- Möbius syndrome
-
Möbius syndrome Classification and external resources 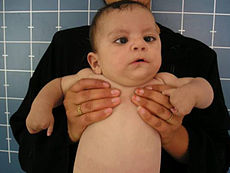
A child with oromandibular-limb hypogenesis-Möbius syndrome. Notice the expressionless face (due to bilateral VII nerve palsies) and missing fingers.ICD-10 Q87.0 ICD-9 352.6 OMIM 157900 DiseasesDB 31978 eMedicine neuro/612 MeSH D020331 Möbius syndrome (also spelled Moebius) is an extremely rare congenital neurological disorder which is characterized by facial paralysis and the inability to move the eyes from side to side. Most people with Möbius syndrome are born with complete facial paralysis and cannot close their eyes or form facial expressions. Limb and chest wall abnormalities sometimes occur with the syndrome. Most people with Möbius syndrome have normal intelligence, although their lack of facial expression is sometimes incorrectly taken to be due to dullness or unfriendliness. It is named for Paul Julius Möbius, a neurologist who first described the syndrome in 1888.[1]
Contents
Clinical features
Möbius syndrome results from the underdevelopment of the VI and VII cranial nerves.[2] The VI cranial nerve controls lateral eye movement, and the VII cranial nerve controls facial expression. People with Möbius syndrome are born with facial paralysis and the inability to move their eyes laterally. Often, the upper lip is retracted due to muscle shrinkage.[3] Occasionally, the cranial nerves V and VIII are affected.[2] If cranial VIII is affected, the person experiences hearing loss.
It is estimated that there are, on average, 2 to 20 cases of Möbius syndrome per million births.[4][5] Although its rarity often leads to late diagnosis, infants with this disorder can be identified at birth by a "mask-like" lack of expression that is detectable during crying or laughing and by an inability to suck while nursing because of paresis (palsy) of the sixth and seventh cranial nerves. Also, because a person with Möbius syndrome cannot follow objects by moving their eyes from side to side, they turn their head instead.
Other symptoms that sometimes occur with Möbius syndrome are:
- Limb abnormalities—clubbed feet, missing fingers or toes
- Chest-wall abnormalities (Poland Syndrome)
- Crossed eyes (strabismus)
- Difficulty in breathing and/or in swallowing
- Corneal erosion resulting from difficulty in blinking
Children with Möbius syndrome may have delayed speech because of paralysis of the lips. However, with speech therapy, most people with Möbius syndrome can develop understandable speech.[6] Möbius syndrome has been associated with increased occurrence of the symptoms of autism.[7] However, some children with Möbius syndrome are mistakenly labeled as mentally retarded or autistic because of their expressionless faces, strabismus, and frequent drooling.
Treatment
There is no single course of medical treatment or cure for Möbius syndrome. Treatment is supportive and in accordance with symptoms. If they have difficulty nursing, infants may require feeding tubes or special bottles to maintain sufficient nutrition. Physical, occupational, and speech therapy can improve motor skills and coordination and can lead to better control of speaking and eating abilities. Often, frequent lubrication with eye drops is sufficient to combat dry eye that results from impaired blinking. Surgery can correct crossed eyes, protect the cornea via tarsorraphy, and improve limb and jaw deformities. Sometimes called smile surgery by the media, muscle transfers grafted from the thigh to the corners of the mouth can be performed to provide the ability to smile. Although "smile surgery" may provide the ability to smile, the procedure is complex and can take twelve hours for each side of the face. Also, the surgery cannot be considered a "cure" for Möbius syndrome, because it does not improve the ability to form other facial expressions.
Living with Möbius syndrome
Many people with Möbius syndrome lead full lives and experience personal and professional success.[8] Facial expression is important in social interaction, and other people may have difficulty recognizing the emotions of people with Möbius. A person with Möbius syndrome who cannot smile may appear unfriendly or uninterested in a conversation. However, friends and family who are familiar with the person with Möbius syndrome learn to recognize other signals of emotion such as body language, and they sometimes report forgetting that the person has facial paralysis altogether.[9] People with Möbius syndrome can use alternative methods to communicate emotion—such as body language, posture, and vocal tone.[10]
Pathological picture
The causes of Möbius syndrome are poorly understood. Möbius syndrome is thought to result from a vascular disruption (temporary loss of bloodflow) in the brain during prenatal development.[2] There could be many reasons that a vascular disruption leading to Möbius syndrome might occur. Most cases do not appear to be genetic. However, genetic links have been found in a few families. Some maternal trauma may result in impaired or interrupted blood flow (ischemia) or lack of oxygen (hypoxia) to a developing fetus. Some cases are associated with reciprocal translocation between chromosomes or maternal illness. In the majority of cases of Möbius syndrome in which autosomal dominant inheritance is suspected, sixth and seventh cranial nerve paralysis (palsy) occurs without associated limb abnormalities.
The use of drugs and a traumatic pregnancy may also be linked to the development of Mobius syndrome. The use of the drugs misoprostol or thalidomide by women during pregnancy has been linked to the development of Möbius syndrome in some cases. Misoprostol is used to induce abortions in Brazil and Argentina as well as in the United States. Misoprostol abortions are successful 90% of the time, meaning that 10% of the time the pregnancy continues. Studies show that the use of misoprostal during pregnancy increases the risk of developing Möbius syndrome by a factor of 30. While this is a dramatic increase in risk, the incidence of Möbius syndrome without misoprostal use is estimated at one in 50000 to 100000 births (making the incidence of Möbius syndrome with misoprostal use, less than one in 1000 births).[11][12] The use of cocaine (which also has vascular effects) has been implicated in Möbius syndrome.[13]
Some researchers have suggested that the underlying problem of this disorder could be congenital hypoplasia or agenesis of the cranial nerve nuclei. Certain symptoms associated with Möbius syndrome may be caused by incomplete development of facial nerves, other cranial nerves, and other parts of the central nervous system.
Genetic links to 13q12.2[14] and 1p22[15] have been suggested.
Oral/dental concerns
Neonatal Period
When a child is born with Möbius syndrome, there may be difficulty in closing the mouth or swallowing. The tongue may fasciculate (quiver) or be hypotonic (low muscle tone). The tongue may be larger or smaller than average. There may be low tone of the muscles of the soft palate, pharynges, and the masticatory system. The palate may be arched excessively (a high palate), because the tongue does not form a suction that would normally shape the palate down further. The palate may have a groove (this may be partially due to intubation early on if it is for an extended period of time) or may be cleft (incompletely formed). The opening to the mouth may be small. Feeding problems may become a critical issue early on if adequate nutrition is difficult.
Primary Dentition
The primary (baby) teeth generally start coming in by 6 months of age, and all 20 teeth may be in by two and a half years of age. The eruption timing varies greatly. There may be an incomplete formation of the enamel on the teeth (enamel hypoplasia) that makes the teeth more vulnerable to caries (cavities). There may be missing teeth eruptions. If the infant is not closing down properly, the lower jaws become more noticeably deficient (micrognathia or retrognathia). The front teeth may not touch when the child closes down because the back teeth have overerrupted or because of incomplete formation of the maxilla. This condition is called an anterior open bite and has facial/skeletal implications. The saliva may be thick, or the infant may have a dry mouth.
Transitional Dentition
Between age 5 and 7, most children start losing their primary teeth. Occasionally, some primary teeth are slow to exfoliate (fall out), and the dentist may want to remove a primary tooth early to prevent orthodontic problems. Likewise, premature loss of primary teeth may create orthodontic problems later on. When a tooth is lost prematurely, removable or fixed spacers may be needed to prevent the shifting of teeth. Interceptive orthodontic treatment can be initiated at this stage of development to help with crowding or to help relate the upper and lower jaws. Consistent with a high palate is a narrow arch shape of the upper teeth as they line up in the mouth. This may cause the upper front teeth to flare out and become more prone to fracture if accidentally hit. Interceptive orthodontics has an important role in this situation. Appliances that expand the upper arch tend to bring the front teeth back into a more-normal position. Some appliances can even help allow the front teeth to close to normal in an open-bite situation. The mouth and lips may tend to get dry with the Möbius patient. Lack of a good oral seal (lips together) allows the gingiva (gums) to get dry and may get inflamed and irritated.
Permanent Dentition
After the last primary tooth is lost, usually around the age of twelve, final orthodontic treatment can be initiated. A patient that has not been able to close or swallow well probably will have an open bite, deficient lower-jaw growth, a narrow archform with crowded teeth, and upper anterior flaring of teeth. Orthognathic (jaw) surgery may be indicated. This should be completed in most situations before the smile surgery where the gracilis muscle is grafted to the face.
References
- ^ Möbius, P. J. (1888). "Ueber angeborene doppelseitige Abducens-Facialis-Lahmung". Münchener medizinische Wochenschrift 35: 91–4.
- ^ a b c Briegel W (August 2006). "Neuropsychiatric findings of Möbius sequence — a review". Clin. Genet. 70 (2): 91–7. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.2006.00649.x. PMID 16879188. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/resolve/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pubmed&issn=0009-9163&date=2006&volume=70&issue=2&spage=91.
- ^ Al Kaissi A, Grill F, Safi H, Ben Ghachem M, Ben Chehida F, Klaushofer K (2007). "Craniocervical junction malformation in a child with Oromandibular-limb hypogenesis-Möbius syndrome". Orphanet J Rare Dis 2: 2. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-2-2. PMC 1774563. PMID 17210070. http://www.ojrd.com/content/2//2.
- ^ Kuklík M (2000). "Poland-Möbius syndrome and disruption spectrum affecting the face and extremities: a review paper and presentation of five cases". Acta Chir Plast 42 (3): 95–103. PMID 11059047.
- ^ Verzijl HT, van der Zwaag B, Cruysberg JR, Padberg GW (August 2003). "Möbius syndrome redefined: a syndrome of rhombencephalic maldevelopment". Neurology 61 (3): 327–33. PMID 12913192. http://www.neurology.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12913192.
- ^ Meyerson MD, Foushee DR (June 1978). "Speech, language and hearing in Moebius syndrome: a study of 22 patients". Dev Med Child Neurol 20 (3): 357–65. PMID 208901.
- ^ Gillberg C, Steffenburg S (March 1989). "Autistic behaviour in Moebius syndrome". Acta Paediatr Scand 78 (2): 314–6. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.1989.tb11076.x. PMID 2929356.
- ^ Meyerson MD (May 2001). <0231:RASIAW>2.0.CO;2 "Resiliency and success in adults with Moebius syndrome". Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 38 (3): 231–5. doi:10.1597/1545-1569(2001)038<0231:RASIAW>2.0.CO;2. PMID 11386430. http://www.cpcjournal.org/doi/full/10.1597/1545-1569(2001)038<0231:RASIAW>2.0.CO;2.
- ^ Goldblatt D, Williams D (January 1986). ""I an sniling!": Möbius' syndrome inside and out". J. Child Neurol. 1 (1): 71–8. PMID 3298396. http://jcn.sagepub.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=3298396.
- ^ Bogart KR, Matsumoto D (March 2010). "Living with moebius syndrome: adjustment, social competence, and satisfaction with life". Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 47 (2): 134–42. doi:10.1597/08-257.1. PMID 20210634. http://www.cpcjournal.org/doi/full/10.1597/08-257.1.
- ^ Koren G, Schuler L (May 2001). "Taking drugs during pregnancy. How safe are the unsafe?". Can Fam Physician 47: 951–3. PMC 2018504. PMID 11398725. http://www.cfp.ca/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=11398725.
- ^ Pastuszak AP, Schuller L, Speck-Martins CF, Coelho KE, Cordello SM, Vargas F et al. (1998). "Use of Misoprostol during pregnancy and Möbius' syndrome in infants". N Engl J Med 338 (26): 1881–5. doi:10.1056/NEJM199806253382604. PMID 9637807. http://content.nejm.org/cgi/reprint/338/26/1881.pdf.
- ^ Puvabanditsin S, Garrow E, Augustin G, Titapiwatanakul R, Kuniyoshi KM (April 2005). "Poland-Möbius syndrome and cocaine abuse: a relook at vascular etiology". Pediatr. Neurol. 32 (4): 285–7. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2004.11.011. PMID 15797189. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0887-8994(04)00567-3.
- ^ Slee JJ, Smart RD, Viljoen DL (June 1991). "Deletion of chromosome 13 in Moebius syndrome". J. Med. Genet. 28 (6): 413–414. doi:10.1136/jmg.28.6.413. PMC 1016909. PMID 1870098. http://jmg.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=1870098.
- ^ Nishikawa M, Ichiyama T, Hayashi T, Furukawa S (February 1997). "Möbius-like syndrome associated with a 1;2 chromosome translocation". Clin. Genet. 51 (2): 122–123. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.1997.tb02433.x. PMID 9112001.
External links
- Moebius Syndrome Foundation & International Conference Information
- Moebius Research Trust
- International Orthoptics Association
- Orthoptics Association of Australia
- "Seeking Emotional Clues Without Facial Cues" by Benedict Carey, New York Times, 5 April 2010
Congenital abnormality · multiple abnormalities (Q87, 759.7) Craniofacial Short stature 1q21.1 deletion syndrome · Aarskog–Scott syndrome · Cockayne syndrome · Cornelia de Lange Syndrome · Dubowitz syndrome · Noonan syndrome · Robinow syndrome · Silver–Russell syndrome · Seckel syndrome · Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome-Turner syndromeLimbs Overgrowth Laurence-Moon-Bardet-Biedl Bardet–Biedl syndrome · Laurence-Moon syndromeCombined/other,
known locus3 (Zimmerman-Laband syndrome) · 4/13 (Fraser syndrome) · 8 (Branchio-oto-renal syndrome) · 12 (Keutel syndrome, Timothy syndrome) · 15 (Marfan syndrome) · 19 (Donohue syndrome)Categories:- Neurological disorders
- Syndromes
- Genetic disorders with OMIM but no gene
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.