- Ongan languages
-
Ongan South Andamanese Geographic
distribution:Andaman Islands Linguistic classification: possibly an independent language family, Andamanese, or Austronesian[1] - Ongan
Subdivisions: JarawaJangil (extinct)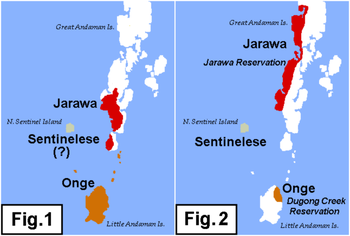
Distribution of the Ongan languages prior to 1850 (Fig. 1) and in 2005 (Fig. 2)Ongan, or South Andamanese, is a small family of two languages, Önge and Jarawa, spoken in the southern Andaman Islands:
- Ongan
A third language, Jangil, extinct sometime between 1895 and 1920, is reported to have been unintelligible with but to have had noticeable connections with Jarawa.
Contents
Classification
The Andaman languages fall into two clear families, Great Andamanese and Ongan, plus one unattested language, Sentinelese. These are generally seen as related, and Sentinelese is assumed to be closest to Ongan. However, the similarities between Great Andamanese and Ongan are so far mainly of a typological and morphological nature, with little demonstrated common vocabulary. As a result, some linguists, including long-range researchers such as Joseph Greenberg, have expressed doubts as to the validity of Andamanese as a family.[2] It has since been proposed that Ongan is distantly related to Austronesian (Blevins 2007).
The two attested Ongan languages are relatively close, and the historical sound reconstruction mostly straightforward:
Proto-Ongan consonant correspondances[3] Proto-Ongan *p *b *t *d *kʷ *k *ɡ *j *w *c *ɟ *m *n *ɲ *ŋ *l *r Jarawa p, b b t d hʷ, h h ɡ, j j w c ɟ m n ɲ ŋ l r Onge b b t, d d, r kʷ, h k, ɡ ɡ, Ø j w c, ɟ ɟ m n ɲ ŋ l, j r/j/l, Ø Proto-Ongan vowel correspondances in open nonfinal syllables[3] Proto-Ongan *i *u *a *e *o (*ə) Jarawa i u a e, ə, o o (ə) Onge i u a e, ə, o o (ə) Grammar
The Ongan languages are agglutinative languages, with an extensive prefix and suffix system.[4][5] They have a noun class system based largely on body parts, in which every noun and adjective may take a prefix according to which body part it is associated with (on the basis of shape, or functional association).[6] Another peculiarity of terms for body parts is that they are inalienably possessed, requiring a possessive adjective prefix to complete them, so one cannot say "head" alone, but only "my, or his, or your, etc. head".[6]
The Ongan pronouns are here represented by Önge:
I, my m- we, our et-, m- thou, thy ŋ- you, your n- he, his, she, her, it, its g- they, their ekw-, n- Judging from the available sources, the Andamanese languages have only two cardinal numbers: one and two and their entire numerical lexicon is one, two, one more, some more, and all.[5]
Bibliography
- Blevins, Juliette (2007), "A Long Lost Sister of Proto-Austronesian? Proto-Ongan, Mother of Jarawa and Onge of the Andaman Islands", Oceanic Linguistics 46 (1): 154–198, doi:10.1353/ol.2007.0015, http://email.eva.mpg.de/~blevins/pdf/webpub2007a.pdf (available here)
- Das Gupta, D., and SR Sharma. A Handbook of the Önge Language. Anthropological Survey of India: Calcutta 1982.
- E. H. Man, Dictionary of the South Andaman Language, British India Press: Bombay 1923.
- Senkuttuvan, R. 2000. The Language of the Jarawa: Phonology. Calcutta: Anthropological Survey of India, Government of India, Ministry of Culture, Youth Affairs, and Sports, Dept. of Culture.
- Sreenathan, M. 2001. Jarwa-Language and Culture. Anthropological Survey of India, Ministry of Culture, Government of India, Kolkata
References
- ^ Blevins, Juliette (2007), "A Long Lost Sister of Proto-Austronesian? Proto-Ongan, Mother of Jarawa and Onge of the Andaman Islands", Oceanic Linguistics 46 (1): 154–198, doi:10.1353/ol.2007.0015, http://email.eva.mpg.de/~blevins/pdf/webpub2007a.pdf
- ^ Greenberg, Joseph (1971). "The Indo-Pacific hypothesis." Current trends in linguistics vol. 8, ed. by Thomas A. Sebeok, 807.71. The Hague: Mouton.
- ^ a b Blevins (2007:163–164)
- ^ Abbi, Anvita (2006). Endangered Languages of the Andaman Islands. Germany: Lincom GmbH.
- ^ a b Temple, Richard C. (1902). A Grammar of the Andamanese Languages, being Chapter IV of Part I of the Census Report on the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Superintendent's Printing Press: Port Blair.
- ^ a b Burenhult, Niclas (1996). "Deep linguistic prehistory with particular reference to Andamanese." Working Papers 45, 5-24. Lund University: Department of Linguistics
External links
Categories:- Agglutinative languages
- Andamanese languages
- Austronesian languages
- Endangered languages
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
