- M-15 (Michigan highway)
-
This article is about the state highway in Michigan; for other uses, see M15 (disambiguation)
M-15 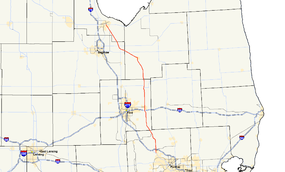
M-15 highlighted in redRoute information Maintained by MDOT Length: 73.664 mi[2] (118.551 km) Existed: ca. 1927[1] – present Tourist
routes:Pathway to Family Fun Recreational Heritage Route Major junctions South end:  US 24 near Clarkston
US 24 near Clarkston I-75 at Clarkston
I-75 at Clarkston
 I-69 near Davison
I-69 near Davison
 M-57 near Otisville
M-57 near Otisville M-46 near Reese
M-46 near ReeseNorth end:  M-25 in Bay City
M-25 in Bay CityLocation Counties: Oakland, Genesee, Tuscola, Saginaw, Bay Highway system Michigan State Trunkline Highway System
Interstate • US • State←  M-14
M-14US 16  →
→M-15 is a north–south state trunkline highway in the US state of Michigan. The southern terminus is a junction with US Highway 24 (US 24) just south of Clarkston on the northwestern edge of the Detroit metropolitan area. The trunkline is a recreational route running north and northwest to the Tri-Cities area. The northern terminus is the junction with M-25 on the east side of Bay City. The total length is 69.673 miles (112.128 km) between the two regions.
The original M-15 designation was used in the northern half of the state in 1919. This designation was wholly replaced by the US 41 on November 11, 1926. This previous designation contained the section of highway in Marquette County that is home to the first painted highway centerline in the nation. Another section in western Marquette County included the first bridge built by the state of Michigan. Within the next year after M-15 was replaced by US 41, the designation was reused for a new highway routing along the current highway. This current highway was extended northerly to eventually end at I-75 in Bay City, before it was scaled back slightly to end in southeast Bay City. A proposed, but unbuilt, extension around the west side of Metro Detroit later became part of the I-275 corridor.
This highway is now a part of the Michigan Heritage Route System, but none of it is located on the National Highway System. A section of the two-lane highway has the local moniker, "Death Alley", where the local sheriff says the highway is poorly designed. The stretch of highway in Genesee County has been the location of 14 traffic fatalities between 2004 and 2009 as reported by The Flint Journal, including that of a 14-year-old local girl.
Contents
Route description
M-15 runs through mostly rural agricultural communities of The Thumb connecting the northern edge of Metro Detroit with the Tri-Cities area. It starts at a junction south of the village of Clarkston in northern Oakland County. The highway runs north along Ortonville Road from the intersection with US 24 (Dixie Highway) near Deer and Middle lakes through Clarkston. Continuing through town on Main Street near Parke Lake, it comes to an interchange with Interstate 75 (I-75) north of the village next to Little Walters Lake. South of Ortonville near Lake Louise and Bald Eagle Lake, M-15 turns northwest between the two lakes. The trunkline becomes State Road at the county line and turns north again near Shinanguag Lake near the Ortonville State Recreation Area outside Goodrich in southeastern Genesee County. South of Davison, M-15 intersects I-69 near the Davison Country Club before running through town. In Otisville, State Road curves around to the west of some small lakes and through town.[3][4]
State Road turns northwesterly again in Millington in southwestern Tuscola County, heading up to Vassar. In Vassar, M-15 intersects and turns northwest along Huron Avenue, a historical routing of M-24, crossing the Cass River in town. Outside Vassar, Huron Avenue becomes Saginaw Road. In western Tuscola County, M-15 intersects M-46 in the community of Richville. The name of the road changes in Saginaw County to Vassar Road, and the trunkline continues northwesterly through the Blumfield Township communities of Blumfield Corners and Arthur. Arthur is located along the highway between the M-83 and M-81 junctions.[3][4]
In Bay County, M-15 follows Tuscola Road where it meets the western terminus of M-138 which runs along Munger Road in Munger. As the highway enters Bay City on the southeast side of town, Tuscola Road leaves the farmlands for residential areas of Bay City. The roadway runs northerwesterly near the St. Stanislaus, St. Patrick and Elm Lawn cemeteries, before turning north on Trumbull Street at 10th Street. The highway follows Trumbull Street for five blocks, where the highway designation ends at a four-way intersection with M-25/Center Avenue. Trumbull Street continues north through this residential section of the city.[3][4]
History
Original designation
On July 1, 1919, the original routing of M-15 was located in the Upper Peninsula (UP). It ran from the state line along the Menominee River in Menominee, connecting with STH-15 in Wisconsin, running north through the UP to Escanaba, Marquette and Houghton. Between Powers and Escanaba, M-15 ran concurrently with M-12. The northern terminus of the highway was at Fort Wilkins in Copper Harbor.[5] The first highway centerline in the nation was painted along a section of the highway in 1917, along the Marquette–Negaunee Road,[6] now a part of Marquette County Road 492.[5][7]
The Peshekee River Bridge, carried M-15 over the Peshekee River in western Marquette County's Michigamme Township . The bridge was built in 1914 in response to the 1913 State Trunk Line Act passed by the Michigan Legislature. This act designated a state trunkline highway network of nearly 3,000 miles (4,828 km). The act further said that the Michigan State Highway Department would design, build and maintain trunkline bridges spanning 30 feet (9 m) or more so long as the local governments improved an adjacent 3 miles (4.8 km) of roads. Marquette County built a mainline road from Marquette west to Michigamme near the county line, this road generally followed what is now known as County Road 492 (CR 492). About 5 miles (8.0 km) west of Marquette on CR 492 is a historical marker at the site of the first center line painted in 1917 along Dead Man's Curve.[6] M-15 continued through Morgan Meadows and crossing the Carp River into the town of Negaunee and connecting with Ishpeming. This road in now known as East Division or "County Road" also former Business M-28. West of Ishpeming in Ishpeming Township, M-15 followed Randal Drive and Westward to North Lake Junction. M-15 made its way along what is now CR 496 and several abandoned sections through Clarksburg and Humboldt Locations and the village of Champion. West of Champion M-15 continued to Michigamme crossing the Peshekee River, Marquette County improved a 3-mile (4.8 km) section in 1913 to encourage the state to build the bridge. The bridge was designed by C.V. Dewart for the department and built by the local firm of Powell and Mitchell in Marquette. The bridge was designated Trunk Line Bridge No. 1 as the first state-built bridge on the trunkline highway system.[8]
The 1925 draft plan for the establishment of the US Highway System would have replaced M-15 with three different US Highways. Between Menominee and Powers, M-15 was to be replaced by US 41. East of Powers to Rapid River, the trunkline would have been US 2. The next segment between Rapid River and Covington was planned as US 102 while the remainder north to Copper Harbor was planned as US 41 In between Powers and Covington, US 41 was planned to follow US 2 west to Iron Mountain and then route of the modern US 141 between Powers and Covington.[9] When the system was announced on November 11, 1926,[10] US 41 was the only US Highway routed along the alignment of M-15. The original map showed US 41 following an unbuilt alignment between Powers and Marquette,[11] but the US 41 designation was instead routed to follow the former M-15.[1]
Current designation
The current routing of M-15 was designated after 1926. The southern end was located at US 10 in Clarkston running north to M-38 and M-24 in Vassar.[1] By the end of 1936, M-15 was extended concurrently along M-24 from Vassar into Bay City.[12] By June 1942, the M-24 concurrency was removed as M-24 was realigned to replace M-85 between Vassar and Caro.[13][14] By July 1, 1960, the northern end was extended to run concurrently with M-25 and BUS US 23 to US 23 on the west side of Bay City.[15] This M-15/M-25 routing was extended again in the next year to end at the new I-75/US 10/US 23 freeway.[16] These two northerly extensions were both reversed and scaled back in 1970. M-15's northern end is moved back to M-25/Center Avenue in Bay City, its current location.[17][18] At some time after the 1993 beginning of the program,[19] M-15 was named the "Pathway to Family Fun" Recreational Heritage Route in the Michigan Heritage Route system.[20] Running roughly parallel to I-75, the route has not been added to the National Highway System,[21] a system of roadways considered important to the nation's economy, defense and mobility.[22]
The state highway map in 1933 showed a proposed southern extenstion from Clarkston through southern Oakland County, Wayne County into Monroe County.[23] This proposed highway would have bypassed Metro Detroit to the west through Farmington, Northville, Plymouth and Belleville. The full highway was never built, and M-15 was never extended south of Clarkston, but part of this proposal was completed. Much of it later became Haggerty Highway, and part of the I-275 and M-5 corridors.[3][23]
"Death Alley"
M-15 between the Oakland County line and I-69 has been nicknamed by locals as "Death Alley". On April 17, 2009, The Flint Journal reported that between 2004 and April 2009, 14 people have died on the stretch of road in car accidents. The most recent was a 14-year-old girl from Lapeer County, who died from her injuries on April 15, nine days after she crashed in a head-on collision on April 6, 2009 on M-15 just north of Green Road in Goodrich. The accident happened when her brother swerved to avoid a stopped car. The truck he was driving crossed into the path of an oncoming sport-utility vehicle. When Genesee County Sheriff Robert J. Pickell was asked about the stretch, he said the road suffers from a bad design, including a lack of turn lanes. He was quoted as saying, "It's a death trap," to which he then added the question, "How many people have to die before something is done?"[24]
Pickell said he plans to write a letter to the Michigan Department of Transportation (MDOT) about these fatality statistics asking for action by the state. Other local government officials have called for solutions to safety issues on the roadway. An employee of the real estate agency near the accident scene said that something should be done to fix the narrow two-lane highway in the area. MDOT said that the state looks at roadways after every fatal crash to determine what improvements could be made. MDOT Bay Region engineer Robert Ranck, Jr. was quoted in the article as saying, "We do not just let them go."[24]
Major intersections
County Location Mile[2][25] Destinations Notes Oakland Independence Charter Township 0.000  US 24 (Dixie Highway) – Toledo
US 24 (Dixie Highway) – Toledo1.781  I-75 – Flint, Detroit
I-75 – Flint, DetroitExit 91 on I-75 Genesee Davison Township 25.586  I-69 – Port Huron, Lansing
I-69 – Port Huron, LansingExit 145 on I-69 Forest Township 37.532  M-57 – Clio, Montrose, Chesaning
M-57 – Clio, Montrose, ChesaningTuscola Denmark Township 56.645  M-46 – Saginaw, Kingston, Sandusky
M-46 – Saginaw, Kingston, SanduskySaginaw Blumfield Township 60.365  M-83 – Frankenmuth
M-83 – Frankenmuth62.034  M-81 – Saginaw, Caro
M-81 – Saginaw, CaroBay Merritt Township 67.665  M-138 – Fairgrove, Akron
M-138 – Fairgrove, AkronBay City 73.664 
 M-25 / LMCT (Center Avenue)
M-25 / LMCT (Center Avenue)1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi References
- ^ a b c Michigan State Highway Department (December 1, 1927). Official Highway Service Map (Map). Cartography by MSHD.
- ^ a b Michigan Department of Transportation (2009). Control Section/Physical Reference Atlas (Map). http://mdotwas1.mdot.state.mi.us/public/maps/pr/. Retrieved July 26, 2009.
- ^ a b c d Michigan Department of Transportation (2009). Official Department of Transportation Map (Map). 1 in.:15 mi/1 cm:9 km. Section J12–L13.
- ^ a b c Google, Inc. Google Maps – Overview map of M-15 (Map). Cartography by Google, Inc. http://maps.google.com/maps?f=d&source=s_d&saddr=U.S.+24+%26amp%3B+Michigan+15,+Independence,+MI+48346&daddr=43.208179,-83.513947+to:Center+Ave+%26+M-15,+Bay+City,+MI&hl=en&geocode=FeTciwIdZyIH-yl55k5OfJckiDHvk62rXDUiew%3B%3BFV86mQIdFkkA-ymjhtFrmOEjiDF-a5ZpTiP9YQ&mra=dpe&mrcr=0&mrsp=1&sz=10&via=1&sll=43.159305,-83.683835&sspn=0.947661,1.025848&ie=UTF8&z=10. Retrieved February 1, 2010.
- ^ a b Michigan State Highway Department (1919). State of Michigan: Upper Peninsula (Map). Cartography by MSHD.
- ^ a b Kulsea, Bill; Shawver, Tom (1980). Making Michigan Move: A History of Michigan Highways and the Michigan Department of Transportation. Lansing, MI: Michigan Department of Transportation. p. 10.
- ^ Google, Inc. Google Maps – Negaunee, Michigan (Map). Cartography by Google, Inc. http://maps.google.com/maps?f=q&hl=en&geocode=&q=Negaunee,+MI&ie=UTF8&hq=&hnear=Negaunee,+Marquette,+Michigan&ll=46.52332,-87.528248&spn=0.111735,0.193634&z=13. Retrieved February 1, 2010.
- ^ "US 41 (Abandoned) / Peshekee River Bridge". Michigan Department of Transportation. April 23, 2002. http://www.michigan.gov/mdot/0,1607,7-151-9620_11154_11188-30382--,00.html. Retrieved January 18, 2008.
- ^ Report of Joint Board on Interstate Highways, October 30, 1925, Approved by the Secretary of Agriculture, November 18, 1925
- ^ Weingroff, Richard F. (January 9, 2009). "From Names to Numbers: The Origins of the U.S. Numbered Highway System". Federal Highway Administration. http://wwwcf.fhwa.dot.gov/infrastructure/numbers.cfm. Retrieved April 21, 2009.
- ^ Bureau of Public Roads (1926) (PDF). United States System of Highways (Map). http://www.okladot.state.ok.us/hqdiv/p-r-div/maps/misc-maps/1926us.pdf. Retrieved May 10, 2008.
- ^ Michigan State Highway Department (December 15, 1936). 1936/7 Official Michigan Highway Map (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally (Winter ed.). Section J12.
- ^ Michigan State Highway Department (July 1, 1941). 1941 Official Michigan Highway Map (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally (Summer ed.). Section J13.
- ^ Michigan State Highway Department (June 1, 1942). 1942 Official Michigan Highway Map (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally (Summer ed.). Section J13.
- ^ Michigan State Highway Department (1960). Official Highway Map (Map). Section J12. (Includes all changes through July 1, 1960)
- ^ Michigan State Highway Department (1961). Official Highway Map (Map). Section J12. (Includes all changes through July 1, 1961)
- ^ Michigan Department of State Highways (1970). Official Highway Map (Map). 1 in.:14.5 mi.. Section J12.
- ^ Michigan Department of State Highways (1971). Official Highway Map (Map). 1 in.:14.5 mi.. Section J12.
- ^ "Drive Home Our Heritage". Michigan Department of Transportation. January 29, 2010. http://www.michigan.gov/mdot/0,1607,7-151-9621_11041_11209-217276--,00.html. Retrieved February 1, 2010.
- ^ "Interactive Heritage Route Listing". Michigan Department of Transportation. November 5, 2009. http://www.michigan.gov/mdot/0,1607,7-151-9621_11041_11209-220123--,00.html. Retrieved February 1, 2010.
- ^ Michigan Department of Transportation (April 23, 2006) (PDF). National Highway System, Michigan (Map). http://www.michigan.gov/documents/MDOT_NHS_Statewide_150626_7.pdf. Retrieved February 4, 2008.
- ^ "The National Highway System". Federal Highway Administration. August 27, 2008. http://www.fhwa.dot.gov/planning/nhs/. Retrieved May 27, 2009.
- ^ a b Michigan State Highway Department (May 1, 1933). Official Highway Service Map (Map). Cartography by H.M. Gousha.
- ^ a b Morrison, Julie (April 17, 2009). "Teen dies after crash on 'death alley'". The Flint Journal. http://www.mlive.com/news/flint/index.ssf/2009/04/4yearold_lapeer_girl_jessica_m.html. Retrieved April 18, 2009.
- ^ "MDOT Physical Reference Finder Application". Michigan Department of Transportation. 2009. http://www.mcgi.state.mi.us/prfinder/. Retrieved April 9, 2010.
External links
Categories:- State highways in Michigan
- Dixie Highway
- Bay City, Michigan
- Transportation in Genesee County, Michigan
- Transportation in Bay County, Michigan
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


