- Ethylamphetamine
-
Ethylamphetamine 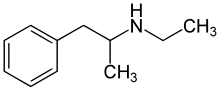
Systematic (IUPAC) name N-ethyl-1-phenyl-propan-2-amine Clinical data Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status Schedule 1 Routes Oral, Sublingual, Insufflated (Snorted), Inhaled (Vaporized), Intravenous, Rectal Pharmacokinetic data Metabolism Hepatic Excretion Renal Identifiers CAS number 457-87-4 ATC code A08AA06 PubChem CID 9982 ChemSpider 9588 
KEGG D07114 
ChEMBL CHEMBL276443 
Chemical data Formula C11H17N Mol. mass 163.259 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Ethylamphetamine (Apetinil, Adiparthrol), also known as etilamfetamine or N-ethylamphetamine, is a stimulant drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. It was invented in the early 1900s and was subsequently used as an anorectic or appetite suppressant in the 1950s,[1] but was not as commonly used as other amphetamines such as amphetamine, methamphetamine, and benzphetamine, and was largely discontinued once newer drugs such as phenmetrazine were introduced.
Contents
Chemistry
The molecular structure of ethylamphetamine is analogous to amphetamine's.[Note 1] It is a substituted amphetamine, with an ethyl group on the amphetamine backbone.[Note 2][Note 3]
Recreational use
Ethylamphetamine can be used as a recreational drug and, while its prevalence is less than amphetamine's, it is still encountered as a substance taken for recreational purposes.
Ethylamphetamine produces effects similar to amphetamine and methamphetamine, its potency being slightly greater than amphetamine's and lesser than methamphetamine's.[Note 4]
See also
- 3-Fluoroethamphetamine
- Dimethylamphetamine
- Fenfluramine
- Isopropylamphetamine
- Propylamphetamine
References
Notes
- ^ Amphetamine is a substituted phenethylamine with a methyl group at RA position.
- ^ The ethyl group of ethylamphetamine is at RN position, hence the name N-ethylamphetamine.
- ^ Ethylamphetamine is structurally similar to N-methylamphetamine (methamphetamine), the ethyl group being replaced in methamphetamine with a methyl group.
- ^ Ethylamphetamine's higher potency may make its risk of causing abuse, dependence and/or addiction greater compared to amphetamine.
Stimulants (N06B) Adamantanes Adaphenoxate • Adapromine • Amantadine • Bromantane • Chlodantane • Gludantane • Memantine • Midantane
Adenosine antagonists 8-Chlorotheophylline • 8-Cyclopentyltheophylline • 8-Phenyltheophylline • Aminophylline • Caffeine • CGS-15943 • Dimethazan • Paraxanthine • SCH-58261 • Theobromine • TheophyllineAlkylamines Arylcyclohexylamines Benocyclidine • Dieticyclidine • Esketamine • Eticyclidine • Gacyclidine • Ketamine • Phencyclamine • Phencyclidine • Rolicyclidine • Tenocyclidine • Tiletamine
Benzazepines 6-Br-APB • SKF-77434 • SKF-81297 • SKF-82958
Cholinergics A-84543 • A-366,833 • ABT-202 • ABT-418 • AR-R17779 • Altinicline • Anabasine • Arecoline • Cotinine • Cytisine • Dianicline • Epibatidine • Epiboxidine • GTS-21 • Ispronicline • Nicotine • PHA-543,613 • PNU-120,596 • PNU-282,987 • Pozanicline • Rivanicline • Sazetidine A • SIB-1553A • SSR-180,711 • TC-1698 • TC-1827 • TC-2216 • TC-5619 • Tebanicline • UB-165 • Varenicline • WAY-317,538
Convulsants Anatoxin-a • Bicuculline • DMCM • Flurothyl • Gabazine • Pentetrazol • Picrotoxin • Strychnine • Thujone
Eugeroics Adrafinil • Armodafinil • CRL-40941 • Modafinil
Oxazolines 4-Methylaminorex • Aminorex • Clominorex • Cyclazodone • Fenozolone • Fluminorex • Pemoline • Thozalinone
Phenethylamines 1-(4-Methylphenyl)-2-aminobutane • 1-Phenyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)pentan-3-one • 1-Methylamino-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)propane • 2-Fluoroamphetamine • 2-Fluoromethamphetamine • 2-OH-PEA • 2-Phenyl-3-aminobutane • 2-Phenyl-3-methylaminobutane • 2,3-MDA • 3-Fluoroamphetamine • 3-Fluoroethamphetamine • 3-Fluoromethcathinone • 3-Methoxyamphetamine • 3-Methylamphetamine • 3,4-DMMC • 4-BMC • 4-Ethylamphetamine • 4-FA • 4-FMA • 4-MA • 4-MMA • 4-MTA • 6-FNE • Alfetamine • α-Ethylphenethylamine • Amfecloral • Amfepentorex • Amfepramone • Amidephrine • Amphetamine (Dextroamphetamine, Levoamphetamine) • Amphetaminil • Arbutamine • β-Methylphenethylamine • β-Phenylmethamphetamine • Benfluorex • Benzedrone • Benzphetamine • BDB (J) • BOH (Hydroxy-J) • BPAP • Buphedrone • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Butylone • Cathine • Cathinone • Chlorphentermine • Cinnamedrine • Clenbuterol • Clobenzorex • Cloforex • Clortermine • D-Deprenyl • Denopamine • Dimethoxyamphetamine • Dimethylamphetamine • Dimethylcathinone (Dimethylpropion, Metamfepramone) • Dobutamine • DOPA (Dextrodopa, Levodopa) • Dopamine • Dopexamine • Droxidopa • EBDB (Ethyl-J) • Ephedrine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Epinine (Deoxyepinephrine) • Etafedrine • Ethcathinone (Ethylpropion) • Ethylamphetamine (Etilamfetamine) • Ethylnorepinephrine (Butanefrine) • Ethylone • Etilefrine • Famprofazone • Fenbutrazate • Fencamine • Fenethylline • Fenfluramine (Dexfenfluramine) • Fenmetramide • Fenproporex • Flephedrone • Fludorex • Furfenorex • Gepefrine • HMMA • Hordenine • Ibopamine • IMP • Indanylamphetamine • Isoetarine • Isoethcathinone • Isoprenaline (Isoproterenol) • L-Deprenyl (Selegiline) • Lefetamine • Lisdexamfetamine • Lophophine (Homomyristicylamine) • Manifaxine • MBDB (Methyl-J; "Eden") • MDA (Tenamfetamine) • MDBU • MDEA ("Eve") • MDMA ("Ecstasy", "Adam") • MDMPEA (Homarylamine) • MDOH • MDPR • MDPEA (Homopiperonylamine) • Mefenorex • Mephedrone • Mephentermine • Metanephrine • Metaraminol • Methamphetamine (Desoxyephedrine, Methedrine; Dextromethamphetamine, Levomethamphetamine) • Methoxamine • Methoxyphenamine • MMA • Methcathinone (Methylpropion) • Methedrone • Methoxyphenamine • Methylone • MMDA • MMDMA • MMMA • Morazone • N-Benzyl-1-phenethylamine • N,N-Dimethylphenethylamine • Naphthylamphetamine • Nisoxetine • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Norfenefrine • Norfenfluramine • Normetanephrine • Octopamine • Orciprenaline • Ortetamine • Oxilofrine • Paredrine (Norpholedrine, Oxamphetamine, Mycadrine) • PBA • PCA • PHA • Pargyline • Pentorex (Phenpentermine) • Pentylone • Phendimetrazine • Phenmetrazine • Phenpromethamine • Phentermine • Phenylalanine • Phenylephrine (Neosynephrine) • Phenylpropanolamine • Pholedrine • PIA • PMA • PMEA • PMMA • PPAP • Prenylamine • Propylamphetamine • Pseudoephedrine • Radafaxine • Ropinirole • Salbutamol (Albuterol; Levosalbutamol) • Sibutramine • Synephrine (Oxedrine) • Theodrenaline • Tiflorex (Flutiorex) • Tranylcypromine • Tyramine • Tyrosine • Xamoterol • Xylopropamine • Zylofuramine
Piperazines Piperidines 1-Benzyl-4-(2-(diphenylmethoxy)ethyl)piperidine • 1-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1-(piperidin-2-yl)butane • 2-Benzylpiperidine • 2-Methyl-3-phenylpiperidine • 3,4-Dichloromethylphenidate • 4-Benzylpiperidine • 4-Methylmethylphenidate • Desoxypipradrol • Difemetorex • Diphenylpyraline • Ethylphenidate • Methylnaphthidate • Methylphenidate (Dexmethylphenidate) • N-Methyl-3β-propyl-4β-(4-chlorophenyl)piperidine • Nocaine • Phacetoperane • Pipradrol • SCH-5472
Pyrrolidines 2-Diphenylmethylpyrrolidine • α-PPP • α-PBP • α-PVP • Diphenylprolinol • MDPPP • MDPBP • MDPV • MPBP • MPHP • MPPP • MOPPP • Naphyrone • PEP • Prolintane • Pyrovalerone
Tropanes 3-CPMT • 3'-Chloro-3α-(diphenylmethoxy)tropane • 3-Pseudotropyl-4-fluorobenzoate • 4'-Fluorococaine • AHN-1055 • Altropane (IACFT) • Brasofensine • CFT (WIN 35,428) • β-CIT (RTI-55) • Cocaethylene • Cocaine • Dichloropane (RTI-111) • Difluoropine • FE-β-CPPIT • FP-β-CPPIT • Ioflupane (123I) • Norcocaine • PIT • PTT • RTI-31 • RTI-32 • RTI-51 • RTI-105 • RTI-112 • RTI-113 • RTI-117 • RTI-120 • RTI-121 (IPCIT) • RTI-126 • RTI-150 • RTI-154 • RTI-171 • RTI-177 • RTI-183 • RTI-193 • RTI-194 • RTI-199 • RTI-202 • RTI-204 • RTI-229 • RTI-241 • RTI-336 • RTI-354 • RTI-371 • RTI-386 • Salicylmethylecgonine • Tesofensine • Troparil (β-CPT, WIN 35,065-2) • Tropoxane • WF-23 • WF-33 • WF-60
Others 1-(Thiophen-2-yl)-2-aminopropane • 2-Amino-1,2-dihydronaphthalene • 2-Aminoindane • 2-Aminotetralin • 2-MDP • 2-Phenylcyclohexylamine • 2-Phenyl-3,6-dimethylmorpholine • 3-Benzhydrylmorpholine • 3,3-Diphenylcyclobutanamine • 5-(2-Aminopropyl)indole • 5-Iodo-2-aminoindane • AL-1095 • Amfonelic acid • Amineptine • Amiphenazole • Atipamezole • Atomoxetine (Tomoxetine) • Bemegride • Benzydamine • BTQ • BTS 74,398 • Carphedon • Ciclazindol • Cilobamine • Clofenciclan • Cropropamide • Crotetamide • Cypenamine • D-161 • Diclofensine • Dimethocaine • Efaroxan • Etamivan • EXP-561 • Fencamfamine • Fenpentadiol • Feprosidnine • G-130 • Gamfexine • Gilutensin • GSK1360707F • GYKI-52895 • Hexacyclonate • Idazoxan • Indanorex • Indatraline • JNJ-7925476 • JZ-IV-10 • Lazabemide • Leptacline • Levopropylhexedrine • Lomevactone • LR-5182 • Mazindol • Meclofenoxate • Medifoxamine • Mefexamide • Mesocarb • Methastyridone • Methiopropamine • N-Methyl-3-phenylnorbornan-2-amine • Nefopam • Nikethamide • Nomifensine • O-2172 • Oxaprotiline • Phthalimidopropiophenone • PNU-99,194 • Propylhexedrine • PRC200-SS • Rasagiline • Rauwolscine • Rubidium chloride • Setazindol • Tametraline • Tandamine • Trazium • UH-232 • Yohimbine
See also Sympathomimetic aminesAdrenergics Receptor ligands Agonists: 5-FNE • 6-FNE • Amidephrine • Anisodamine • Anisodine • Cirazoline • Dipivefrine • Dopamine • Ephedrine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Indanidine • Levonordefrin • Metaraminol • Methoxamine • Methyldopa • Midodrine • Naphazoline • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Octopamine • Oxymetazoline • Phenylephrine • Phenylpropanolamine • Pseudoephedrine • Synephrine • Tetrahydrozoline
Antagonists: Abanoquil • Adimolol • Ajmalicine • Alfuzosin • Amosulalol • Arotinolol • Atiprosin • Benoxathian • Buflomedil • Bunazosin • Carvedilol • CI-926 • Corynanthine • Dapiprazole • DL-017 • Domesticine • Doxazosin • Eugenodilol • Fenspiride • GYKI-12,743 • GYKI-16,084 • Indoramin • Ketanserin • L-765,314 • Labetalol • Mephendioxan • Metazosin • Monatepil • Moxisylyte (Thymoxamine) • Naftopidil • Nantenine • Neldazosin • Nicergoline • Niguldipine • Pelanserin • Phendioxan • Phenoxybenzamine • Phentolamine • Piperoxan • Prazosin • Quinazosin • Ritanserin • RS-97,078 • SGB-1,534 • Silodosin • SL-89.0591 • Spiperone • Talipexole • Tamsulosin • Terazosin • Tibalosin • Tiodazosin • Tipentosin • Tolazoline • Trimazosin • Upidosin • Urapidil • Zolertine
* Note that many TCAs, TeCAs, antipsychotics, ergolines, and some piperazines like buspirone, trazodone, nefazodone, etoperidone, and mepiprazole all antagonize α1-adrenergic receptors as well, which contributes to their side effects such as orthostatic hypotension.Agonists: (R)-3-Nitrobiphenyline • 4-NEMD • 6-FNE • Amitraz • Apraclonidine • Brimonidine • Cannabivarin • Clonidine • Detomidine • Dexmedetomidine • Dihydroergotamine • Dipivefrine • Dopamine • Ephedrine • Ergotamine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Esproquin • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Guanabenz • Guanfacine • Guanoxabenz • Levonordefrin • Lofexidine • Medetomidine • Methyldopa • Mivazerol • Naphazoline • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Phenylpropanolamine • Piperoxan • Pseudoephedrine • Rilmenidine • Romifidine • Talipexole • Tetrahydrozoline • Tizanidine • Tolonidine • Urapidil • Xylazine • Xylometazoline
Antagonists: 1-PP • Adimolol • Aptazapine • Atipamezole • BRL-44408 • Buflomedil • Cirazoline • Efaroxan • Esmirtazapine • Fenmetozole • Fluparoxan • GYKI-12,743 • GYKI-16,084 • Idazoxan • Mianserin • Mirtazapine • MK-912 • NAN-190 • Olanzapine • Phentolamine • Phenoxybenzamine • Piperoxan • Piribedil • Rauwolscine • Rotigotine • SB-269,970 • Setiptiline • Spiroxatrine • Sunepitron • Tolazoline • Yohimbine
* Note that many atypical antipsychotics and azapirones like buspirone and gepirone (via metabolite 1-PP) antagonize α2-adrenergic receptors as well.βAgonists: 2-FNE • 5-FNE • Amibegron • Arbutamine • Arformoterol • Arotinolol • BAAM • Bambuterol • Befunolol • Bitolterol • Broxaterol • Buphenine • Carbuterol • Cimaterol • Clenbuterol • Denopamine • Deterenol • Dipivefrine • Dobutamine • Dopamine • Dopexamine • Ephedrine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Etafedrine • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Fenoterol • Formoterol • Hexoprenaline • Higenamine • Indacaterol • Isoetarine • Isoprenaline (Isoproterenol) • Isoxsuprine • Labetalol • Levonordefrin • Levosalbutamol • Mabuterol • Methoxyphenamine • Methyldopa • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Orciprenaline • Oxyfedrine • Phenylpropanolamine • Pirbuterol • Prenalterol • Ractopamine • Procaterol • Pseudoephedrine • Reproterol • Rimiterol • Ritodrine • Salbutamol (Albuterol) • Salmeterol • Solabegron • Terbutaline • Tretoquinol • Tulobuterol • Xamoterol • Zilpaterol • Zinterol
Antagonists: Acebutolol • Adaprolol • Adimolol • Afurolol • Alprenolol • Alprenoxime • Amosulalol • Ancarolol • Arnolol • Arotinolol • Atenolol • Befunolol • Betaxolol • Bevantolol • Bisoprolol • Bopindolol • Bormetolol • Bornaprolol • Brefonalol • Bucindolol • Bucumolol • Bufetolol • Buftiralol • Bufuralol • Bunitrolol • Bunolol • Bupranolol • Burocrolol • Butaxamine • Butidrine • Butofilolol • Capsinolol • Carazolol • Carpindolol • Carteolol • Carvedilol • Celiprolol • Cetamolol • Cicloprolol • Cinamolol • Cloranolol • Cyanopindolol • Dalbraminol • Dexpropranolol • Diacetolol • Dichloroisoprenaline • Dihydroalprenolol • Dilevalol • Diprafenone • Draquinolol • Dropranolol • Ecastolol • Epanolol • Ericolol • Ersentilide • Esatenolol • Esmolol • Esprolol • Eugenodilol • Exaprolol • Falintolol • Flestolol • Flusoxolol • Hydroxycarteolol • Hydroxytertatolol • ICI-118,551 • Idropranolol • Indenolol • Indopanolol • Iodocyanopindolol • Iprocrolol • Isoxaprolol • Isamoltane • Labetalol • Landiolol • Levobetaxolol • Levobunolol • Levocicloprolol • Levomoprolol • Medroxalol • Mepindolol • Metalol • Metipranolol • Metoprolol • Moprolol • Nadolol • Nadoxolol • Nafetolol • Nebivolol • Neraminol • Nifenalol • Nipradilol • Oberadilol • Oxprenolol • Pacrinolol • Pafenolol • Pamatolol • Pargolol • Parodilol • Penbutolol • Penirolol • PhQA-33 • Pindolol • Pirepolol • Practolol • Primidolol • Procinolol • Pronethalol • Propafenone • Propranolol • Ridazolol • Ronactolol • Soquinolol • Sotalol • Spirendolol • SR 59230A • Sulfinalol • TA-2005 • Talinolol • Tazolol • Teoprolol • Tertatolol • Terthianolol • Tienoxolol • Tilisolol • Timolol • Tiprenolol • Tolamolol • Toliprolol • Tribendilol • Trigevolol • Xibenolol • XipranololReuptake inhibitors Selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors: Amedalin • Atomoxetine (Tomoxetine) • Ciclazindol • Daledalin • Esreboxetine • Lortalamine • Mazindol • Nisoxetine • Reboxetine • Talopram • Talsupram • Tandamine • Viloxazine; Norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors: Amineptine • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Fencamine • Fencamfamine • Lefetamine • Levophacetoperane • LR-5182 • Manifaxine • Methylphenidate • Nomifensine • O-2172 • Radafaxine; Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors: Bicifadine • Desvenlafaxine • Duloxetine • Eclanamine • Levomilnacipran • Milnacipran • Sibutramine • Venlafaxine; Serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors: Brasofensine • Diclofensine • DOV-102,677 • DOV-21,947 • DOV-216,303 • JNJ-7925476 • JZ-IV-10 • Methylnaphthidate • Naphyrone • NS-2359 • PRC200-SS • SEP-225,289 • SEP-227,162 • Tesofensine; Tricyclic antidepressants: Amitriptyline • Butriptyline • Cianopramine • Clomipramine • Desipramine • Dosulepin • Doxepin • Imipramine • Lofepramine • melitracen • Nortriptyline • Protriptyline • Trimipramine; Tetracyclic antidepressants: Amoxapine • Maprotiline • Mianserin • Oxaprotiline • Setiptiline; Others: Cocaine • CP-39,332 • EXP-561 • Fezolamine • Ginkgo biloba • Indeloxazine • Nefazodone • Nefopam • Pridefrine • Tapentadol • Tedatioxetine • Teniloxazine • Tramadol • ZiprasidoneReleasing agents Morpholines: Fenbutrazate • Morazone • Phendimetrazine • Phenmetrazine; Oxazolines: 4-Methylaminorex • Aminorex • Clominorex • Cyclazodone • Fenozolone • Fluminorex • Pemoline • Thozalinone; Phenethylamines (also amphetamines, cathinones, phentermines, etc): 2-OH-PEA • 4-CAB • 4-FA • 4-FMA • 4-MA • 4-MMA • Alfetamine • Amfecloral • Amfepentorex • Amfepramone • Amphetamine (Dextroamphetamine, Levoamphetamine) • Amphetaminil • β-Me-PEA • BDB • Benzphetamine • BOH • Buphedrone • Butylone • Cathine • Cathinone • Clobenzorex • Clortermine • D-Deprenyl • Dimethylamphetamine • Dimethylcathinone (Dimethylpropion, metamfepramone) • DMA • DMMA • EBDB • Ephedrine • Ethcathinone • Ethylamphetamine • Ethylone • Famprofazone • Fenethylline • Fenproporex • Flephedrone • Fludorex • Furfenorex • Hordenine • IAP • IMP • L-Deprenyl (Selegiline) • Lisdexamfetamine • Lophophine • MBDB • MDA (Tenamfetamine) • MDEA • MDMA • MDMPEA • MDOH • MDPEA • Mefenorex • Mephedrone • Mephentermine • Methamphetamine (Dextromethamphetamine, Levomethamphetamine) • Methcathinone • Methedrone • Methylone • NAP • Ortetamine • Paredrine • pBA • pCA • Pentorex (Phenpentermine) • Phenethylamine • Pholedrine • Phenpromethamine • Phentermine • Phenylpropanolamine • pIA • Prenylamine • Propylamphetamine • Pseudoephedrine • Tiflorex • Tyramine • Xylopropamine • Zylofuramine; Piperazines: 2C-B-BZP • BZP • MBZP • mCPP • MDBZP • MeOPP • pFPP; Others: 2-Amino-1,2-dihydronaphthalene • 2-Aminoindane • 2-Aminotetralin • 2-Benzylpiperidine • 4-Benzylpiperidine • 5-IAI • Clofenciclan • Cyclopentamine • Cypenamine • Cyprodenate • Feprosidnine • Gilutensin • Heptaminol • Hexacyclonate • Indanorex • Isometheptene • Methylhexanamine • Octodrine • Phthalimidopropiophenone • Propylhexedrine (Levopropylhexedrine) • TuaminoheptaneEnzyme inhibitors 3,4-DihydroxystyreneDBHCGS-19281A • SKF-64139 • SKF-7698Nonselective: Benmoxin • Caroxazone • Echinopsidine • Furazolidone • Hydralazine • Indantadol • Iproclozide • Iproniazid • Isocarboxazid • Isoniazid • Linezolid • Mebanazine • Metfendrazine • Nialamide • Octamoxin • Paraxazone • Phenelzine • Pheniprazine • Phenoxypropazine • Pivalylbenzhydrazine • Procarbazine • Safrazine • Tranylcypromine; MAO-A selective: Amiflamine • Bazinaprine • Befloxatone • Befol • Brofaromine • Cimoxatone • Clorgiline • Esuprone • Harmala alkaloids (Harmine, Harmaline, Tetrahydroharmine, Harman, Norharman, etc) • Methylene Blue • Metralindole • Minaprine • Moclobemide • Pirlindole • Sercloremine • Tetrindole • Toloxatone • Tyrima; MAO-B selective: D-Deprenyl • Selegiline (L-Deprenyl) • Ladostigil • Lazabemide • Milacemide • Mofegiline • Pargyline • Rasagiline • Safinamide
* Note that MAO-B inhibitors also influence norepinephrine/epinephrine levels since they inhibit the breakdown of their precursor dopamine.COMTOthers Ferrous Iron (Fe2+) • S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine • Vitamin B3 (Niacin, Nicotinamide → NADPH) • Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine, Pyridoxamine, Pyridoxal → Pyridoxal Phosphate) • Vitamin B9 (Folic acid → Tetrahydrofolic acid) • Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) • Zinc (Zn2+)OthersActivity enhancers: BPAP • PPAP; Release blockers: Bethanidine • Bretylium • Guanadrel • Guanazodine • Guanclofine • Guanethidine • Guanoxan; Toxins: Oxidopamine (6-Hydroxydopamine)List of adrenergic drugsDopaminergics Receptor ligands AgonistsAdamantanes: Amantadine • Memantine • Rimantadine; Aminotetralins: 7-OH-DPAT • 8-OH-PBZI • Rotigotine • UH-232; Benzazepines: 6-Br-APB • Fenoldopam • SKF-38,393 • SKF-77,434 • SKF-81,297 • SKF-82,958 • SKF-83,959; Ergolines: Bromocriptine • Cabergoline • Dihydroergocryptine • Lisuride • LSD • Pergolide; Dihydrexidine derivatives: 2-OH-NPA • A-86,929 • Ciladopa • Dihydrexidine • Dinapsoline • Dinoxyline • Doxanthrine; Others: A-68,930 • A-77,636 • A-412,997 • ABT-670 • ABT-724 • Aplindore • Apomorphine • Aripiprazole • Bifeprunox • BP-897 • CY-208,243 • Dizocilpine • Etilevodopa • Flibanserin • Ketamine • Melevodopa • Modafinil • Pardoprunox • Phencyclidine • PD-128,907 • PD-168,077 • PF-219,061 • Piribedil • Pramipexole • Propylnorapomorphine • Pukateine • Quinagolide • Quinelorane • Quinpirole • RDS-127 • Ro10-5824 • Ropinirole • Rotigotine • Roxindole • Salvinorin A • SKF-89,145 • Sumanirole • Terguride • Umespirone • WAY-100,635AntagonistsTypical antipsychotics: Acepromazine • Azaperone • Benperidol • Bromperidol • Clopenthixol • Chlorpromazine • Chlorprothixene • Droperidol • Flupentixol • Fluphenazine • Fluspirilene • Haloperidol • Loxapine • Mesoridazine • Methotrimeprazine • Nemonapride • Penfluridol • Perazine • Periciazine • Perphenazine • Pimozide • Prochlorperazine • Promazine • Sulforidazine • Sulpiride • Sultopride • Thioridazine • Thiothixene • Trifluoperazine • Triflupromazine • Trifluperidol • Zuclopenthixol; Atypical antipsychotics: Amisulpride • Asenapine • Blonanserin • Cariprazine • Carpipramine • Clocapramine • Clozapine • Gevotroline • Iloperidone • Lurasidone • Melperone • Molindone • Mosapramine • Olanzapine • Paliperidone • Perospirone • Piquindone • Quetiapine • Remoxipride • Risperidone • Sertindole • Tiospirone • Ziprasidone • Zotepine; Antiemetics: AS-8112 • Alizapride • Bromopride • Clebopride • Domperidone • Metoclopramide • Thiethylperazine; Others: Amoxapine • Buspirone • Butaclamol • Ecopipam • EEDQ • Eticlopride • Fananserin • L-745,870 • Nafadotride • Nuciferine • PNU-99,194 • Raclopride • Sarizotan • SB-277,011-A • SCH-23,390 • SKF-83,959 • Sonepiprazole • Spiperone • Spiroxatrine • Stepholidine • Tetrahydropalmatine • Tiapride • UH-232 • YohimbineReuptake inhibitors PlasmalemmalDAT inhibitorsPiperazines: DBL-583 • GBR-12,935 • Nefazodone • Vanoxerine; Piperidines: BTCP • Desoxypipradrol • Dextromethylphenidate • Difemetorex • Ethylphenidate • Methylnaphthidate • Methylphenidate • Phencyclidine • Pipradrol; Pyrrolidines: Diphenylprolinol • Methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) • Naphyrone • Prolintane • Pyrovalerone; Tropanes: β-CPPIT • Altropane • Brasofensine • CFT • Cocaine • Dichloropane • Difluoropine • FE-β-CPPIT • FP-β-CPPIT • Ioflupane (123I) • Iometopane • RTI-112 • RTI-113 • RTI-121 • RTI-126 • RTI-150 • RTI-177 • RTI-229 • RTI-336 • Tenocyclidine • Tesofensine • Troparil • Tropoxane • WF-11 • WF-23 • WF-31 • WF-33; Others: Adrafinil • Armodafinil • Amfonelic acid • Amineptine • Benzatropine (Benztropine) • Bromantane • BTQ • BTS-74,398 • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Ciclazindol • Diclofensine • Dimethocaine • Diphenylpyraline • Dizocilpine • DOV-102,677 • DOV-21,947 • DOV-216,303 • Etybenzatropine (Ethylbenztropine) • EXP-561 • Fencamine • Fencamfamine • Fezolamine • GYKI-52,895 • Indatraline • Ketamine • Lefetamine • Levophacetoperane • LR-5182 • Manifaxine • Mazindol • Medifoxamine • Mesocarb • Modafinil • Nefopam • Nomifensine • NS-2359 • O-2172 • Pridefrine • Propylamphetamine • Radafaxine • SEP-225,289 • SEP-227,162 • Sertraline • Sibutramine • Tametraline • Tedatioxetine • TripelennamineVMAT inhibitorsReleasing agents Morpholines: Fenbutrazate • Morazone • Phendimetrazine • Phenmetrazine; Oxazolines: 4-Methylaminorex (4-MAR, 4-MAX) • Aminorex • Clominorex • Cyclazodone • Fenozolone • Fluminorex • Pemoline • Thozalinone; Phenethylamines (also amphetamines, cathinones, phentermines, etc): 2-Hydroxyphenethylamine (2-OH-PEA) • 4-CAB • 4-Methylamphetamine (4-MA) • 4-Methylmethamphetamine (4-MMA) • Alfetamine • Amfecloral • Amfepentorex • Amfepramone • Amphetamine (Dextroamphetamine, Levoamphetamine) • Amphetaminil • β-Methylphenethylamine (β-Me-PEA) • Benzodioxolylbutanamine (BDB) • Benzodioxolylhydroxybutanamine (BOH) • Benzphetamine • Buphedrone • Butylone • Cathine • Cathinone • Clobenzorex • Clortermine • D-Deprenyl • Dimethoxyamphetamine (DMA) • Dimethoxymethamphetamine (DMMA) • Dimethylamphetamine • Dimethylcathinone (Dimethylpropion, metamfepramone) • Ethcathinone (Ethylpropion) • Ethylamphetamine • Ethylbenzodioxolylbutanamine (EBDB) • Ethylone • Famprofazone • Fenethylline • Fenproporex • Flephedrone • Fludorex • Furfenorex • Hordenine • Lophophine (Homomyristicylamine) • Mefenorex • Mephedrone • Methamphetamine (Desoxyephedrine, Methedrine; Dextromethamphetamine, Levomethamphetamine) • Methcathinone (Methylpropion) • Methedrone • Methoxymethylenedioxyamphetamine (MMDA) • Methoxymethylenedioxymethamphetamine (MMDMA) • Methylbenzodioxolylbutanamine (MBDB) • Methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA, tenamfetamine) • Methylenedioxyethylamphetamine (MDEA) • Methylenedioxyhydroxyamphetamine (MDOH) • Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) • Methylenedioxymethylphenethylamine (MDMPEA, homarylamine) • Methylenedioxyphenethylamine (MDPEA, homopiperonylamine) • Methylone • Ortetamine • Parabromoamphetamine (PBA) • Parachloroamphetamine (PCA) • Parafluoroamphetamine (PFA) • Parafluoromethamphetamine (PFMA) • Parahydroxyamphetamine (PHA) • Paraiodoamphetamine (PIA) • Paredrine (Norpholedrine, Oxamphetamine) • Phenethylamine (PEA) • Pholedrine • Phenpromethamine • Prenylamine • Propylamphetamine • Tiflorex (Flutiorex) • Tyramine (TRA) • Xylopropamine • Zylofuramine; Piperazines: 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-bromobenzylpiperazine (2C-B-BZP) • Benzylpiperazine (BZP) • Methoxyphenylpiperazine (MeOPP, paraperazine) • Methylbenzylpiperazine (MBZP) • Methylenedioxybenzylpiperazine (MDBZP, piperonylpiperazine); Others: 2-Amino-1,2-dihydronaphthalene (2-ADN) • 2-Aminoindane (2-AI) • 2-Aminotetralin (2-AT) • 4-Benzylpiperidine (4-BP) • 5-IAI • Clofenciclan • Cyclopentamine • Cypenamine • Cyprodenate • Feprosidnine • Gilutensin • Heptaminol • Hexacyclonate • Indanylaminopropane (IAP) • Indanorex • Isometheptene • Methylhexanamine • Naphthylaminopropane (NAP) • Octodrine • Phthalimidopropiophenone • Propylhexedrine (Levopropylhexedrine) • Tuaminoheptane (Tuamine)Enzyme inhibitors PAH inhibitors3,4-DihydroxystyreneTH inhibitorsNonselective: Benmoxin • Caroxazone • Echinopsidine • Furazolidone • Hydralazine • Indantadol • Iproclozide • Iproniazid • Isocarboxazid • Isoniazid • Linezolid • Mebanazine • Metfendrazine • Nialamide • Octamoxin • Paraxazone • Phenelzine • Pheniprazine • Phenoxypropazine • Pivalylbenzhydrazine • Procarbazine • Safrazine • Tranylcypromine; MAO-A selective: Amiflamine • Bazinaprine • Befloxatone • Befol • Brofaromine • Cimoxatone • Clorgiline • Esuprone • Harmala alkaloids • Methylene Blue • Metralindole • Minaprine • Moclobemide • Pirlindole • Sercloremine • Tetrindole • Toloxatone • Tyrima; MAO-B selective: D-Deprenyl • L-Deprenyl (Selegiline) • Ladostigil • Lazabemide • Milacemide • Pargyline • Rasagiline • SafinamideDBH inhibitorsOthers L-Phenylalanine → L-Tyrosine → L-DOPA (Levodopa)Ferrous iron (Fe2+) • Tetrahydrobiopterin • Vitamin B3 (Niacin, Nicotinamide → NADPH) • Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine, Pyridoxamine, Pyridoxal → Pyridoxal phosphate) • Vitamin B9 (Folic acid → Tetrahydrofolic acid) • Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) • Zinc (Zn2+)OthersActivity enhancers: Benzofuranylpropylaminopentane (BPAP) • Phenylpropylaminopentane (PPAP); Toxins: Oxidopamine (6-Hydroxydopamine)List of dopaminergic drugsPhenethylamines Phenethylamines Psychedelics: 2C-B • 2C-B-FLY • 2C-C • 2C-D • 2C-E • 2C-F • 2C-G • 2C-I • 2C-N • 2C-P • 2C-SE • 2C-T • 2C-T-2 • 2C-T-4 • 2C-T-7 • 2C-T-8 • 2C-T-9 • 2C-T-13 • 2C-T-15 • 2C-T-17 • 2C-T-21 • 2C-TFM • 2C-YN • Allylescaline • DESOXY • Escaline • Isoproscaline • Jimscaline • Macromerine • MEPEA • Mescaline • Metaescaline • Methallylescaline • Proscaline • Psi-2C-T-4 • TCB-2
Stimulants: 2-OH-PEA • β-Me-PEA • Hordenine • N-Me-PEA • Phenethylamine (PEA)
Entactogens: Lophophine • MDPEA • MDMPEA
Others: BOH • DMPEAAmphetamines
PhenylisopropylaminesPsychedelics: 3C-BZ • 3C-E • 3C-P • Aleph • Beatrice • Bromo-DragonFLY • D-Deprenyl • DMA • DMCPA • DMMDA • DOB • DOC • DOEF • DOET • DOI • DOM • DON • DOPR • DOTFM • Ganesha • MMDA • MMDA-2 • Psi-DOM • TMA • TeMA
Stimulants: 4-MA • 4-MMA • 4-MTA • 5-IT • Alfetamine • Amfecloral • Amfepentorex • Amphetamine (Dextroamphetamine, Levoamphetamine) • Amphetaminil • Benfluorex • Benzphetamine • Cathine • Clobenzorex • Dimethylamphetamine • Ephedrine (EPH) • Ethylamphetamine • Fencamfamine • Fencamine • Fenethylline • Fenfluramine (Dexfenfluramine) • Fenproporex • Fludorex • Furfenorex • Isopropylamphetamine • Lefetamine • Mefenorex • Methamphetamine (Dextromethamphetamine, Levomethamphetamine) • Methoxyphenamine • MMA • Norfenfluramine • Oxilofrine • Ortetamine • PBA • PCA • Phenpromethamine • PFA • PFMA • PIA • PMA • PMEA • PMMA • Phenylpropanolamine (PPA) • Prenylamine • Propylamphetamine • Pseudoephedrine (PSE) • Sibutramine • Tiflorex (Flutiorex) • Tranylcypromine • Xylopropamine • Zylofuramine
Entactogens: 5-APDB • 6-APB • 6-APDB • EDA • IAP • MDA • MDEA • MDHMA (FLEA) • MDMA ("Ecstasy") • MDOH • MMDMA • NAP • TAP
Others: Amiflamine • DFMDA • D-Deprenyl • L-Deprenyl (Selegiline)Phentermines Stimulants: Chlorphentermine • Cloforex • Clortermine • Etolorex • Mephentermine • Pentorex (Phenpentermine) • Phentermine
Entactogens: MDPH • MDMPHCathinones Stimulants: Amfepramone • Brephedrone • Buphedrone • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Cathinone (Propion) • Dimethylcathinone (Dimethylpropion, Metamfepramone) • Ethcathinone (Ethylpropion) • Flephedrone • Methcathinone (Methylpropion) • Mephedrone • Methedrone
Entactogens: Ethylone • MethylonePhenylisobutylamines Phenylalkylpyrrolidines Stimulants: α-PBP • α-PPP • α-PVP • MDPBP • MDPPP • MDPV • MOPPP • MPBP • MPHP • MPPP • Naphyrone • PEP • Prolintane • PyrovaleroneCatecholamines
(and relatives..)6-FNE • 6-OHDA • α-Me-DA • α-Me-TRA • Adrenochrome • Ciladopa • D-DOPA (Dextrodopa) • Dopamine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Epinine • Fenclonine • Ibopamine • L-DOPA (Levodopa) • L-DOPS (Droxidopa) • L-Phenylalanine • L-Tyrosine • meta-Octopamine • meta-Tyramine • Metanephrine • Metirosine • Methyldopa • Nordefrin (Levonordefrin) • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Normetanephrine • para-Octopamine • para-TyramineMiscellaneous Amidephrine • Arbutamine • Cafedrine • Denopamine • Dobutamine • Dopexamine • Etafedrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Etilefrine • Famprofazone • Gepefrine • Isoprenaline (Isoproterenol) • Isoetarine • Metaraminol • Metaterol • Methoxamine • Norfenefrine • Orciprenaline • Phenylephrine (Neosynephrine) • Phenoxybenzamine • Prenalterol • Pronethalol • Propranolol • Salbutamol (Albuterol; Levosalbutamol) • Synephrine (Oxedrine) • Theodrenaline • XamoterolCategories:- Amphetamines
- Anorectics
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
