Cebuanos, Hiligaynons, Ilokanos, Tagalogs, Warays (Leyte-Samar), Pampangos, Aklanons, and Bicolanos. These people did much to clear the virgin areas of Mindanao and open them to extensive agriculture and industry. In time, the economy of the region began to produce part of its promise.
Muslim Culture
The cultural diversity of the region is the result of a large influx of migrants from the north over a long period of the region's history. Found here are three main cultural groups: the early Filipinos who belong to various indigenous tribes living in the highlands and remote areas of Mindanao, the Muslim Filipinos who were early converts to Islam and who regard the region as their traditional homeland, and the Christian Filipinos who founded settlements and communities in the course of their migrations from other parts of the country.
Mr. Dwight De Leon who is a native of Koronadal and currently based in Manila, is the recognized chronicler of Koronadal's Cultural Events. He also promotes the city as a cultural and Eco-tourism destination. He contributes by giving artistic and cultural inputs to Koronadal's Cultural and Historical Society, whose main function is to preserve and promote the city's cherished artistic and cultural tradition since the time the pioneers established their settlements on the vast plain of the city which the locals affectionately call the Valley of Allah. Mr. De Leon took it upon himself to be Koronadal's repository of facts as regards to culture and tradition of this marvelous city in the south.
Festivals
- Hinugyaw Koronadal (January 10) - is the festival that marks the foundation anniversary of Koronadal as a municipality. it shows the festive spirit of the people of Koronadal with street dancing and night beer parties in the streets of Koronadal
- Cityhood Charter Anniversary (October 8) - is the city charter festival of Koronadal, the name of the festival cam from the other name of Koronadal which is marbel and with the street dancing in the streets mardgiras.
External links
- Koronadal Software Solution
- KoronadalSite "Taga Koronadal Ako Ya"
- Official Website
- City Travel Guide
- Philippine Standard Geographic Code
- RMN Koronadal 639 khz

Lutayan, Sultan Kudarat & Tantangan, South Cotabato 
Banga, South Cotabato 
Tampakan, South Cotabato  Koronadal City
Koronadal City 

Tupi, South Cotabato Municipalities Component City KoronadalHighly Urbanized City (Administratively independent from the province, but grouped under South Cotabato by the National Statistics Office) Cities of the Philippines
Cities of the PhilippinesHighly-urbanized Cities Angeles · Bacolod · Baguio · Butuan · Cagayan de Oro · Caloocan · Cebu · Davao · General Santos · Iligan · Iloilo · Lapu-Lapu · Las Piñas · Lucena · Makati · Malabon · Mandaluyong · Mandaue · Manila · Marikina · Muntinlupa · Navotas · Olongapo · Parañaque · Pasay · Pasig · Puerto Princesa · Quezon City · San Juan · Tacloban · Taguig · Zamboanga
Independent
Component CitiesComponent Cities Alaminos · Antipolo · Bago · Bais · Balanga · Batangas · Batac · Bayawan · Baybay · Bayugan · Biñan · Bislig · Bogo · Borongan · Cabadbaran · Cabanatuan · Cadiz · Calamba · Calapan · Calbayog · Candon · Canlaon · Carcar · Catbalogan · Cauayan · Cavite · Danao · Dapitan · Dasmariñas · Digos · Dipolog · Dumaguete · El Salvador · Escalante · Gapan · Gingoog · Guihulngan · Himamaylan · Iriga · Isabela · Kabankalan · Kidapawan · Koronadal · La Carlota · Lamitan · Laoag · Legazpi · Ligao · Lipa · Maasin · Malaybalay · Malolos · Marawi · Masbate · Mati · Meycauayan · Muñoz · Naga, Cebu · Oroquieta · Ozamiz · Pagadian · Palayan · Panabo · Passi · Roxas · Sagay · Samal · San Carlos, Negros Occidental · San Carlos, Pangasinan · San Fernando, La Union · San Fernando, Pampanga · San Jose · San Jose del Monte · San Pablo · Santa Rosa · Silay · Sipalay · Sorsogon · Surigao · Tabaco · Tabuk · Tacurong · Tagaytay · Tagbilaran · Tagum · Talisay, Cebu · Talisay, Negros Occidental · Tanauan · Tandag · Tangub · Tanjay · Tarlac · Tayabas · Toledo · Trece Martires · Tuguegarao · Urdaneta · Valencia · Victorias · Vigan
Ranking
Largest cities of Mindanao
Mindanao - Philippines 2007 CensusRank City Name Region Pop. Rank City Name Region Pop. 
Davao
1 Davao Davao Region 1,530,365 11 Marawi City ARMM 177,391 
Cagayan de Oro
2 Zamboanga Zamboanga Peninsula 774,407 12 Valencia City Northern Mindanao 162,745 3 Cagayan de Oro Northern Mindanao 553,966 13 Pagadian City Zamboanga Peninsula 161,312 4 General Santos SOCCSKSARGEN 529,542 14 Panabo City Davao Region 159,456 5 Tagum Davao Region 450,526 15 Malaybalay City Northern Mindanao 144,651 6 Iligan Northern Mindanao 318,040 16 Dipolog City Zamboanga Peninsula 141,027 7 Butuan Caraga Region 298,378 17 Surigao City Caraga Region 132,151 8 Cotabato City ARMM 259,153 18 Ozamiz City Northern Mindanao 123,137 9 Digos Davao Region 199,832 19 Gingoog City Northern Mindanao 111,787 10 Koronadal SOCCSKSARGEN 184,573 20 Bislig City Caraga Region 110,009 Categories:- Cities in the Philippines
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.